Patch Tuesday Microsoft fixes actively exploited Windows kernel vulnerability CVE-2025-62215 – Help Net Security
Published on: 2025-11-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Patch Tuesday Microsoft fixes actively exploited Windows kernel vulnerability CVE-2025-62215 – Help Net Security
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
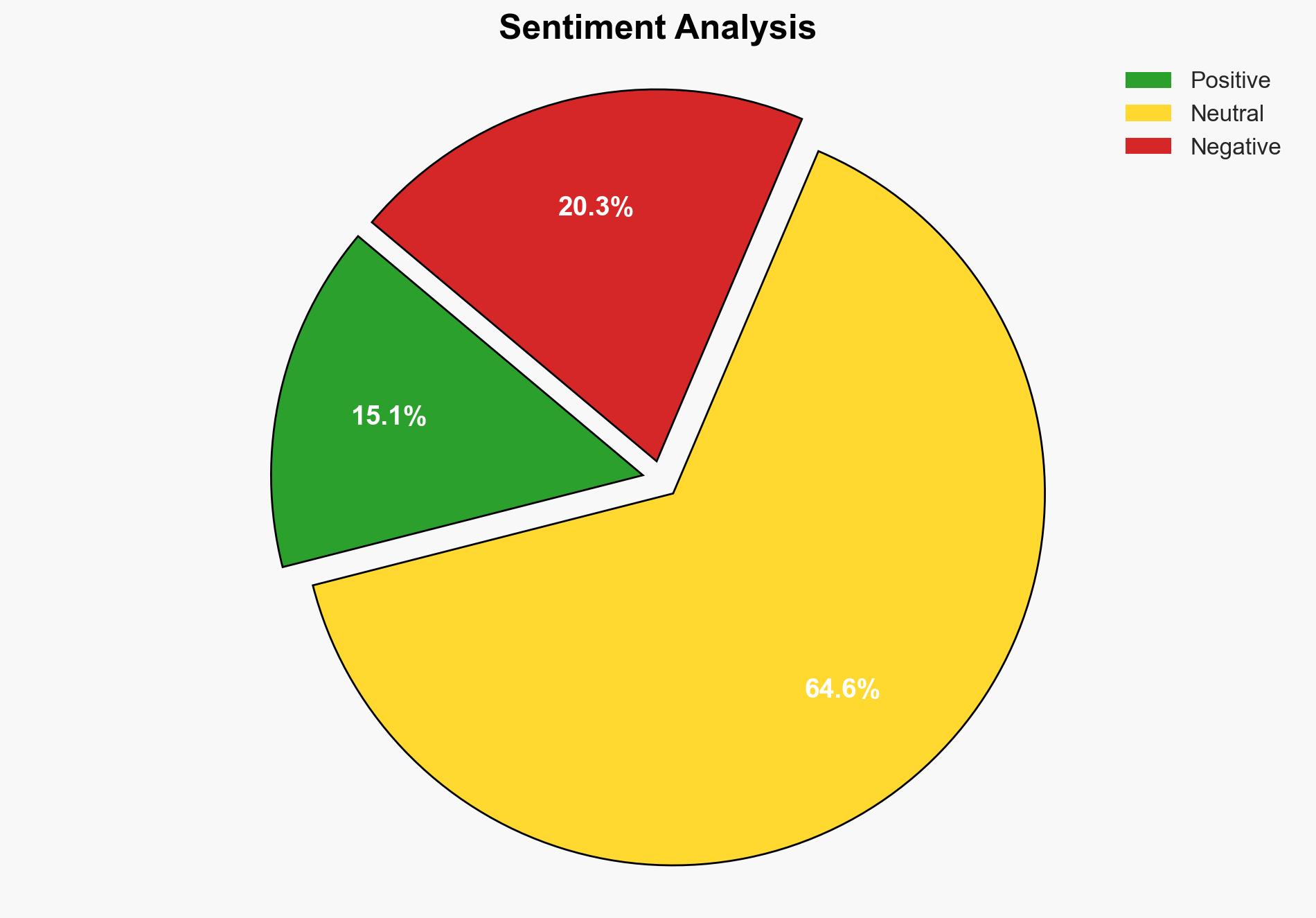
With a moderate confidence level, the most supported hypothesis is that the CVE-2025-62215 vulnerability, while actively exploited, is currently limited in scope due to its reliance on user interaction and the need for specific conditions to be met for successful exploitation. Strategic action should focus on ensuring widespread awareness and prompt application of patches, especially for systems beyond their end-of-life support.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The vulnerability is being exploited in a limited and targeted manner, primarily affecting systems that have not applied the latest patches or are beyond their end-of-life support.
Hypothesis 2: The vulnerability has the potential to be exploited on a larger scale if attackers develop more sophisticated methods to bypass current mitigations and leverage the vulnerability in a more automated fashion.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the current evidence of limited attack scope and the requirement for user interaction, which reduces the potential for widespread exploitation without significant attacker effort.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that Microsoft’s patch will effectively mitigate the vulnerability and that users will promptly apply these updates. A red flag is the potential for attackers to develop new methods to exploit the vulnerability more broadly, especially if systems remain unpatched. Deception indicators could include misinformation about the patch’s effectiveness or the vulnerability’s impact.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The primary risk is the potential for increased exploitation if systems remain unpatched, particularly those beyond end-of-life support. This could lead to escalated cyber threats, including data breaches or system disruptions. Economically, organizations may face increased costs related to incident response and system recovery. Politically, there could be pressure on Microsoft and other stakeholders to enhance security measures and support for legacy systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Ensure all systems are promptly updated with the latest patches, particularly those beyond end-of-life support.
- Increase user awareness regarding the risks of opening suspicious files and the importance of applying security updates.
- Monitor for any new developments or attack vectors related to this vulnerability.
- Best-case scenario: The vulnerability is effectively mitigated through patches and user education, preventing widespread exploitation.
- Worst-case scenario: Attackers develop new methods to exploit the vulnerability on a larger scale, leading to significant disruptions.
- Most-likely scenario: The vulnerability remains a concern for unpatched systems, but widespread exploitation is limited due to effective mitigation efforts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Dustin Childs, Chris Goettl, Adam Barnett, Ben McCarthy
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology