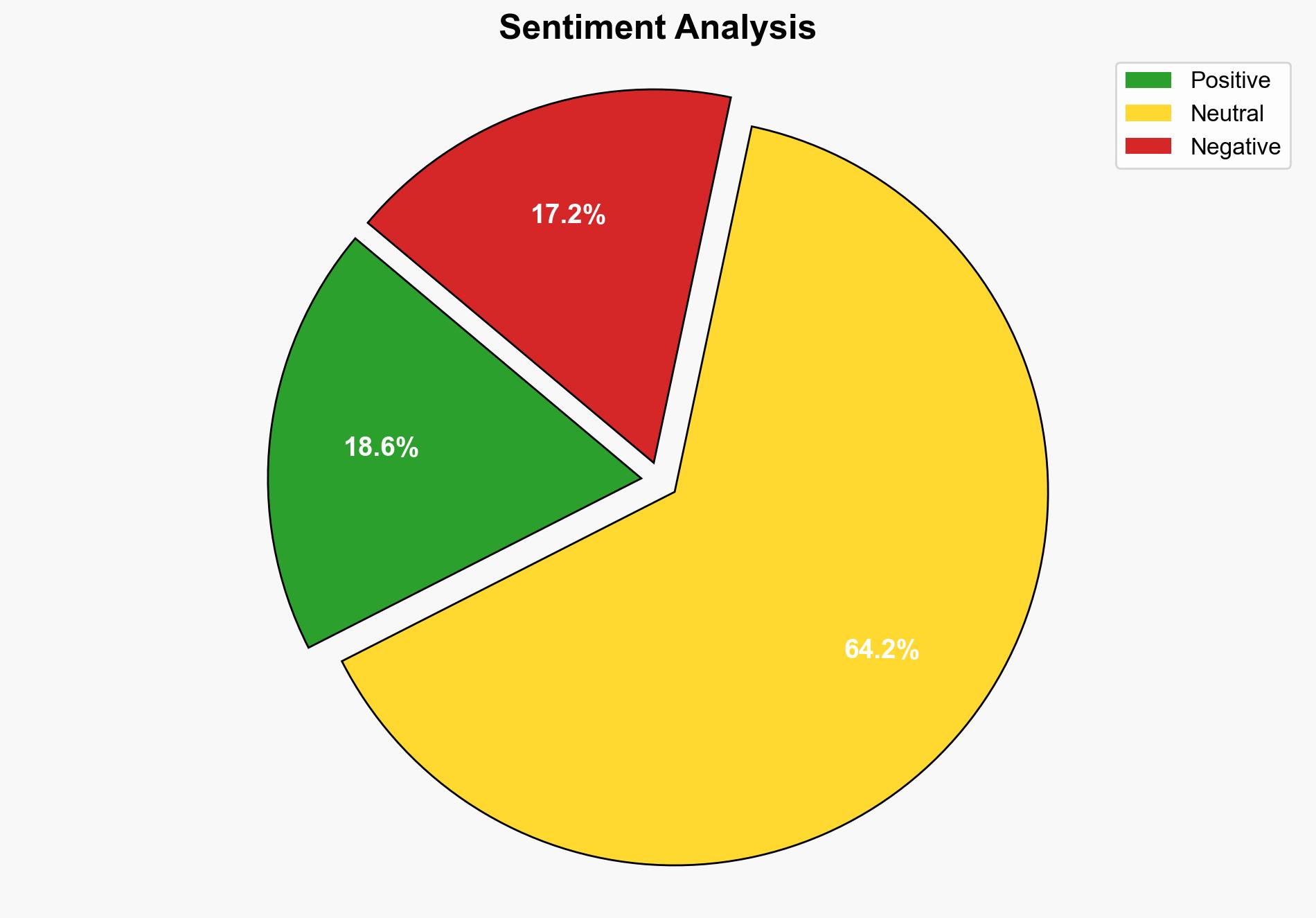
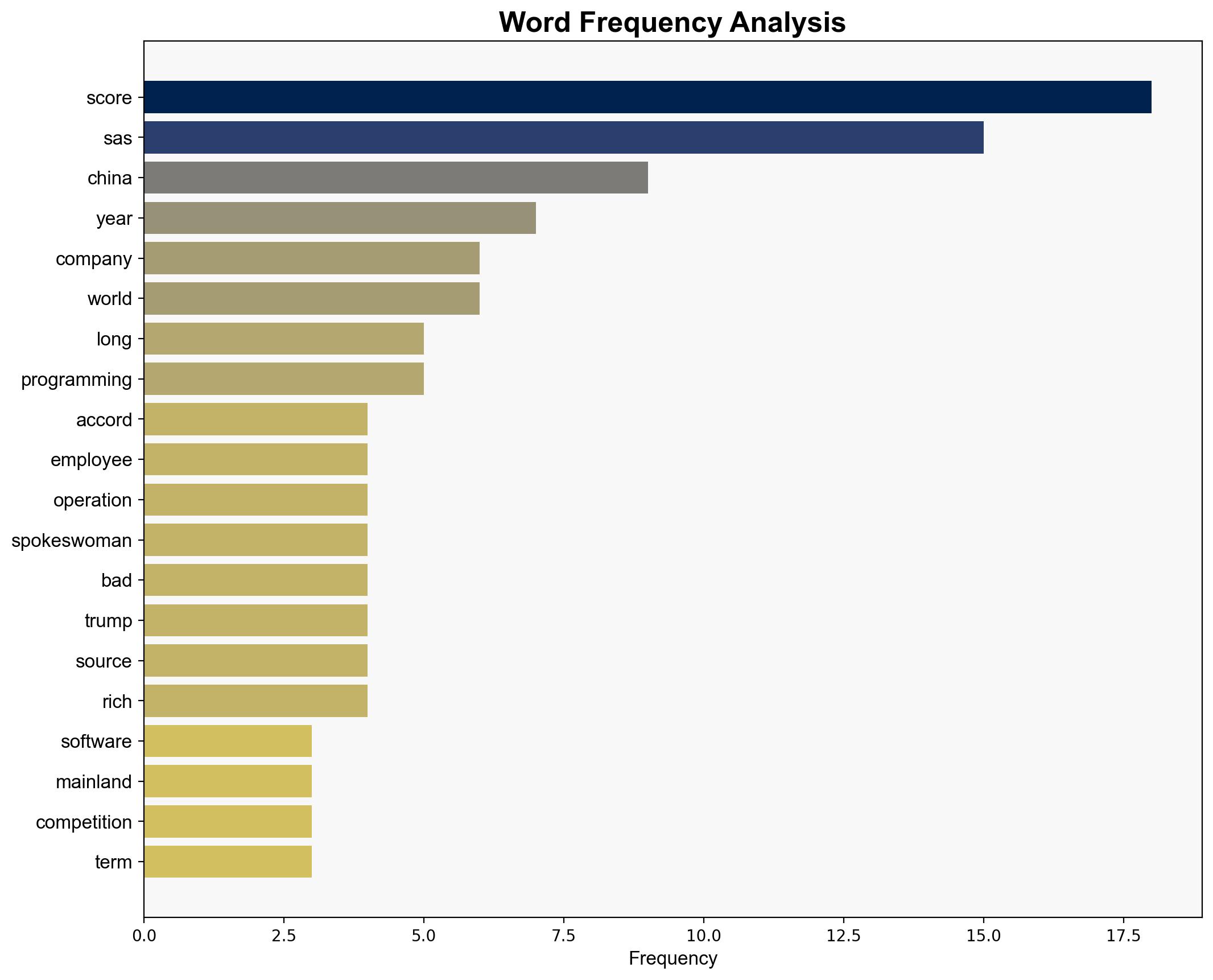
US Software Firm SAS Exits China After 25 Years – Slashdot.org
Published on: 2025-11-06
Intelligence Report: US Software Firm SAS Exits China After 25 Years – Slashdot.org
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The most supported hypothesis is that SAS’s exit from China is primarily driven by geopolitical tensions and strategic realignment rather than solely economic factors. Confidence level: Moderate. It is recommended to monitor SAS’s future strategic moves and the broader impact on US-China business relations.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: SAS’s exit is due to intense domestic competition and thin profit margins in China, making continued operations unsustainable.
Hypothesis 2: The decision is influenced by geopolitical tensions and a strategic shift to optimize global operations, ensuring long-term sustainability.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 2 is better supported. The announcement emphasizes “geopolitical tension” and “organizational optimization,” suggesting a broader strategic realignment beyond immediate economic pressures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions:
– Hypothesis 1 assumes that economic factors alone dictate strategic exits.
– Hypothesis 2 assumes geopolitical factors significantly influence corporate decisions.
Red Flags:
– Lack of specific financial data to support claims of unsustainable profit margins.
– Potential bias in attributing the exit solely to geopolitical factors without considering internal corporate strategy.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exit of SAS could signal a trend of Western firms reassessing their presence in China, potentially leading to a reduction in foreign investment. This may exacerbate US-China tensions and impact global supply chains. Cybersecurity risks could increase as China may seek to develop domestic alternatives to foreign software solutions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor other US firms’ operations in China for similar strategic exits.
- Engage in diplomatic efforts to mitigate geopolitical tensions affecting business operations.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: SAS successfully reallocates resources, enhancing global competitiveness.
- Worst Case: Increased geopolitical tensions lead to broader economic decoupling.
- Most Likely: Gradual strategic realignment by US firms in response to geopolitical and economic pressures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– SAS Institute
– Beijing-based SAS employees
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, geopolitical strategy, US-China relations