Trump’s Collective Punishment of Afghan Migrants: An Ineffective Strategy Against Terrorism
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
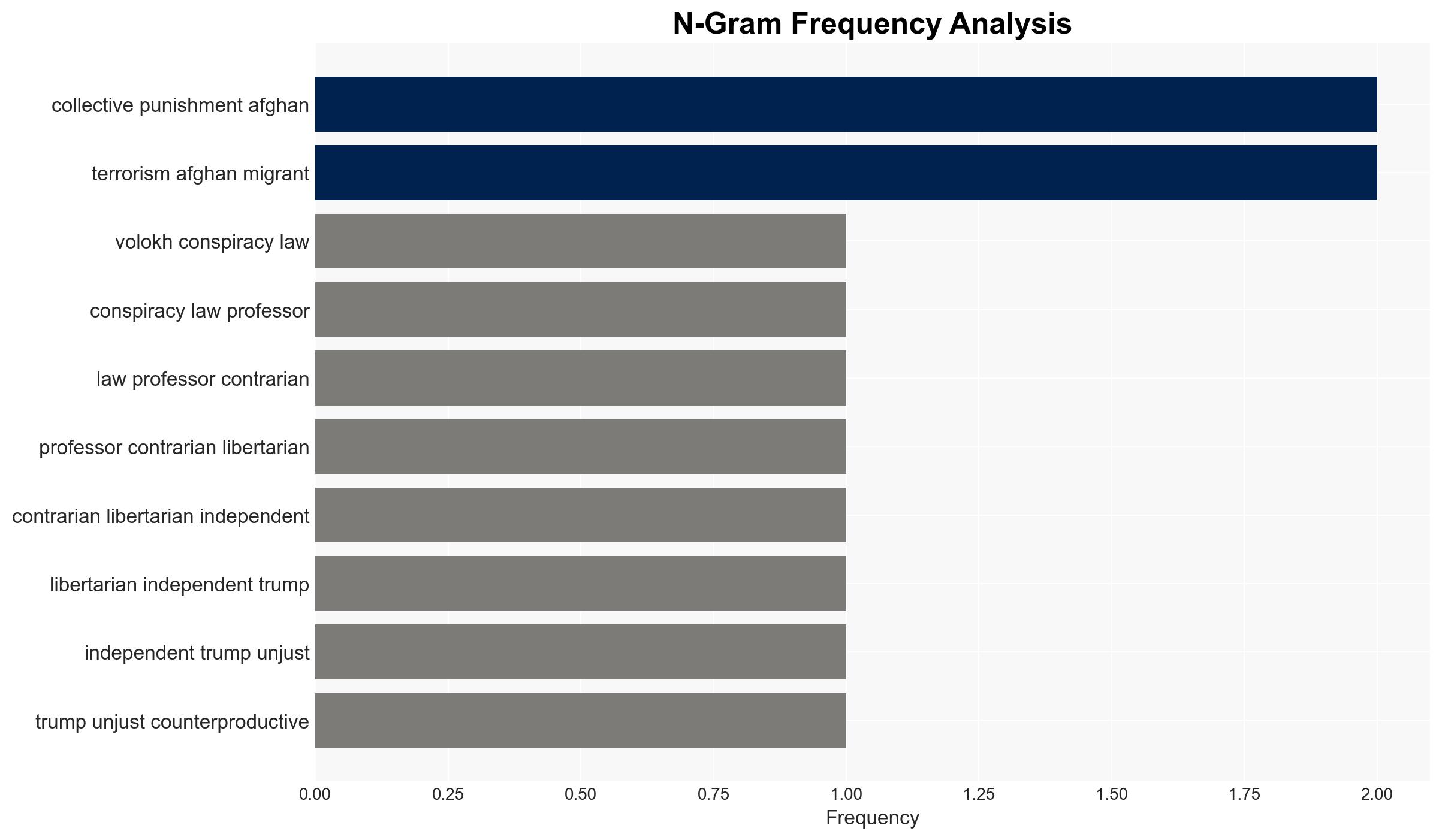
Intelligence Report: Ilya Somin Trump’s Unjust and Counterproductive Collective Punishment of Afghan Migrants
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
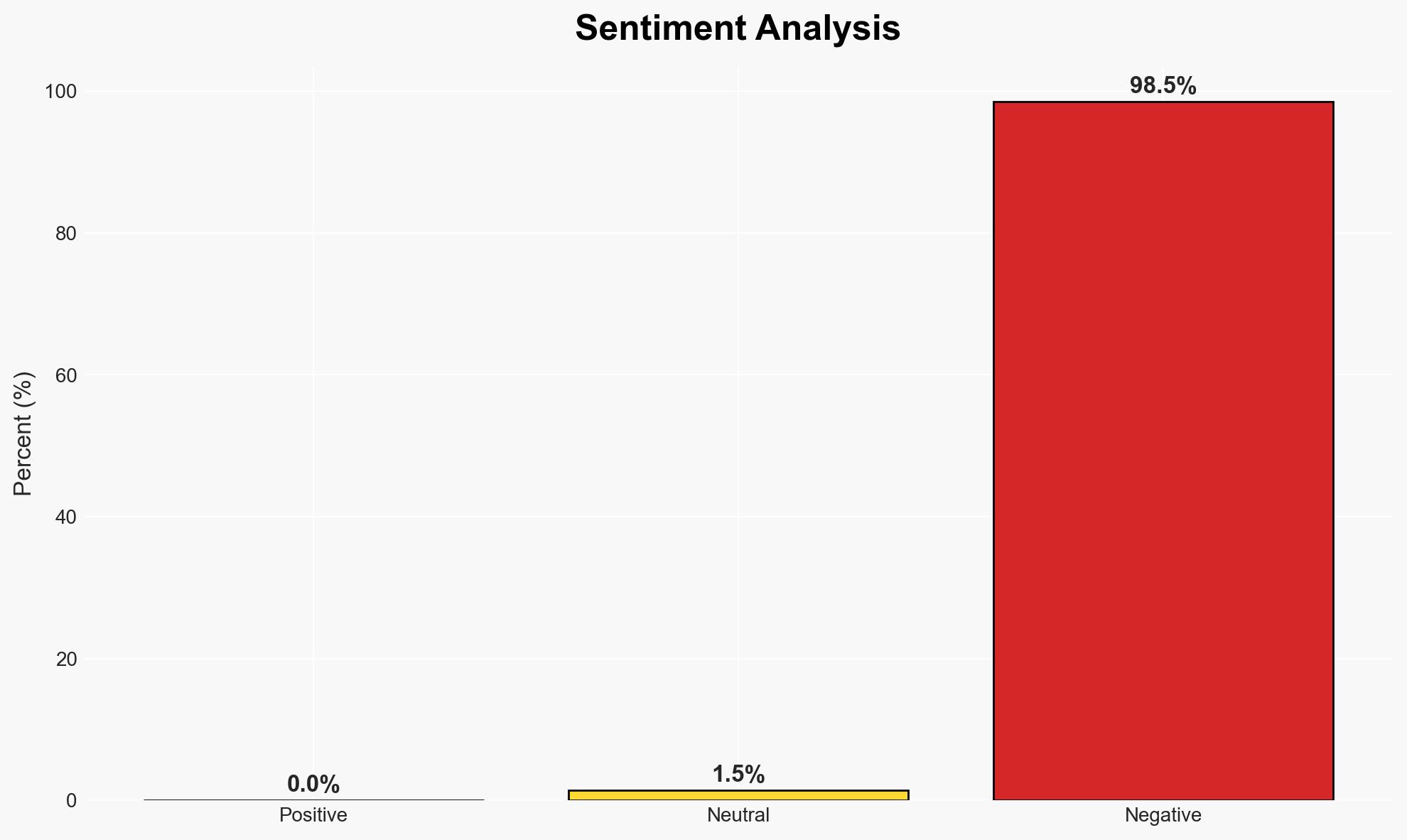
The Trump administration’s decision to suspend immigration processing for Afghan migrants is assessed as unjust and counterproductive, potentially undermining counter-terrorism efforts. This action affects Afghan migrants and could strain U.S. relations with current and future allies. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited data on the specific motivations behind the policy shift.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The suspension of Afghan immigration processing is primarily a security measure intended to prevent potential terrorist threats. Evidence includes the administration’s response to a violent incident involving an Afghan migrant. However, the low historical rate of terrorism among Afghan migrants contradicts this rationale.
- Hypothesis B: The policy is driven by political motives, using security as a pretext to reduce immigration from specific regions. Supporting evidence includes the lack of comprehensive data linking Afghan migrants to terrorism and the potential for ethnic bias in policy formulation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the low incidence of terrorism among Afghan migrants and the potential for political motivations. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include new intelligence on specific threats or changes in policy rhetoric.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Afghan migrants have a low propensity for terrorism; U.S. policy decisions are influenced by both security and political factors; ethnic bias may influence immigration policy.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the motivations behind the policy shift and comprehensive statistics on Afghan migrant involvement in terrorism.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential confirmation bias in interpreting migrant-related incidents; political bias in policy decisions; possible manipulation of threat narratives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
This development could exacerbate tensions between the U.S. and its allies, particularly those involved in counter-terrorism efforts. It may also affect domestic social cohesion and perceptions of U.S. immigration policy.
- Political / Geopolitical: Strained relations with allies and partners who oppose the policy; potential diplomatic backlash.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Undermining trust with local allies in conflict zones, potentially reducing cooperation in counter-terrorism efforts.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased propaganda or misinformation campaigns exploiting perceived ethnic bias in U.S. policies.
- Economic / Social: Potential negative impact on Afghan communities in the U.S. and increased social tensions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive review of the policy’s impact on security and alliances; engage with Afghan community leaders to mitigate social tensions.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to maintain trust with allies; enhance vetting processes without broadly punitive measures.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Policy is revised to balance security and humanitarian concerns, strengthening alliances.
- Worst Case: Policy leads to significant diplomatic fallout and reduced cooperation in counter-terrorism efforts.
- Most Likely: Continued policy debate with incremental adjustments based on political and security developments.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
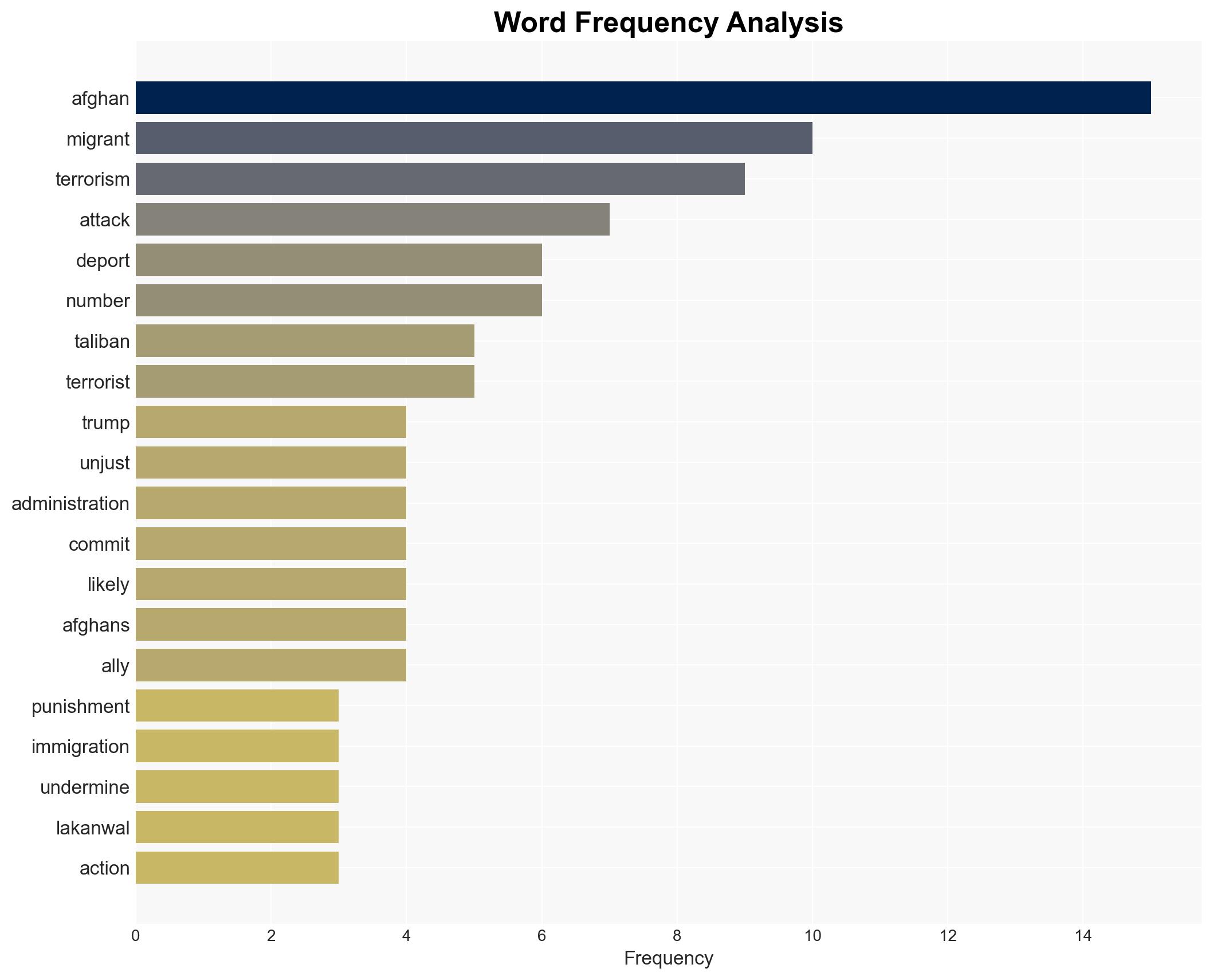
7. Thematic Tags
Counter-Terrorism, immigration policy, ethnic bias, U.S.-Afghan relations, security measures, political motivations, migrant rights
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us