NHS manager who raped young girls after grooming them on Snapchat jailed for 28 years – BBC News
Published on: 2025-11-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: NHS manager who raped young girls after grooming them on Snapchat jailed for 28 years – BBC News
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
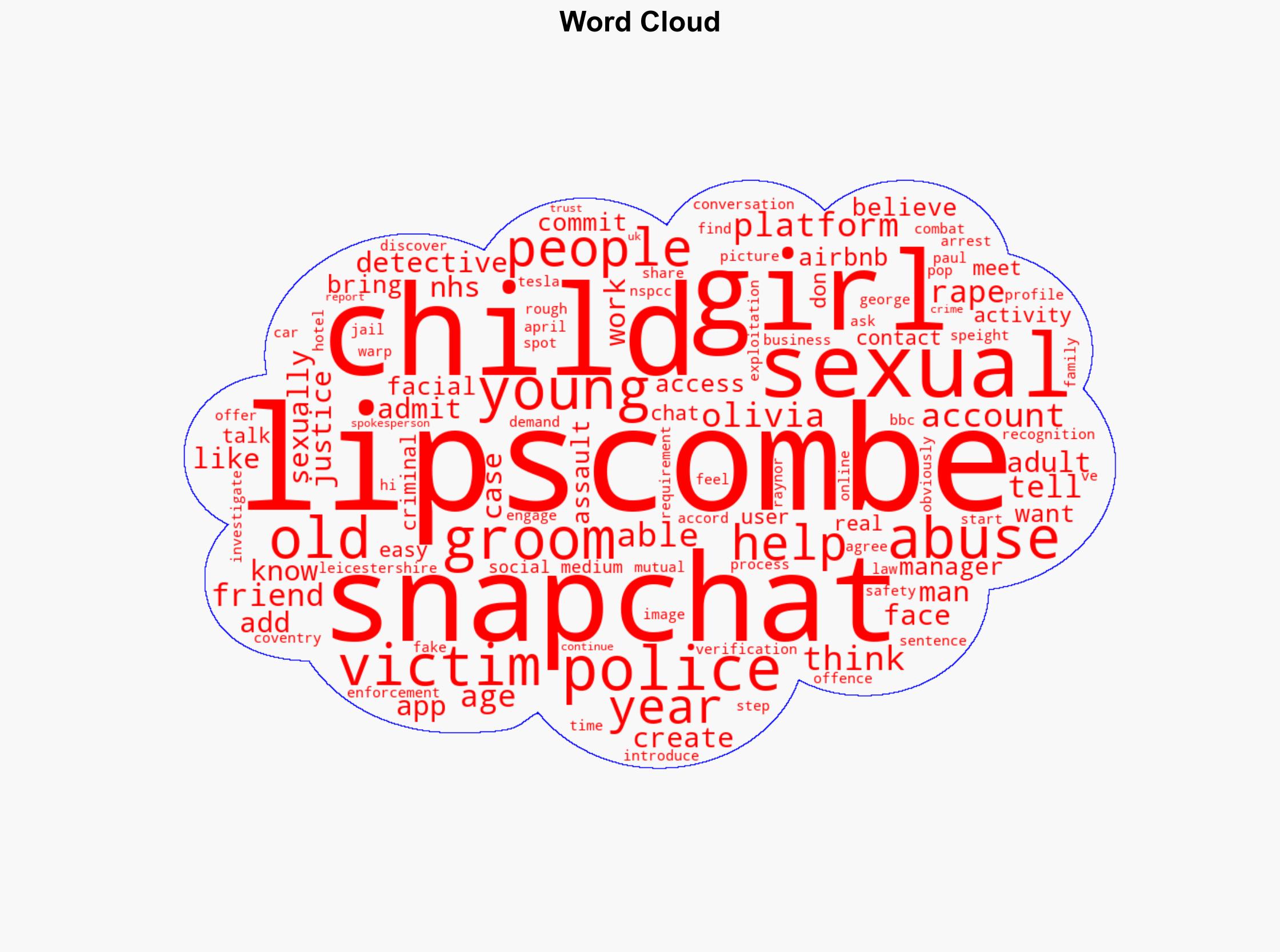
With a high confidence level, it is assessed that the exploitation of social media platforms by individuals like Paul Lipscombe represents a significant and evolving threat to child safety. The most supported hypothesis is that inadequate safeguards on social media platforms enable predatory behavior, necessitating enhanced regulatory measures and technological solutions to protect minors. Recommended actions include strengthening platform security measures and fostering collaboration between tech companies and law enforcement.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The primary factor enabling Lipscombe’s criminal activities was the lack of robust age verification and monitoring mechanisms on social media platforms like Snapchat.
Hypothesis 2: Lipscombe’s ability to exploit social media for grooming was primarily due to his sophisticated manipulation techniques and the inherent vulnerabilities of young users, rather than platform deficiencies.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely, as the evidence indicates systemic issues with platform security and user verification, which facilitated Lipscombe’s activities. The introduction of new child protection measures by Snapchat suggests recognition of these vulnerabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that social media platforms have insufficiently robust mechanisms to prevent adult predators from contacting minors. It is also assumed that regulatory frameworks are not keeping pace with technological advancements.
Red Flags: The case highlights potential deception indicators, such as the use of fake identities and manipulation of victim vulnerabilities. The sophistication of Lipscombe’s methods suggests possible gaps in law enforcement’s ability to detect and prevent such activities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The case underscores the risk of social media platforms being exploited for criminal activities, posing significant threats to child safety. There is a potential for increased public demand for stricter regulations, which could impact platform operations and user privacy. Additionally, failure to address these issues could lead to reputational damage for tech companies and erosion of public trust.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Implement advanced age verification technologies and enhance monitoring of user interactions on social media platforms. Strengthen collaboration between tech companies and law enforcement to improve detection and response to predatory activities.
- Best Scenario: Successful implementation of enhanced security measures leads to a significant reduction in online grooming cases.
- Worst Scenario: Continued exploitation of platform vulnerabilities results in increased incidents of child exploitation and public backlash.
- Most-likely Scenario: Incremental improvements in platform security and regulatory measures lead to gradual reduction in exploitation cases, with ongoing challenges in balancing privacy and security.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Paul Lipscombe – Former NHS manager and convicted criminal.
Snapchat – Social media platform used for grooming activities.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Child Safety, Social Media Regulation, Law Enforcement Collaboration
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology