AI’s Impact on Cyber Resilience: Trust as the New Battlefield for Defenders and Criminals
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The war on trust how AI is rewriting the rules of cyber resilience
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
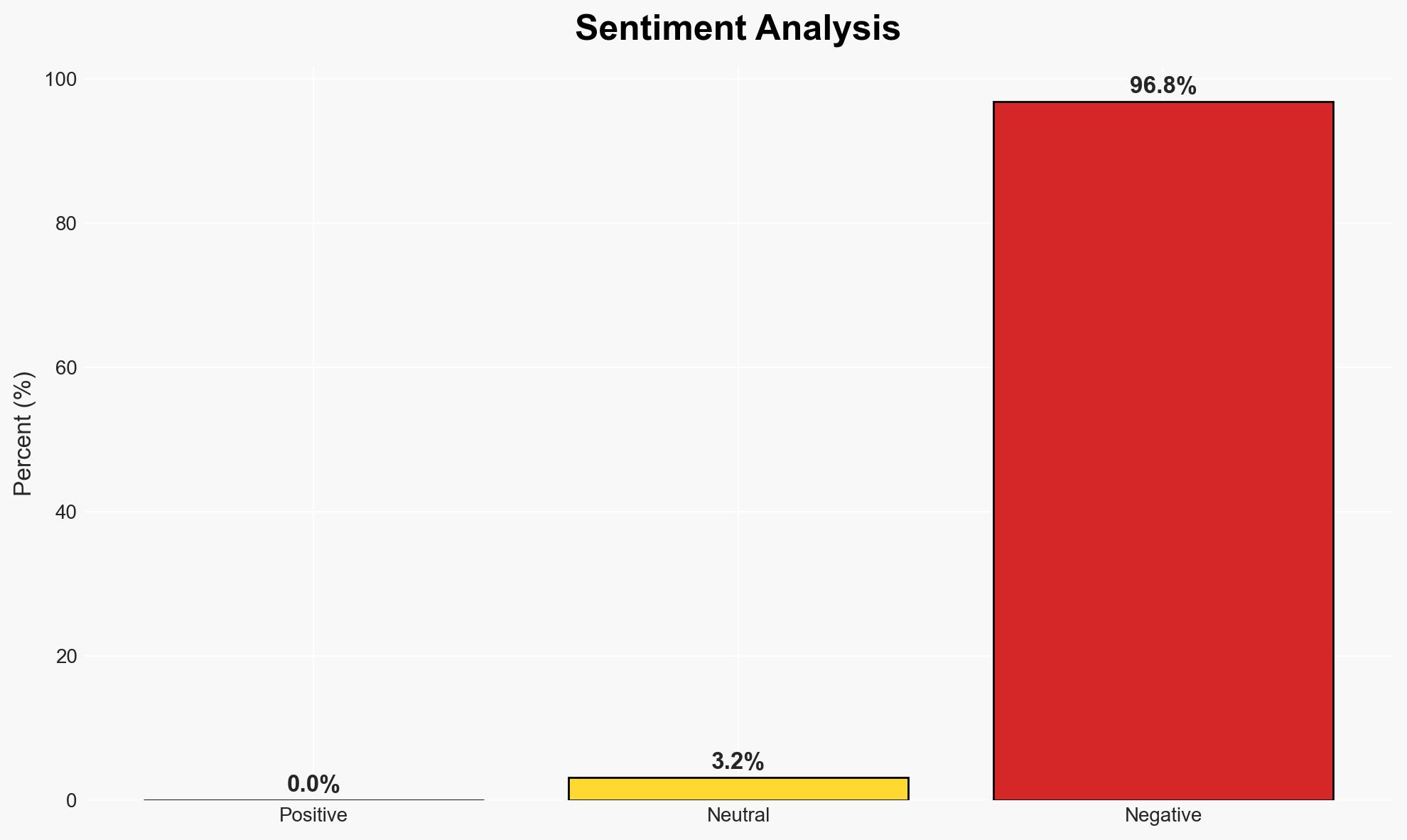
The integration of AI in cyber operations is fundamentally altering the landscape of cyber resilience, with trust being a primary target. AI enhances both offensive and defensive capabilities, creating a high-stakes environment where the ability to detect and respond to social engineering attacks is critical. This development affects businesses globally, with moderate confidence in the assessment that AI-driven defenses will become essential to counteract increasingly sophisticated threats.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: AI is primarily empowering cybercriminals by enabling more sophisticated social engineering attacks, leading to increased breaches. Evidence includes AI’s ability to mimic human behavior and emotions with precision. However, the extent of AI’s impact on the overall increase in cyber incidents remains uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: AI is equally empowering defenders, providing advanced tools for detecting deception and validating integrity, thus enhancing cyber resilience. Supporting evidence includes the development of AI-driven detection systems that identify behavioral anomalies. The effectiveness of these systems in real-world scenarios is yet to be fully validated.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the documented advancements in AI-driven defense tools that can continuously learn and adapt to new threats. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include a significant increase in successful AI-driven attacks or breakthroughs in AI defense capabilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: AI technology will continue to advance at a rapid pace; Organizations will adopt AI-driven defense tools; Cybercriminals will increasingly utilize AI for attacks; Trust remains a critical vulnerability in cyber operations.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the success rate of AI-driven attacks versus defenses; Comprehensive analysis of AI’s impact on the frequency and severity of breaches.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential over-reliance on AI-driven solutions without adequate human oversight; Source bias from cybersecurity firms promoting AI tools; Manipulation of AI systems by adversaries to create false positives or negatives.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The evolution of AI in cyber operations could lead to an arms race between attackers and defenders, with significant implications across multiple domains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased cyber conflict between nation-states leveraging AI capabilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced AI tools may improve threat detection but also enable more sophisticated terrorist cyber operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: AI-driven attacks and defenses will shape the future of cybersecurity strategies and policies.
- Economic / Social: Increased costs for businesses to implement AI defenses; Potential erosion of public trust in digital systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase monitoring of AI-driven cyber threats; Enhance awareness training focused on social engineering tactics.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Invest in AI-driven defense capabilities; Foster partnerships with AI research institutions to stay ahead of threat developments.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: AI defenses outpace attacker capabilities, reducing breaches. Worst: AI-driven attacks overwhelm defenses, leading to widespread breaches. Most-Likely: A dynamic equilibrium where both attackers and defenders continuously adapt, with periodic breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
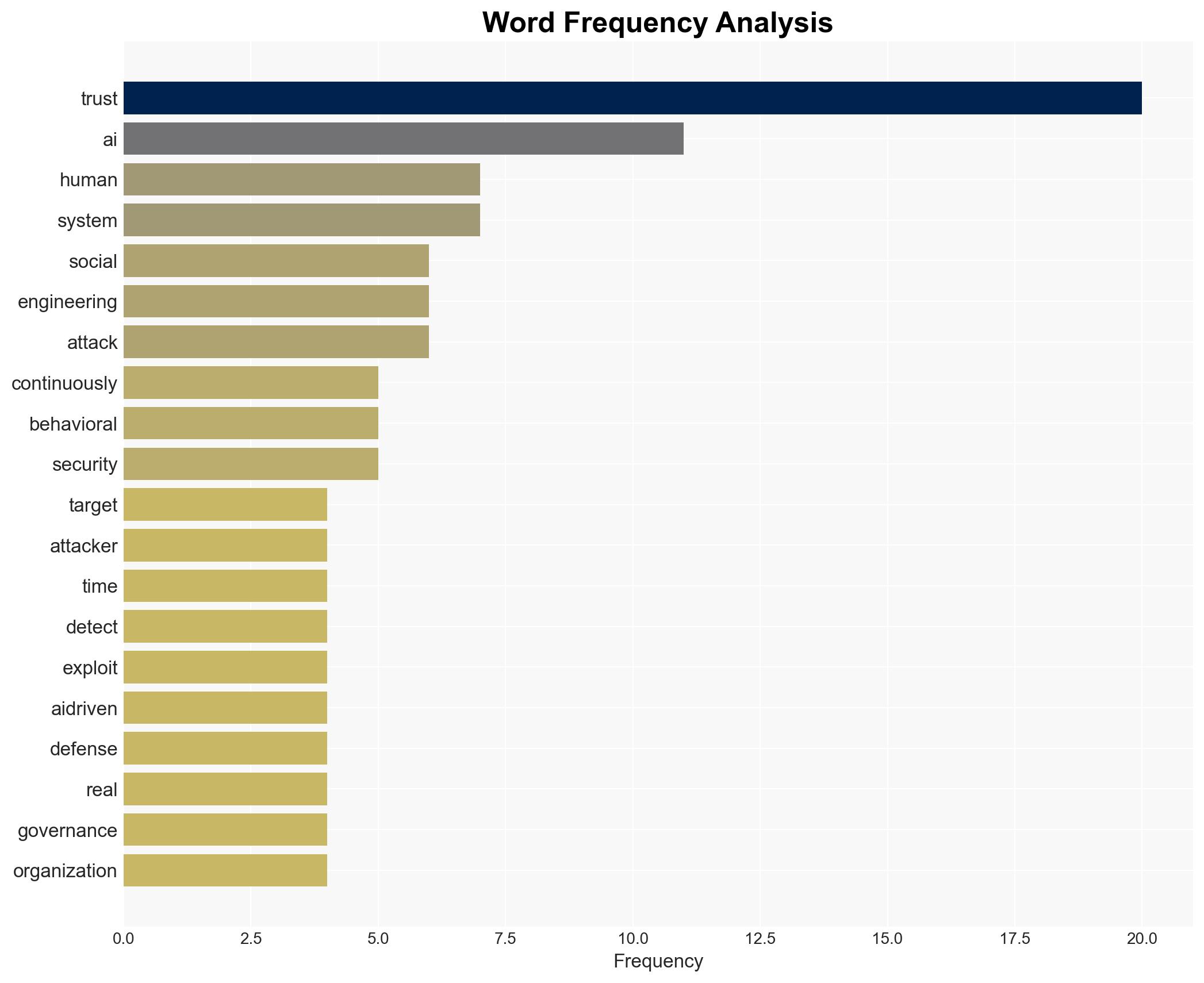
Cybersecurity, cyber resilience, AI-driven defense, social engineering, cybersecurity strategy, trust vulnerability, cyber operations, AI technology
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us