AI-Driven Voice Scam and IoT Malware Surge Highlight Growing Cyber Threat Landscape
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: ThreatsDay Bulletin AI Malware Voice Bot Flaws Crypto Laundering IoT Attacks and 20 More Stories
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
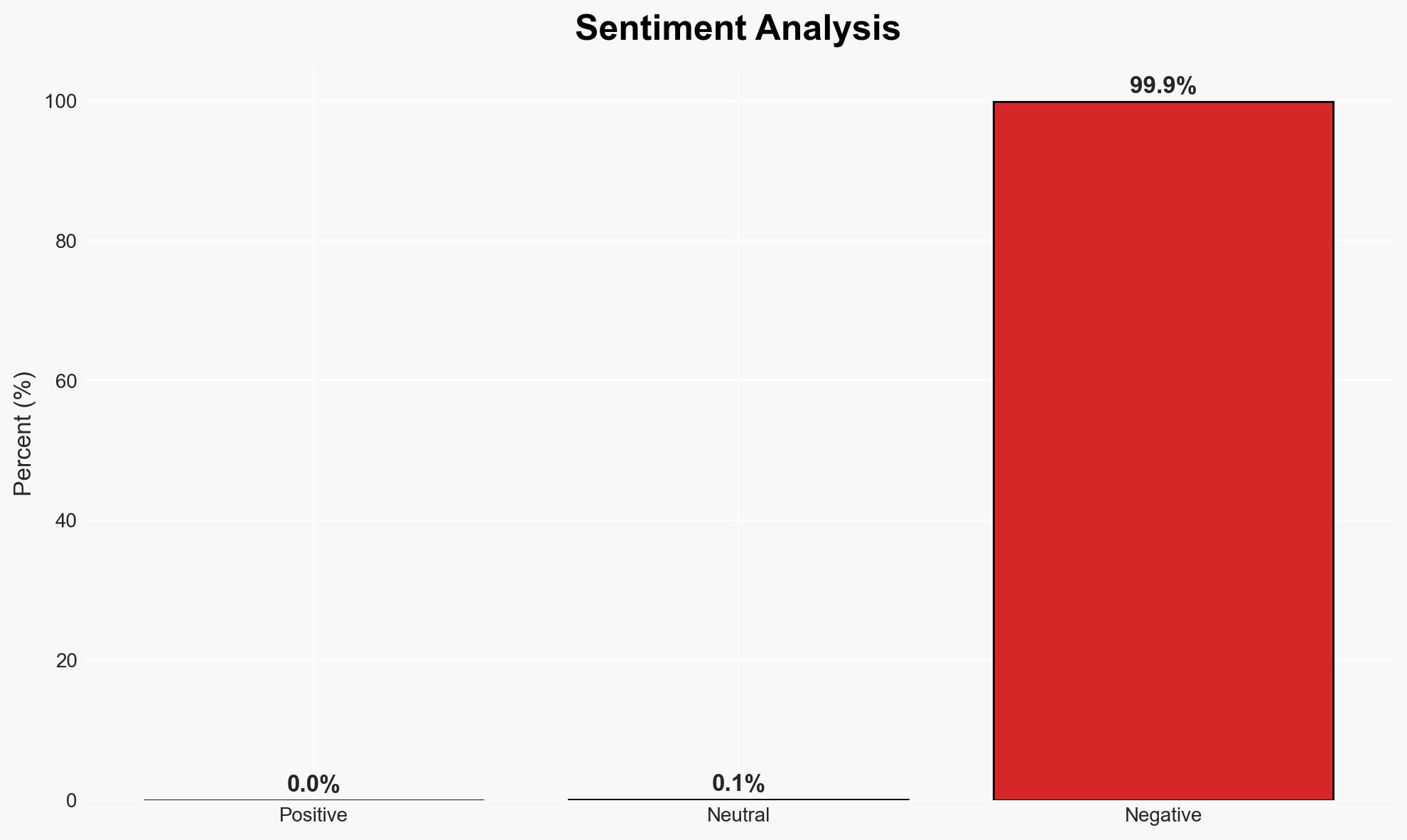
The resurgence of Mirai-based malware in IoT campaigns and the strategic shifts in threat actor behavior pose significant cybersecurity risks, particularly in sectors reliant on IoT devices. The observed activities suggest a potential increase in future DDoS attacks. This assessment is made with moderate confidence due to the complexity and evolving nature of the threat landscape.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The resurgence of Mirai-based malware is primarily a test run for a larger, coordinated attack targeting critical infrastructure. Supporting evidence includes the observed infection of IoT devices and the exploitation of known vulnerabilities. However, the precise targets and scale remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: The current activity represents opportunistic attacks by disparate threat actors exploiting IoT vulnerabilities for immediate financial gain. This is supported by the lack of a clear, unified target and the historical pattern of similar attacks.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the strategic nature of the observed shifts in threat actor behavior and the potential preparation for larger-scale operations. Indicators such as increased targeting of critical infrastructure could shift this judgment.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: IoT devices will continue to be a primary target due to their widespread vulnerabilities; threat actors have the capability to scale up operations; defensive measures by affected entities remain inadequate.
- Information Gaps: Specific details on the identity and motivations of the threat actors; comprehensive data on the full scope of the current campaign.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing attacks to known actors without conclusive evidence; risk of underestimating the capabilities of emerging threat actors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development could lead to increased vulnerability of critical infrastructure, necessitating enhanced cybersecurity measures. The evolving threat landscape may prompt geopolitical tensions if state actors are implicated.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tension between nations if state-sponsored actors are involved.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of DDoS attacks disrupting essential services, requiring enhanced security protocols.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased sophistication in malware and botnet operations, challenging existing cybersecurity defenses.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact due to disruptions in services and increased costs for cybersecurity measures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of IoT networks, patch known vulnerabilities, and increase awareness among stakeholders about potential threats.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing, and invest in advanced threat detection technologies.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mitigation of threats through coordinated international efforts and improved cybersecurity measures.
- Worst: Large-scale DDoS attacks on critical infrastructure leading to significant disruptions.
- Most-Likely: Continued sporadic attacks with gradual improvements in defensive capabilities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
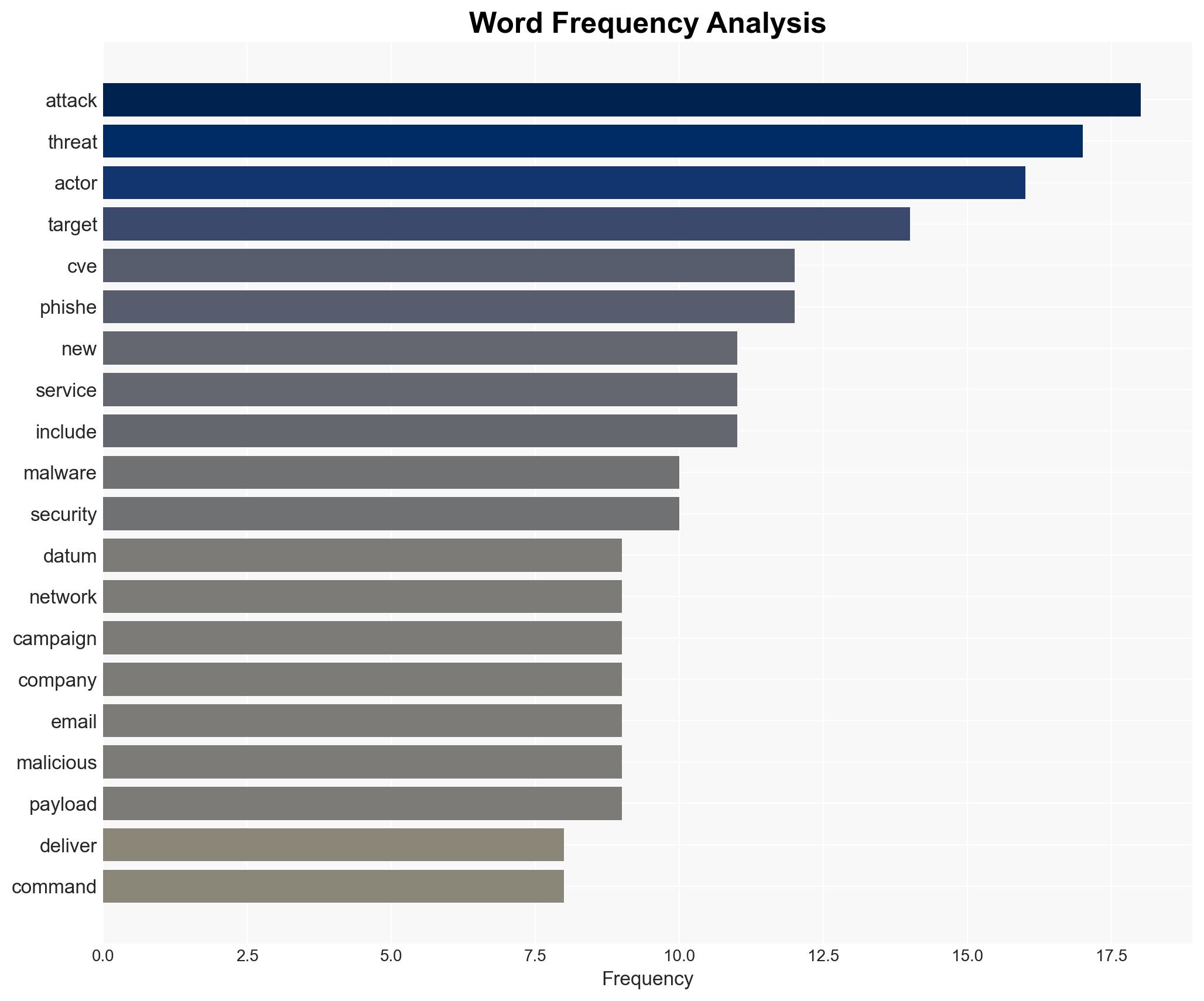
Cybersecurity, IoT vulnerabilities, Mirai malware, DDoS attacks, threat actor behavior, critical infrastructure, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us