Shifts in Global Power Dynamics Transforming the Geopolitical Landscape of the Red Sea Region
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How Global Power Shifts are Playing out in the Red Sea Region of the Mideast
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
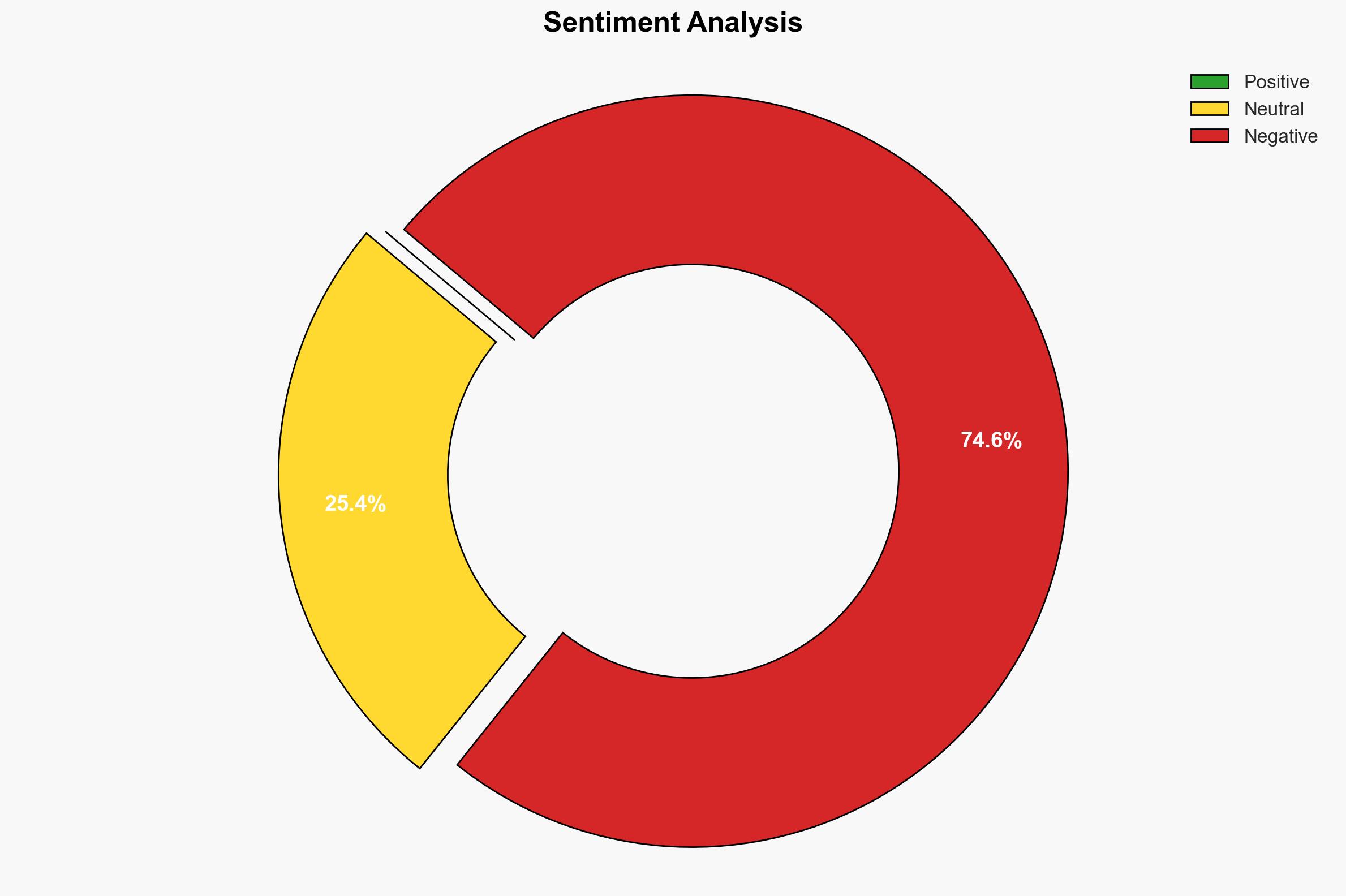
The Red Sea region is becoming a focal point for global power competition, with traditional Western influence declining and emerging powers like China and regional actors increasing their assertiveness. This shift is creating a complex geopolitical environment with potential for increased volatility and conflict. The overall confidence level in this assessment is moderate, given the dynamic and multifaceted nature of the region.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The Red Sea region will continue to see increased influence from non-Western powers, particularly China and Gulf states, due to their strategic investments and military presence. This is supported by the decline in Western geopolitical centrality and the active engagement of these powers in regional infrastructure and security.
- Hypothesis B: Western powers, primarily the United States, will reassert their influence in the Red Sea region through strategic partnerships and increased military presence to counterbalance the growing influence of China and regional actors. This hypothesis is less supported due to current trends of declining Western influence and the complexity of local alliances.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to observable trends of increased Chinese and Gulf state investments and military activities. Indicators that could shift this judgment include significant Western diplomatic or military initiatives in the region.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The geopolitical significance of the Red Sea will continue to attract external powers; regional actors will leverage external rivalries for strategic gains; Western influence will not significantly rebound in the near term.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the specific military capabilities and infrastructure investments by external powers in the region; insights into local political dynamics and alliances.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in underestimating Western strategic interests; risk of deception from regional actors overstating external support to gain leverage.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolving power dynamics in the Red Sea region could lead to increased geopolitical tensions and potential conflicts, impacting global trade routes and regional stability.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regional conflicts as local actors exploit global rivalries; shifts in alliances could destabilize existing power balances.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased military presence by multiple powers may lead to heightened security risks and proxy conflicts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for cyber operations targeting critical infrastructure and information warfare to influence regional narratives.
- Economic / Social: Investments in infrastructure could boost local economies but may also exacerbate social inequalities and tensions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance intelligence monitoring of military and economic activities in the region; engage in diplomatic dialogues with key regional actors.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop strategic partnerships with regional powers; invest in resilience measures to protect critical infrastructure and trade routes.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Stabilization through multilateral cooperation and balanced power influence.
- Worst: Escalation of proxy conflicts leading to broader regional instability.
- Most-Likely: Continued competition with periodic tensions and localized conflicts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
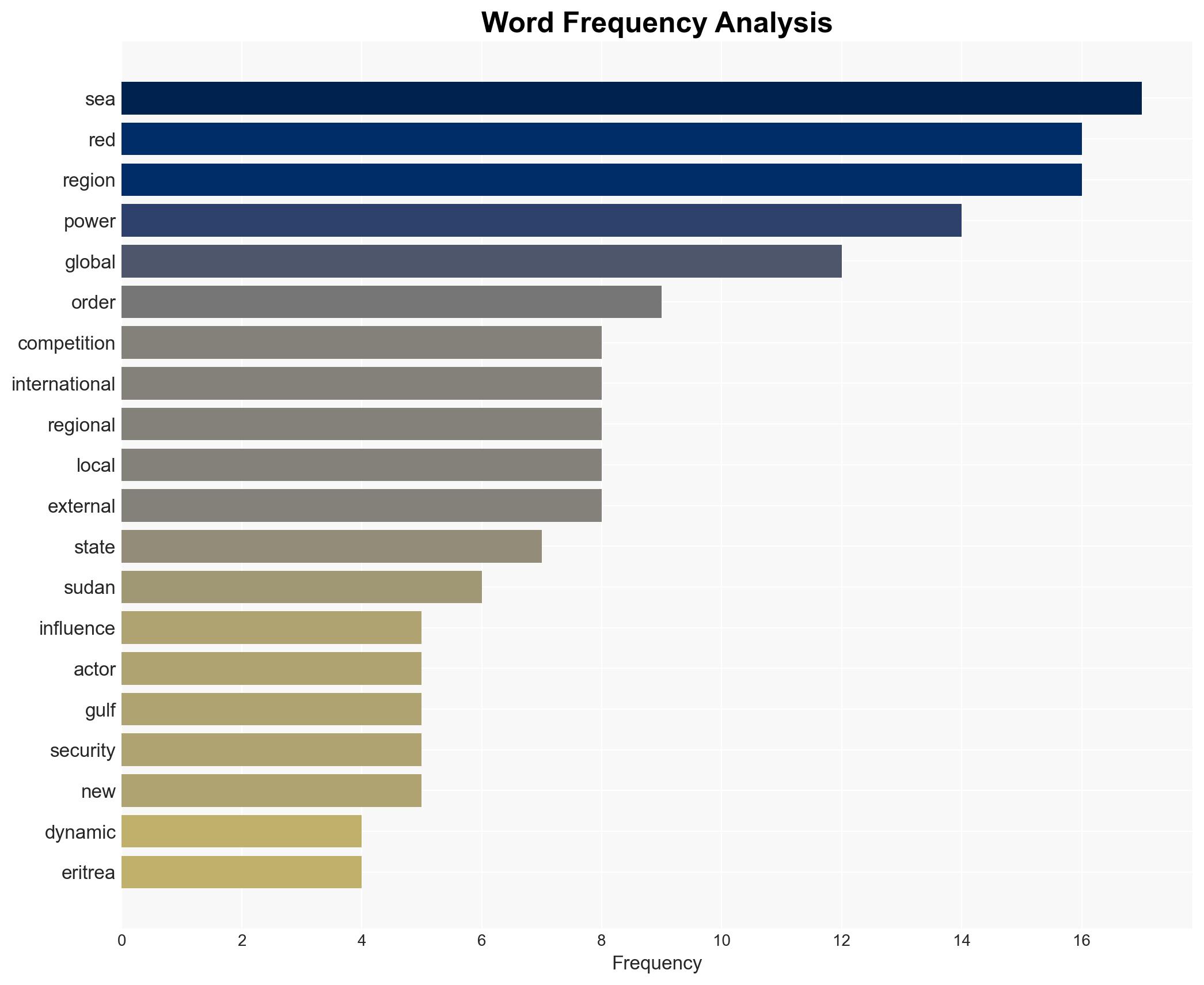
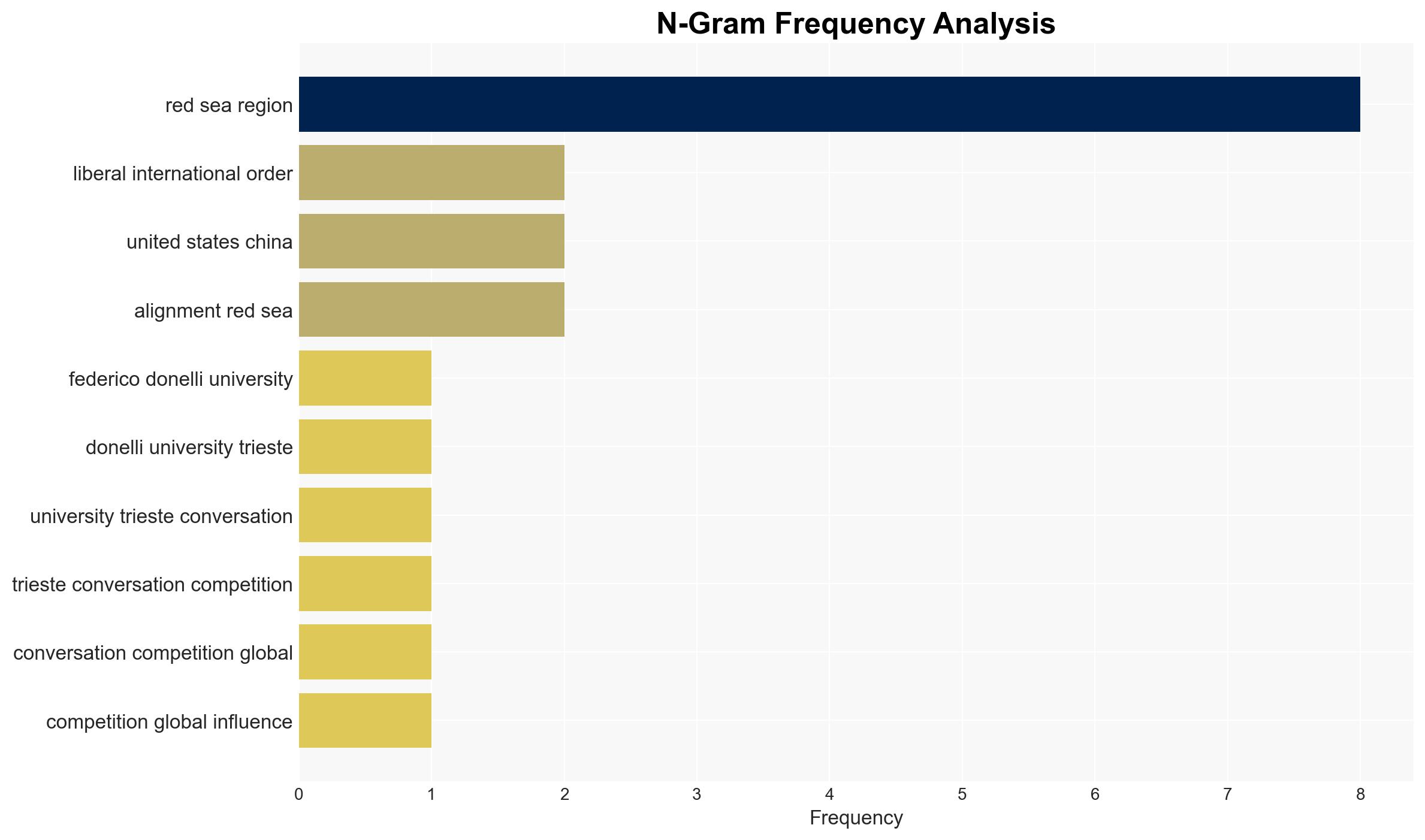
Regional Focus, global power competition, Red Sea region, geopolitical shifts, military presence, regional alliances, infrastructure investment, proxy conflicts
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Deconstruct and track propaganda or influence narratives.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us