Comparing Security: iOS Versus Android’s Approach to User Safety and Privacy
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Is iOS Actually Safer Than Android
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
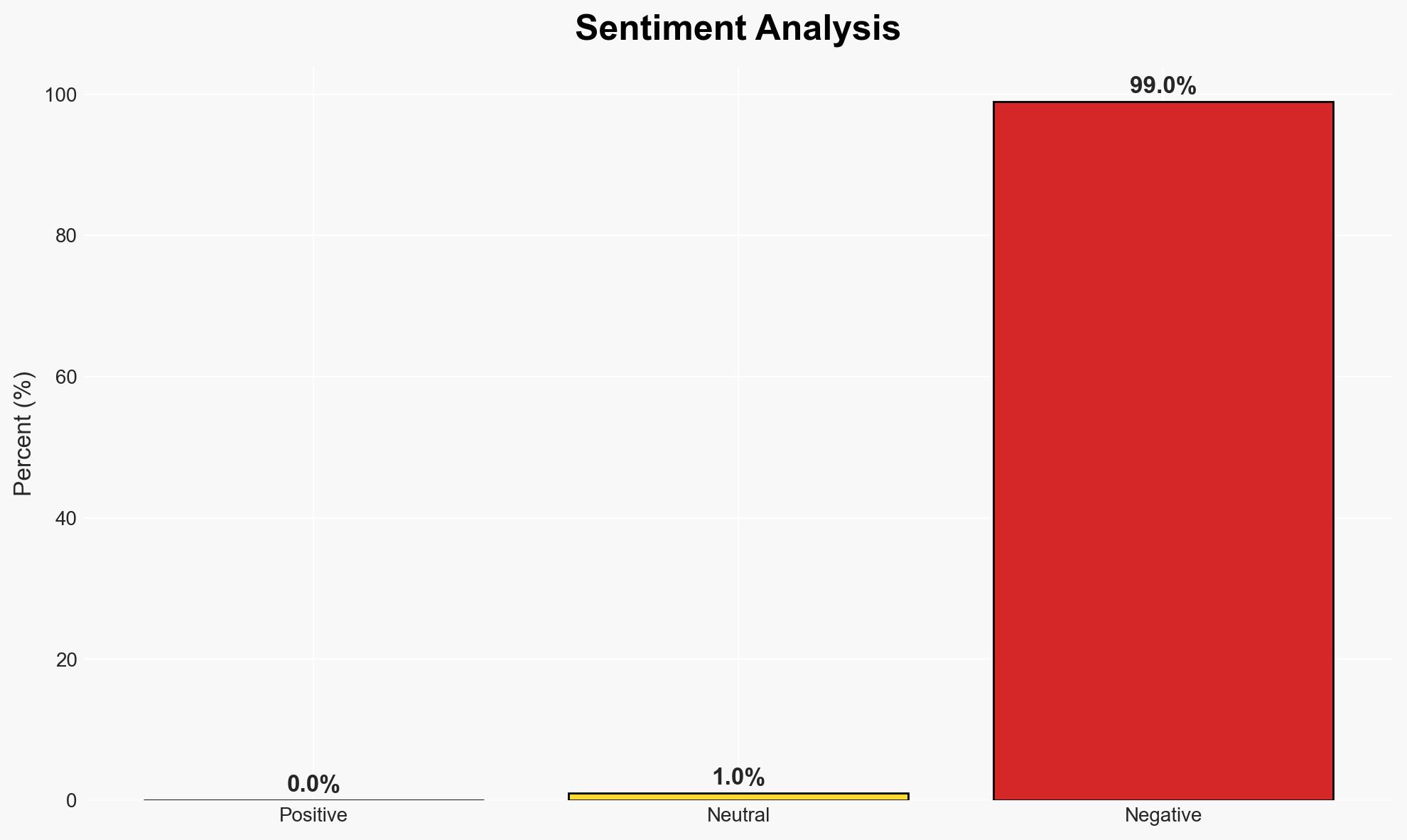
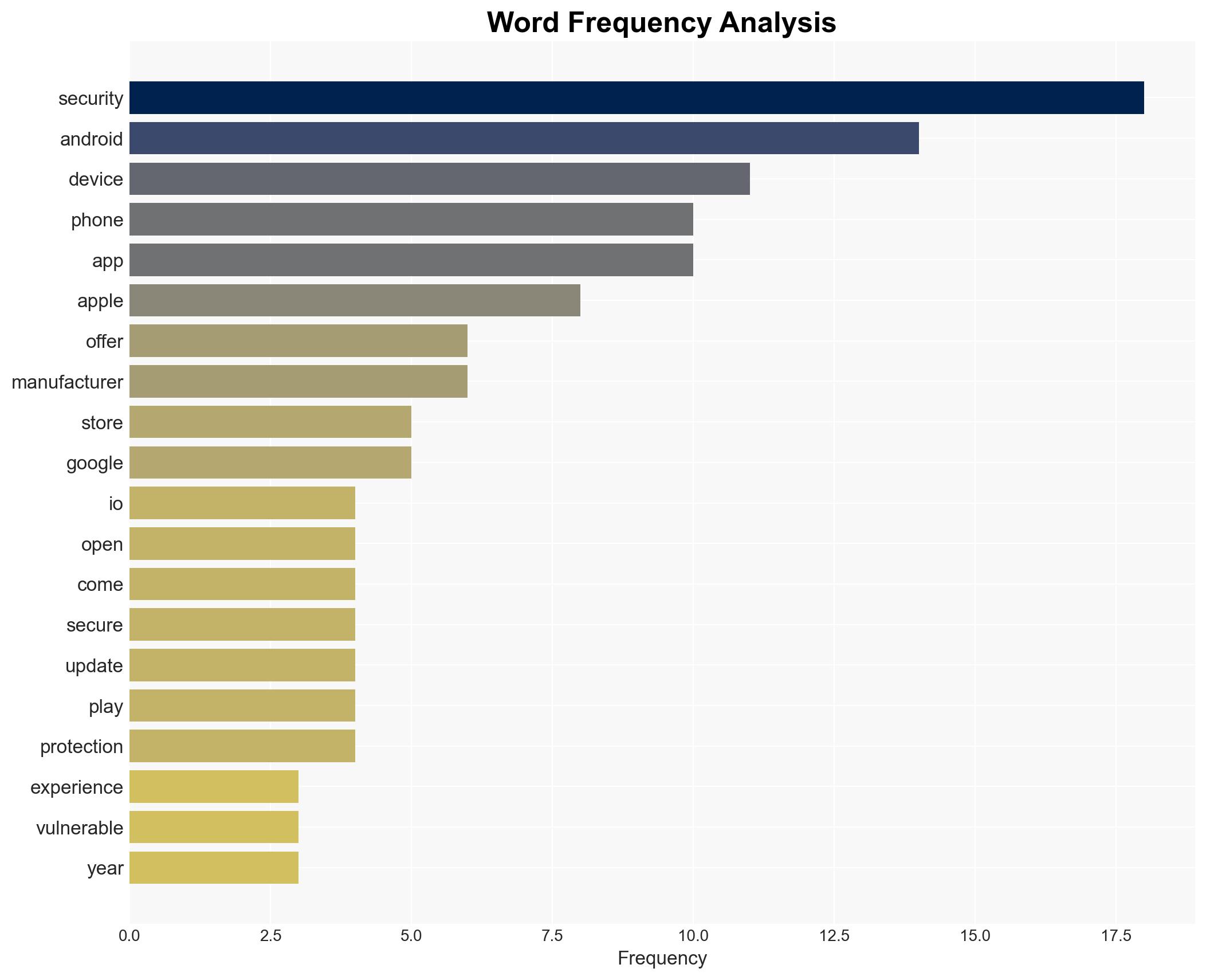
The security comparison between iOS and Android is nuanced, with iOS generally perceived as more secure due to its closed ecosystem and stringent app vetting. However, Android’s open-source nature allows for more customization but also increases vulnerability risks. This assessment holds moderate confidence, considering the variability in security practices across different Android manufacturers.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: iOS is inherently more secure than Android due to Apple’s strict control over its ecosystem, including hardware, software, and app vetting processes. Supporting evidence includes Apple’s standardized security measures and long-term support for devices. Contradicting evidence includes potential vulnerabilities if devices are jailbroken.
- Hypothesis B: Android can be equally secure as iOS if manufacturers implement robust security measures and users adhere to security best practices. Supporting evidence includes Google’s regular security updates and additional security features from manufacturers like Samsung and Google. Contradicting evidence includes the variability in security update policies across different manufacturers.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the standardized and controlled nature of Apple’s ecosystem, which reduces variability in security practices. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include significant improvements in Android’s security update consistency and manufacturer-specific security enhancements.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: iOS’s closed ecosystem inherently provides better security; Android’s open-source nature increases vulnerability; Manufacturer-specific security measures significantly impact Android’s overall security.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the frequency and impact of security breaches across both platforms; Comparative analysis of user adherence to security best practices on both platforms.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from sources favoring one platform over the other; Marketing narratives from Apple and Android manufacturers may exaggerate security claims.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The ongoing debate over iOS versus Android security could influence consumer trust and market dynamics. Enhanced security measures on either platform could shift user preferences and impact market share.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased scrutiny on tech companies’ data protection practices could lead to regulatory changes.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Variability in security across devices could be exploited by malicious actors, impacting national security.
- Cyber / Information Space: The open-source nature of Android may provide more opportunities for cyber-espionage and information manipulation.
- Economic / Social: Consumer confidence in device security can affect purchasing decisions and brand loyalty.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor security update practices of major Android manufacturers; Assess potential vulnerabilities in jailbroken iOS devices.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Encourage collaboration between tech companies and security agencies to enhance device security; Promote user education on security best practices.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Both platforms enhance security measures, reducing vulnerabilities significantly.
- Worst: Major security breach on either platform undermines consumer trust.
- Most-Likely: iOS maintains a slight security advantage, but Android continues to improve through manufacturer-specific enhancements.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, mobile security, iOS, Android, technology policy, consumer protection, digital privacy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us