UN Resolution on Gaza: A Misguided Effort That Lacks Viability and Risks Further Conflict
Published on: 2025-11-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Why The UN Resolution For Trumps Colonial Takeover of Gaza Is Wrong and Will Fail
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
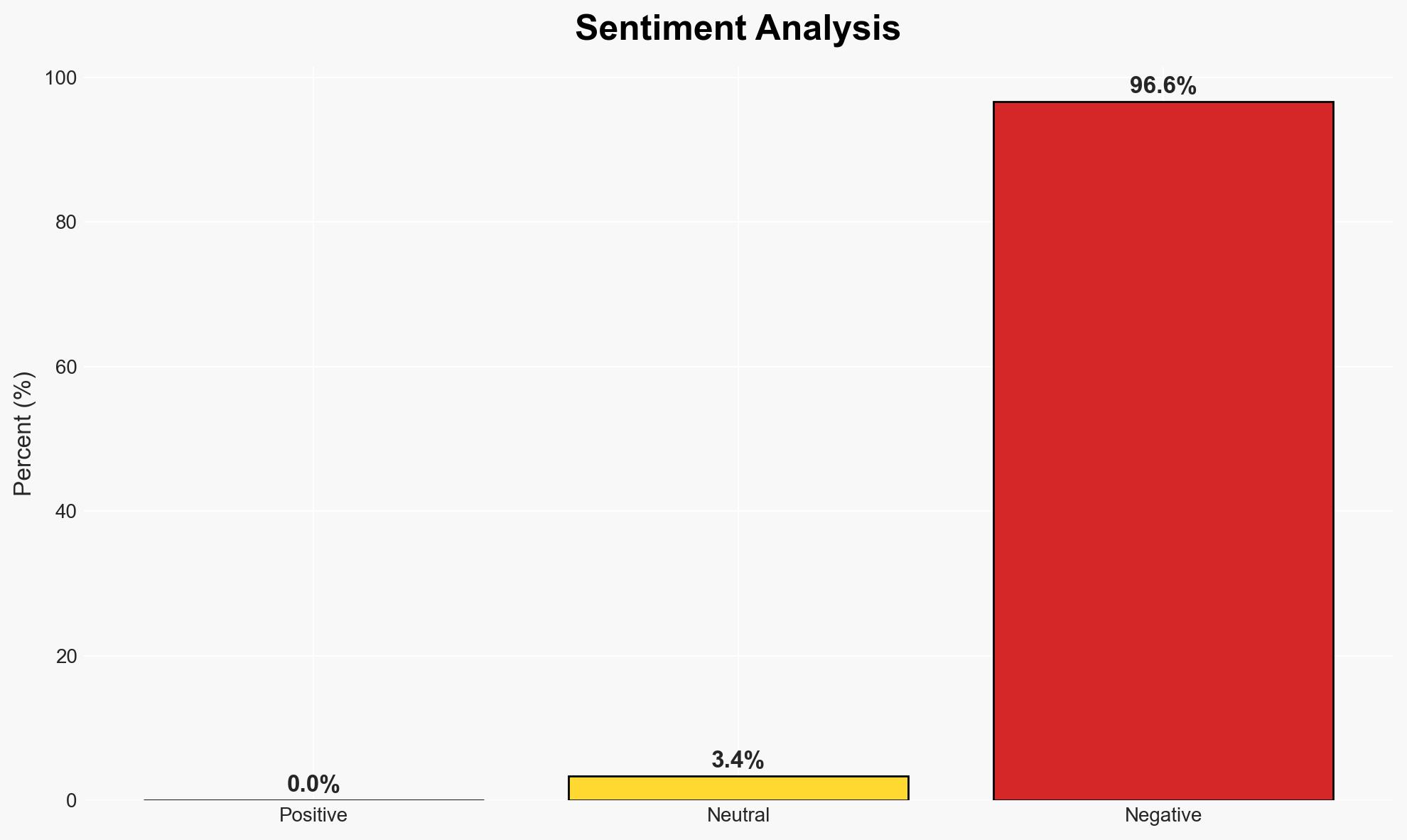
The UN resolution aimed at addressing the Israeli occupation of Palestinian territories, including Gaza, is unlikely to succeed due to geopolitical complexities and lack of enforcement mechanisms. The resolution’s failure to compel Israeli withdrawal or ensure Palestinian self-determination highlights significant international diplomatic challenges. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, considering the historical context and current geopolitical dynamics.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The UN resolution will fail to achieve its objectives due to Israel’s geopolitical influence and the lack of binding enforcement mechanisms. Supporting evidence includes historical precedents of non-compliance and geopolitical support for Israel from key states. Key uncertainties involve potential shifts in international diplomatic stances.
- Hypothesis B: The resolution could succeed if there is a significant shift in international pressure and consensus, potentially leading to Israeli compliance. Contradicting evidence includes the current geopolitical climate and historical resistance to similar resolutions.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the entrenched geopolitical support for Israel and historical patterns of non-compliance with similar resolutions. Indicators that could shift this judgment include changes in U.S. policy or increased diplomatic pressure from influential global actors.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The UN lacks effective enforcement mechanisms; Israel will continue to receive support from key allies; Palestinian self-determination remains a contentious issue.
- Information Gaps: Detailed insights into the internal deliberations of key UN member states and their future diplomatic strategies.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from sources with vested interests in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict; risk of manipulation in diplomatic communications.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The failure of the UN resolution could exacerbate tensions in the region, impacting broader Middle Eastern stability and international diplomatic relations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased polarization within the UN and among member states, complicating future diplomatic efforts.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of regional instability and potential escalation of conflict, impacting counter-terrorism operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased propaganda and misinformation campaigns from involved parties, potentially influencing public opinion and policy decisions.
- Economic / Social: Continued economic hardship and social unrest in Palestinian territories, affecting regional economic stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor diplomatic communications and public statements from key UN member states; engage in dialogue with regional partners to assess potential shifts in policy.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to mitigate potential regional instability; strengthen partnerships with regional allies to support diplomatic efforts.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best Case: Increased international pressure leads to partial compliance and de-escalation.
- Worst Case: Escalation of conflict and further deterioration of regional stability.
- Most Likely: Continued stalemate with periodic diplomatic tensions and minor escalations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
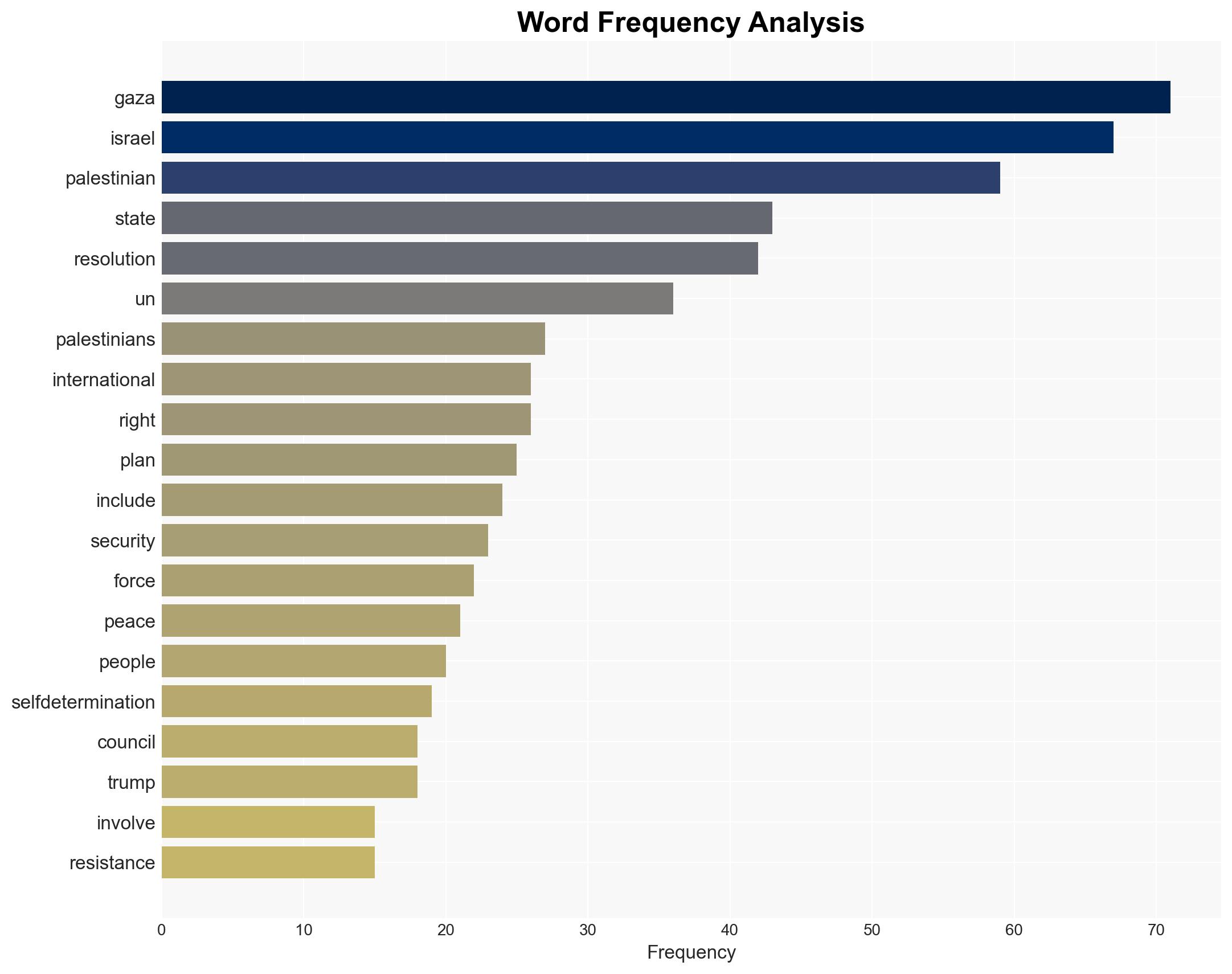
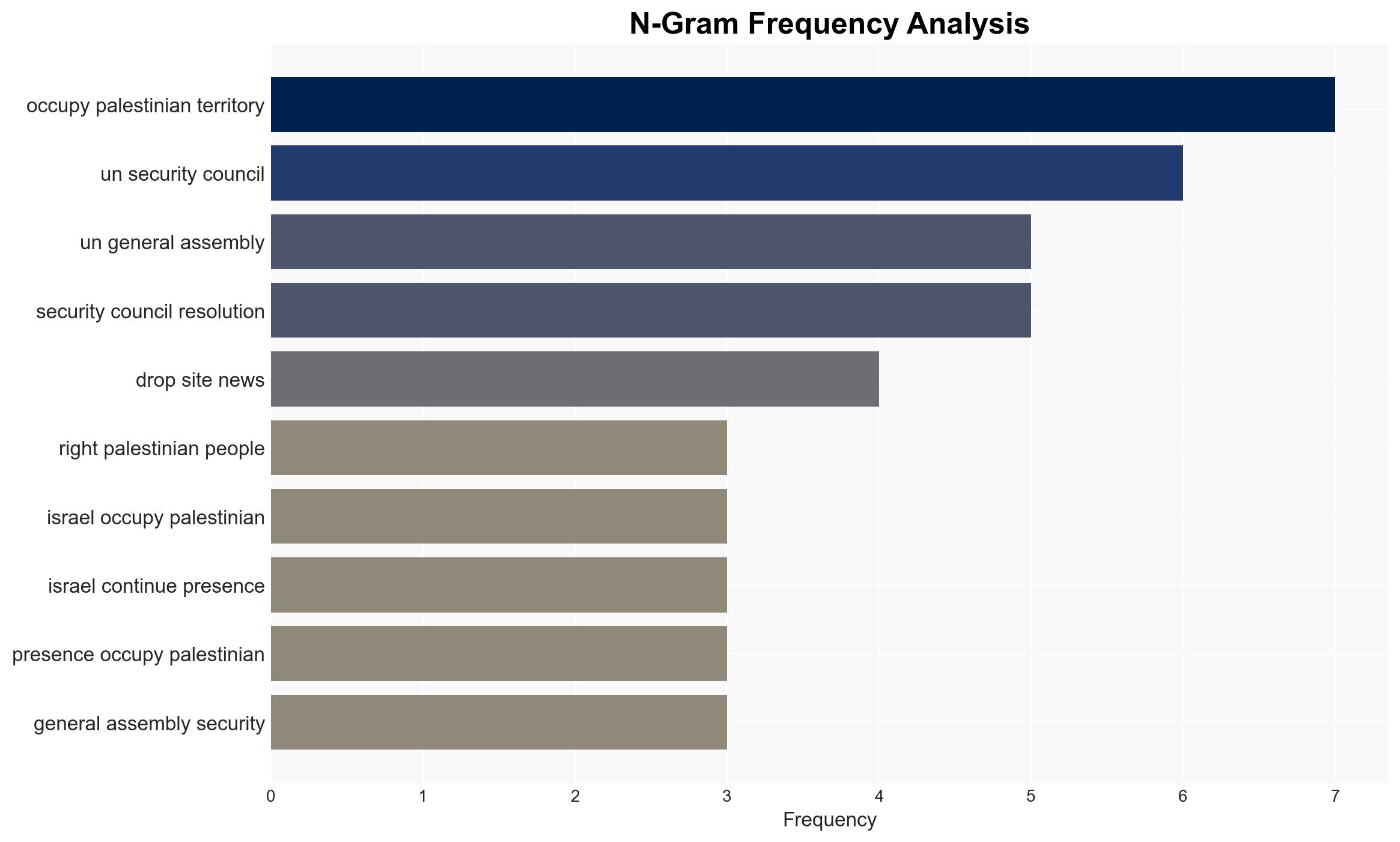
Counter-Terrorism, UN resolutions, Israeli-Palestinian conflict, geopolitical dynamics, international diplomacy, regional stability, enforcement mechanisms, Middle East politics
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Structured challenge to expose and correct biases.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us