Albiriox MaaS Malware Compromises 400 Apps for On-Device Fraud and Remote Screen Control
Published on: 2025-12-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: New Albiriox MaaS Malware Targets 400 Apps for On-Device Fraud and Screen Control
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
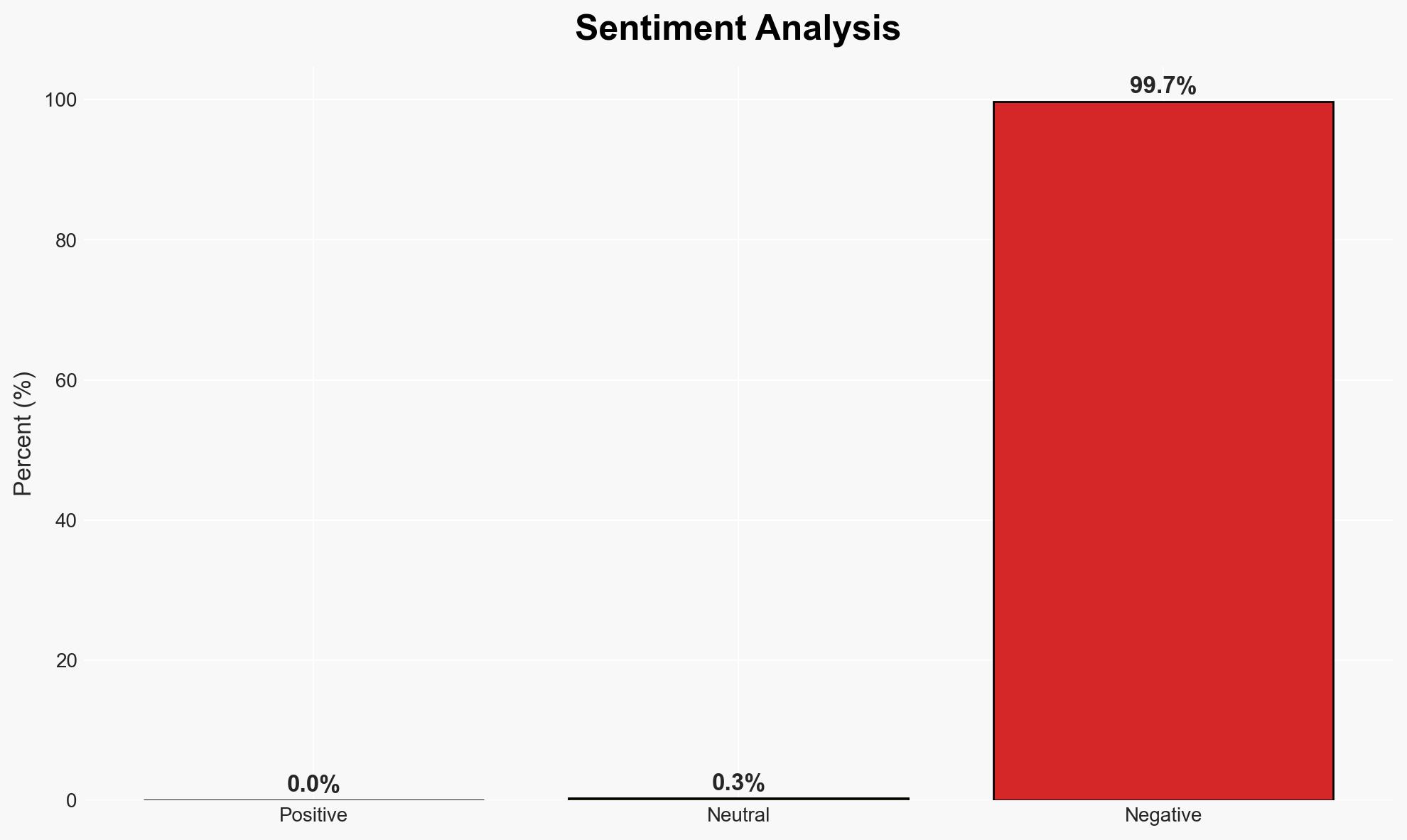
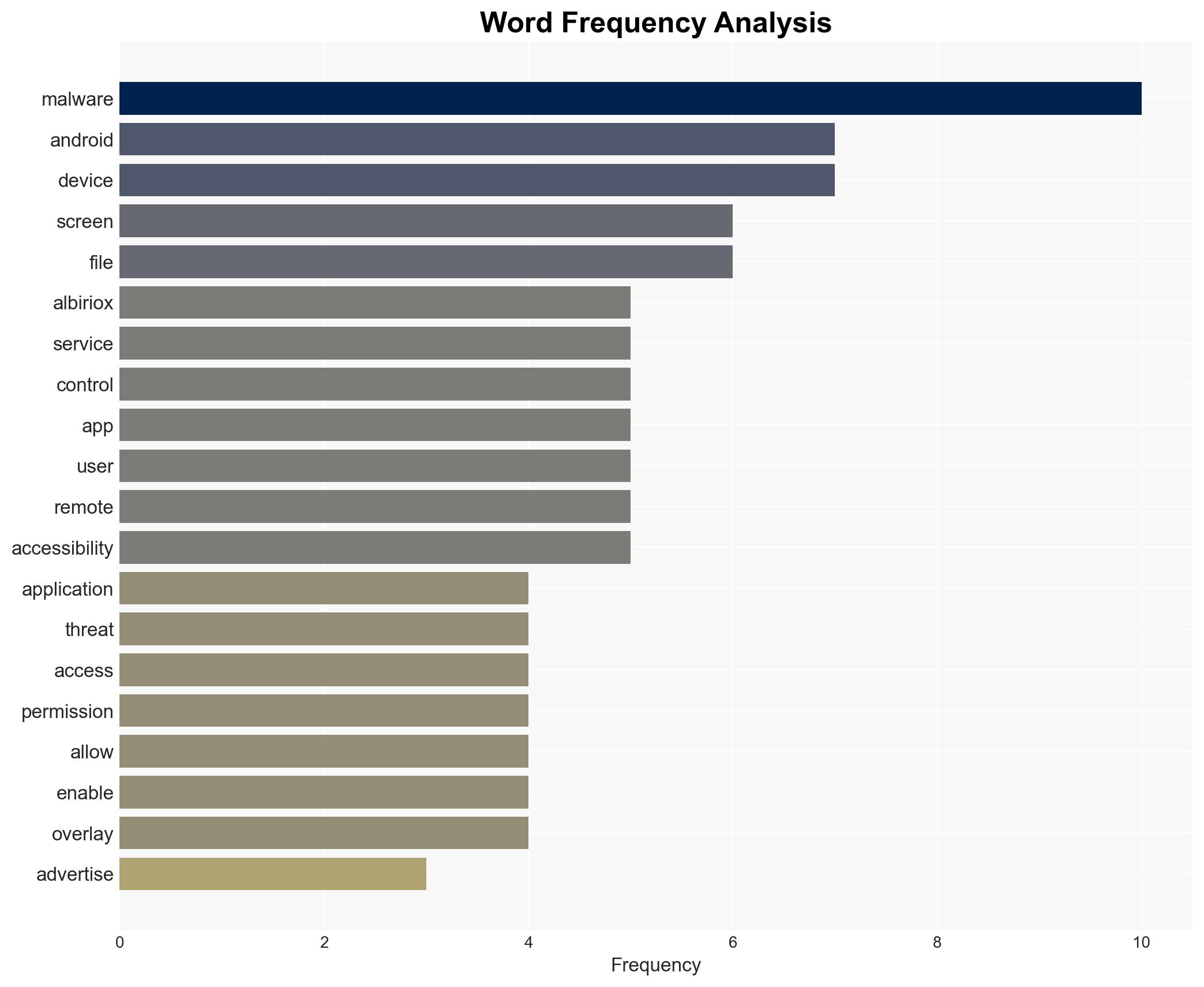
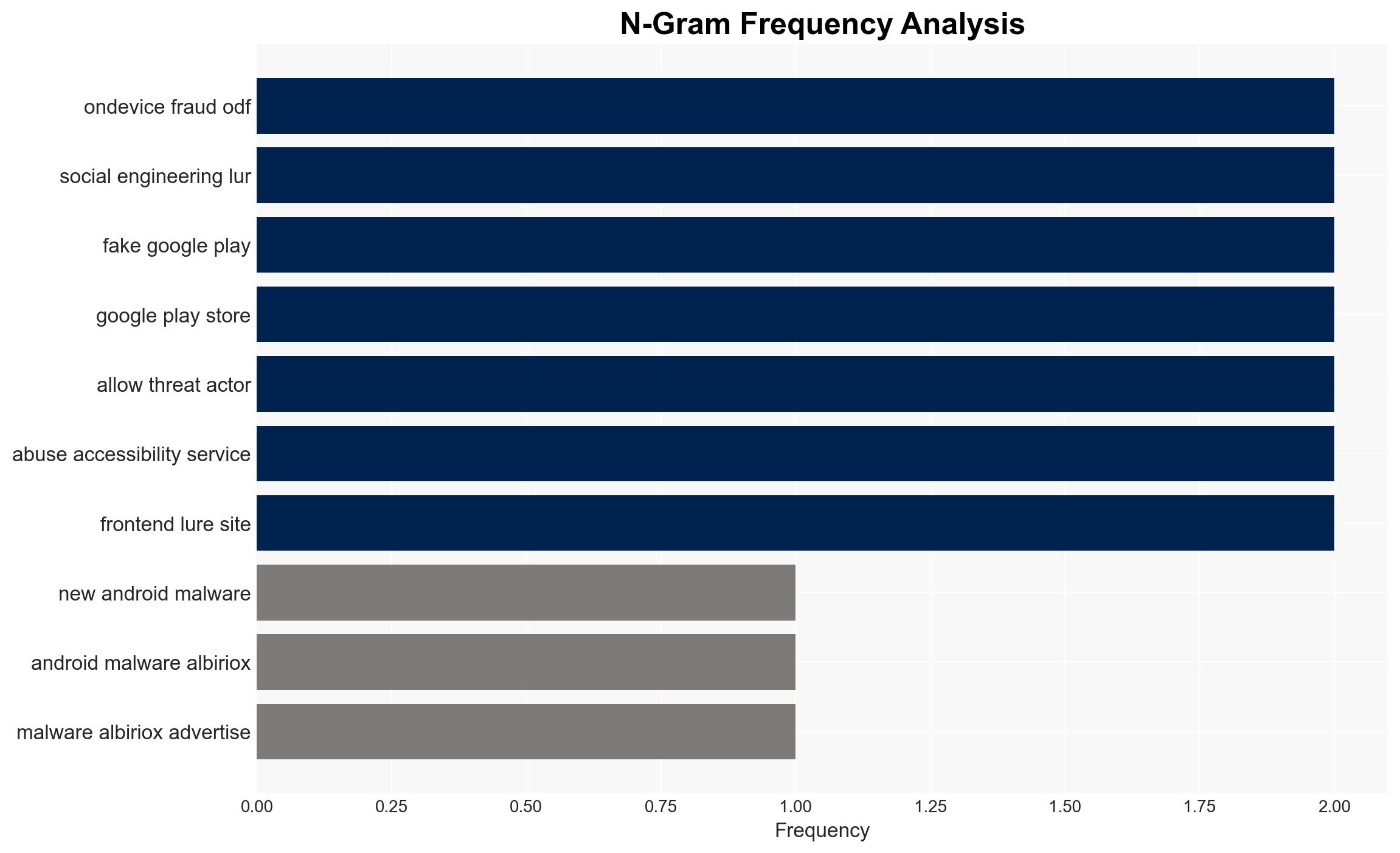
The Albiriox malware, operating under a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model, poses a significant threat to financial and cryptocurrency applications by facilitating on-device fraud and screen control. The malware is likely developed by Russian-speaking actors and is currently targeting Austrian users. The overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the reliance on linguistic and infrastructure analysis.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Albiriox is primarily a tool for financial gain by Russian-speaking cybercriminals targeting financial applications. This is supported by the malware’s capabilities and the linguistic patterns observed. However, the exact identity and motivations of the actors remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: Albiriox could be a state-sponsored tool aimed at destabilizing financial systems in targeted regions. This is less supported due to the lack of direct evidence linking state actors and the focus on financial fraud rather than broader disruption.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the specific targeting of financial applications and the use of cybercrime forums for distribution. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of state sponsorship or changes in targeting patterns.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The actors are motivated by financial gain; the malware’s primary targets are financial applications; the current targeting is limited to Austria.
- Information Gaps: The full extent of the malware’s distribution network; the identities of the actors; potential links to other cybercriminal or state-sponsored groups.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in attributing the malware to Russian-speaking actors based solely on linguistic analysis; the possibility of false flag operations to mislead attribution.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of Albiriox could lead to increased financial fraud incidents and undermine trust in digital financial systems. If the malware’s capabilities are expanded or its targeting broadened, it could have significant geopolitical and economic repercussions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if linked to state actors or if financial systems are destabilized.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced threat environment for financial institutions and potential for cross-border cybercrime collaboration.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased sophistication in malware tactics, potentially influencing future cybercrime trends.
- Economic / Social: Potential loss of consumer confidence in digital financial services, impacting economic stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of financial and cryptocurrency applications; enhance public awareness campaigns on phishing and malware risks.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in advanced detection and response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Effective mitigation and law enforcement actions reduce the threat.
- Worst: Expansion of malware capabilities and targets leads to widespread financial disruption.
- Most-Likely: Continued targeting of financial applications with incremental improvements in malware sophistication.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Federico Valentini, Alessandro Strino, Gianluca Scotti, Simone Mattia (Cleafy Researchers)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, financial fraud, malware, Russian-speaking actors, mobile security, on-device fraud, cybercrime
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us