Cybersecurity Alert: LinkedIn Used by Chinese Spies for Recruitment Amid Rising Crypto Crime and Malware Thre…
Published on: 2025-11-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: ThreatsDay Bulletin 0-Days LinkedIn Spies Crypto Crimes IoT Flaws and New Malware Waves
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
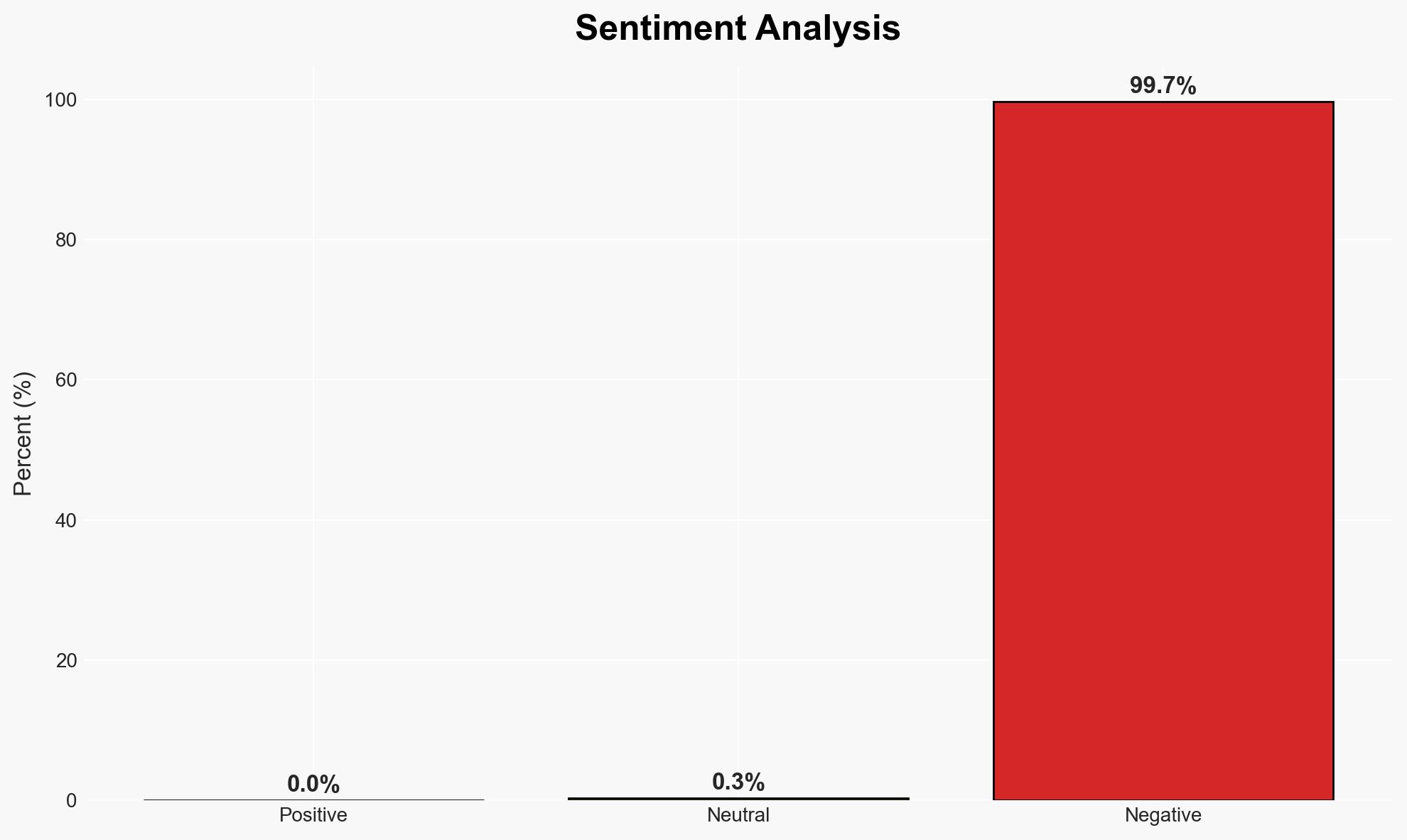
The current cyber threat landscape is characterized by increased espionage activities, notably through LinkedIn, and sophisticated cybercriminal operations targeting IoT devices and cryptocurrency platforms. The most likely hypothesis is that state-sponsored actors, particularly from China, are leveraging professional networks for intelligence gathering, posing significant risks to national security and economic stability. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the potential for misinformation and incomplete data.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: State-sponsored actors, particularly from China, are using LinkedIn to conduct espionage activities, targeting professionals in sensitive sectors. This is supported by MI5 warnings and patterns of outreach consistent with intelligence gathering. However, uncertainties include the scale of operations and the effectiveness of countermeasures.
- Hypothesis B: The increase in LinkedIn espionage activities is primarily driven by independent cybercriminal groups exploiting professional networks for financial gain rather than state objectives. Evidence for this includes the prevalence of cybercrime linked to financial incentives, but it lacks the strategic targeting observed in state-sponsored operations.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the involvement of MI5 and the strategic nature of the targets, which align with state interests. Indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of financial transactions linked to independent groups or a decrease in state-level targeting.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: State actors have the capability and intent to exploit professional networks; LinkedIn remains a viable platform for espionage; current countermeasures are insufficient to deter these activities.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the methods and tools used by these actors; comprehensive statistics on the scale and impact of these operations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in source reporting, particularly from state-affiliated media; risk of deception by state actors to mislead attribution efforts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of these cyber threats could lead to increased geopolitical tensions and necessitate enhanced cybersecurity measures. The interplay between state-sponsored espionage and cybercrime could destabilize economic and security environments.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential escalation in diplomatic tensions between China and Western nations, particularly the UK and EU.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased vulnerability of critical infrastructure and sensitive sectors to espionage and cyberattacks.
- Cyber / Information Space: Heightened risk of data breaches and misinformation campaigns leveraging compromised professional networks.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic disruptions due to compromised corporate and financial data; erosion of trust in digital platforms.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of professional networks for suspicious activities; increase awareness and training for potential targets.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with tech companies to improve platform security; invest in advanced threat detection capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful mitigation of espionage activities through international cooperation and improved cybersecurity measures.
- Worst: Escalation of cyber threats leading to significant economic and security breaches.
- Most-Likely: Continued state-sponsored espionage with periodic disruptions and incremental improvements in countermeasures.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- MI5 (UK’s domestic intelligence agency)
- Chinese Ministry of State Security
- European Commission
- ASIO (Australia’s Security Intelligence Organization)
- Sir Lindsay Hoyle (House of Commons Speaker)
- BBC (as a reporting entity)
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, cyber-espionage, state-sponsored threats, LinkedIn, cryptocurrency, IoT vulnerabilities, malware, geopolitical tensions
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us