Examining GPL Implications for AI Model Training and Licensing Challenges
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The State of GPL Propagation to AI Models
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
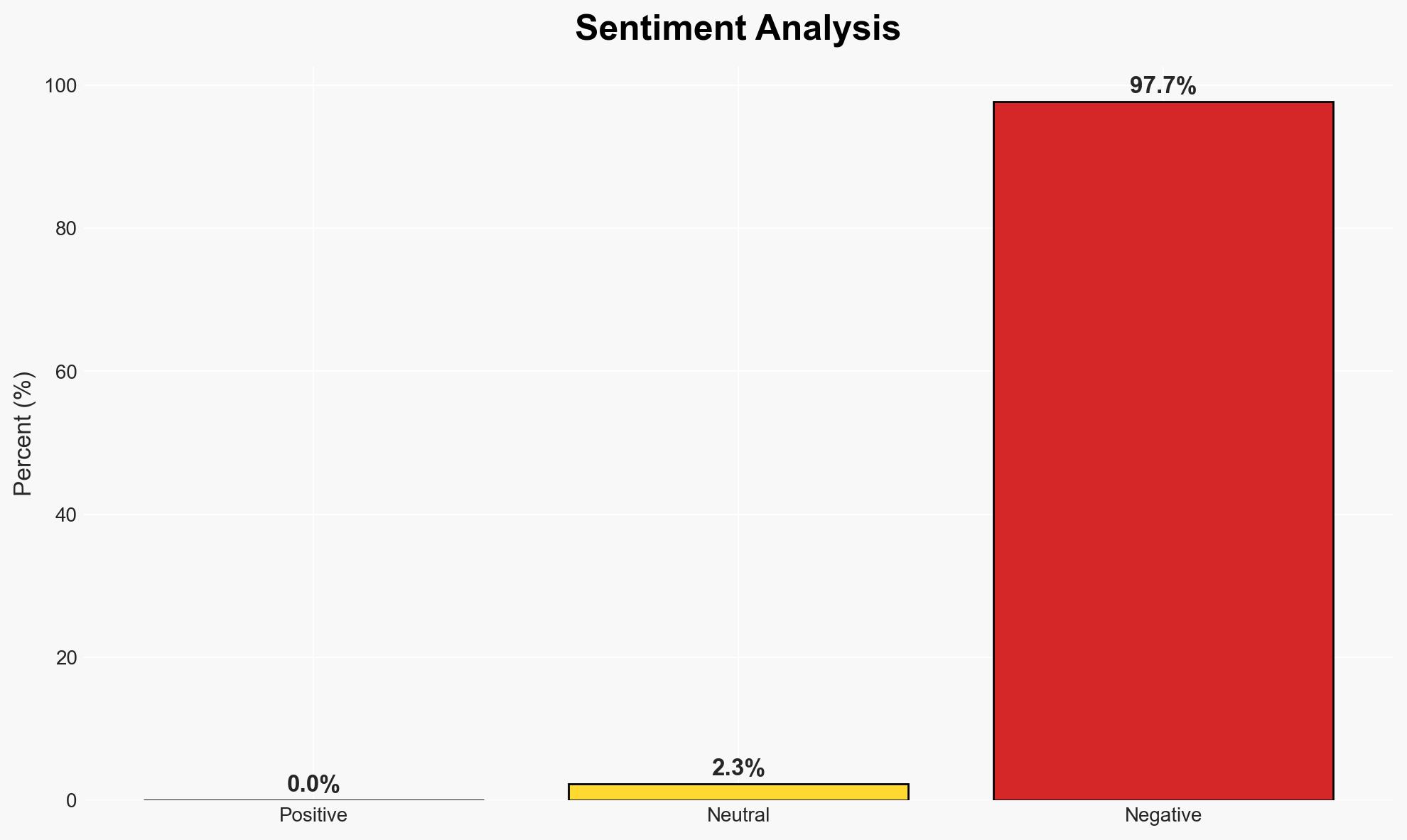
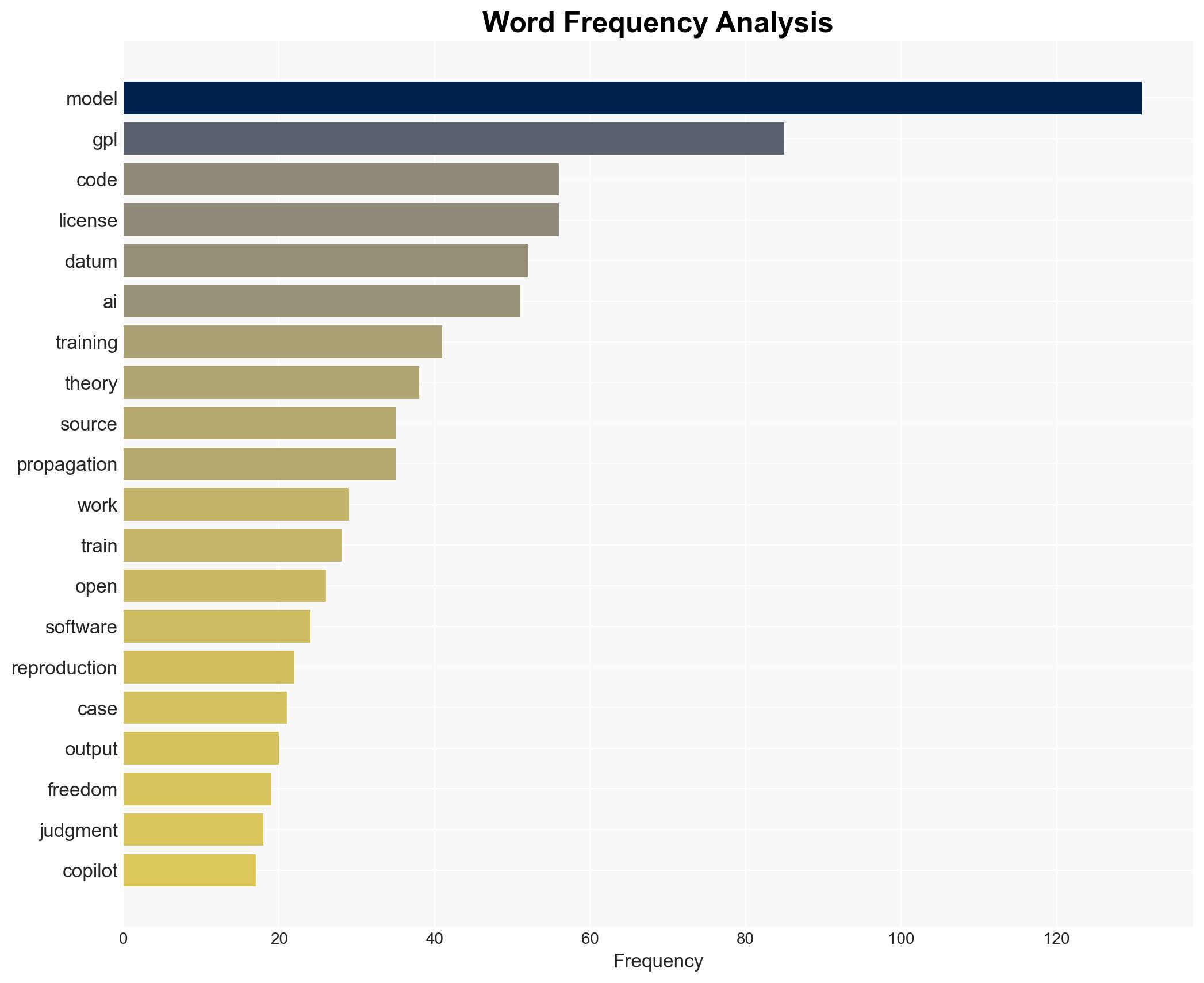
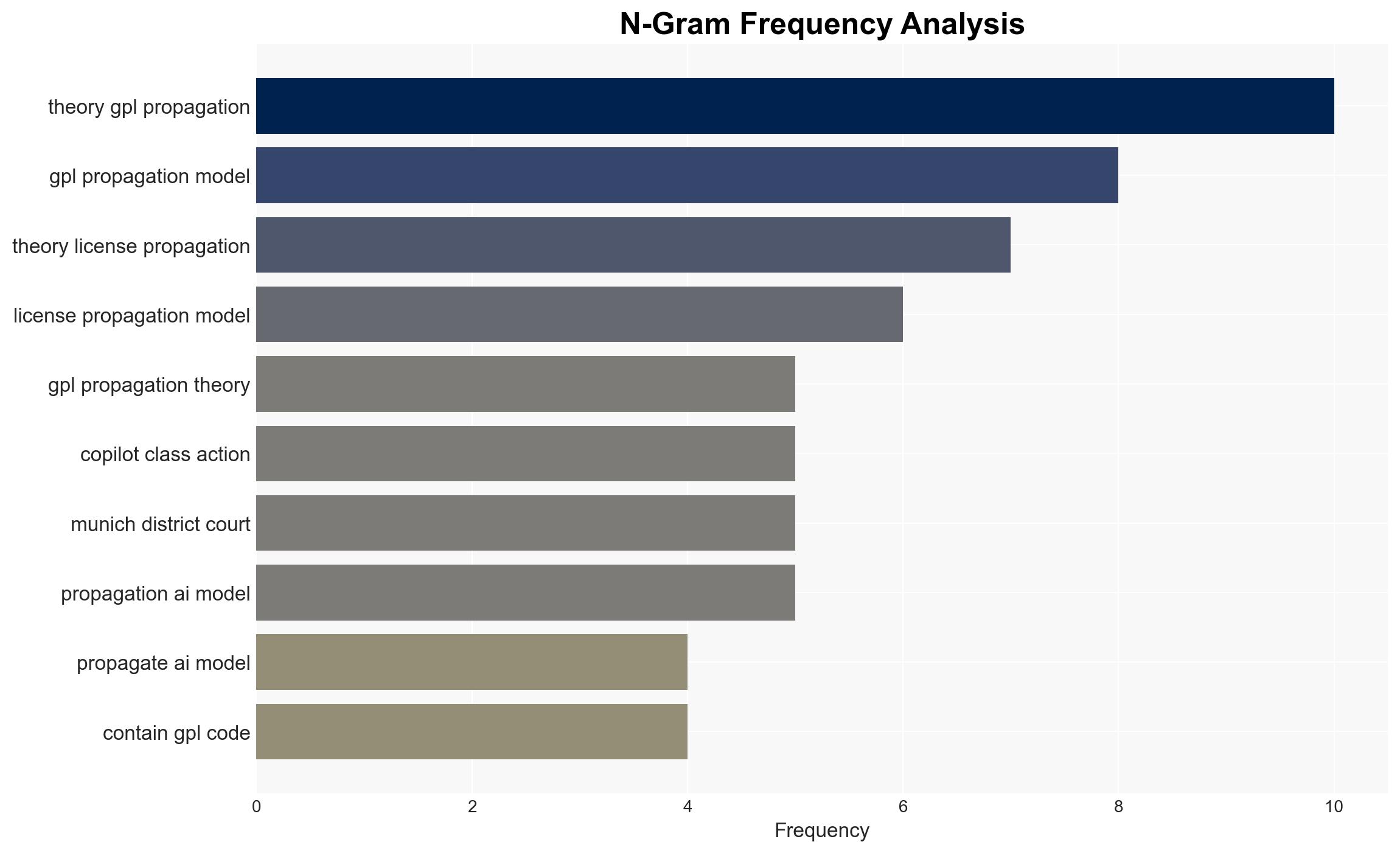
The ongoing legal disputes regarding the propagation of GPL licenses to AI models, such as those involving GitHub Copilot, highlight significant legal and operational uncertainties. The most likely hypothesis is that current legal frameworks are insufficient to address these issues, affecting developers, AI companies, and legal entities. Overall confidence in this judgment is moderate due to ongoing litigation and lack of precedent.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: GPL licenses propagate to AI models trained on GPL-licensed code, requiring these models to be released under the same license. This is supported by the theory that AI models are derivative works. However, ongoing legal challenges and lack of clear judicial rulings create uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: AI models do not constitute derivative works under GPL, and thus are not subject to its copyleft provisions. This is supported by the dismissal of some claims in the GitHub Copilot case, but the issue remains unresolved in broader legal contexts.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the dismissal of claims in the GitHub Copilot case. However, future legal rulings or legislative changes could shift this assessment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI models trained on GPL code could be considered derivative works; legal systems will eventually provide clarity on this issue; current legal frameworks are inadequate for AI-related IP issues.
- Information Gaps: Specific legal definitions of derivative works in the context of AI; outcomes of ongoing and future litigation; potential legislative changes.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in legal interpretations favoring large tech companies; risk of strategic litigation to shape legal precedents.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The resolution of GPL propagation issues could significantly impact AI development and open-source software use. Legal clarity could either stifle innovation or promote compliance and fair use.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for international legal divergence, affecting cross-border AI collaborations.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Limited direct impact, but broader implications for tech industry regulation and compliance.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased scrutiny on AI training data sources and potential for cyber-legal conflicts.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on AI companies due to compliance costs or legal liabilities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor ongoing litigation outcomes; engage with legal experts to assess potential impacts on AI projects.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop compliance strategies for potential GPL propagation rulings; foster partnerships with legal and industry bodies to influence policy development.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Clear legal guidelines emerge, facilitating innovation and compliance.
- Worst: Fragmented legal rulings lead to increased litigation and stifled AI development.
- Most-Likely: Continued legal ambiguity with gradual clarification through case law.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- GitHub, Microsoft, OpenAI, United States District Court for the Northern District of California
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, AI licensing, GPL propagation, open-source software, legal frameworks, intellectual property, AI development, compliance
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us