Critical vulnerabilities in Fluent Bit threaten major cloud providers’ security and operational integrity
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: These worrying security flaws could put every major cloud provider at risk – here’s what we know so far
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
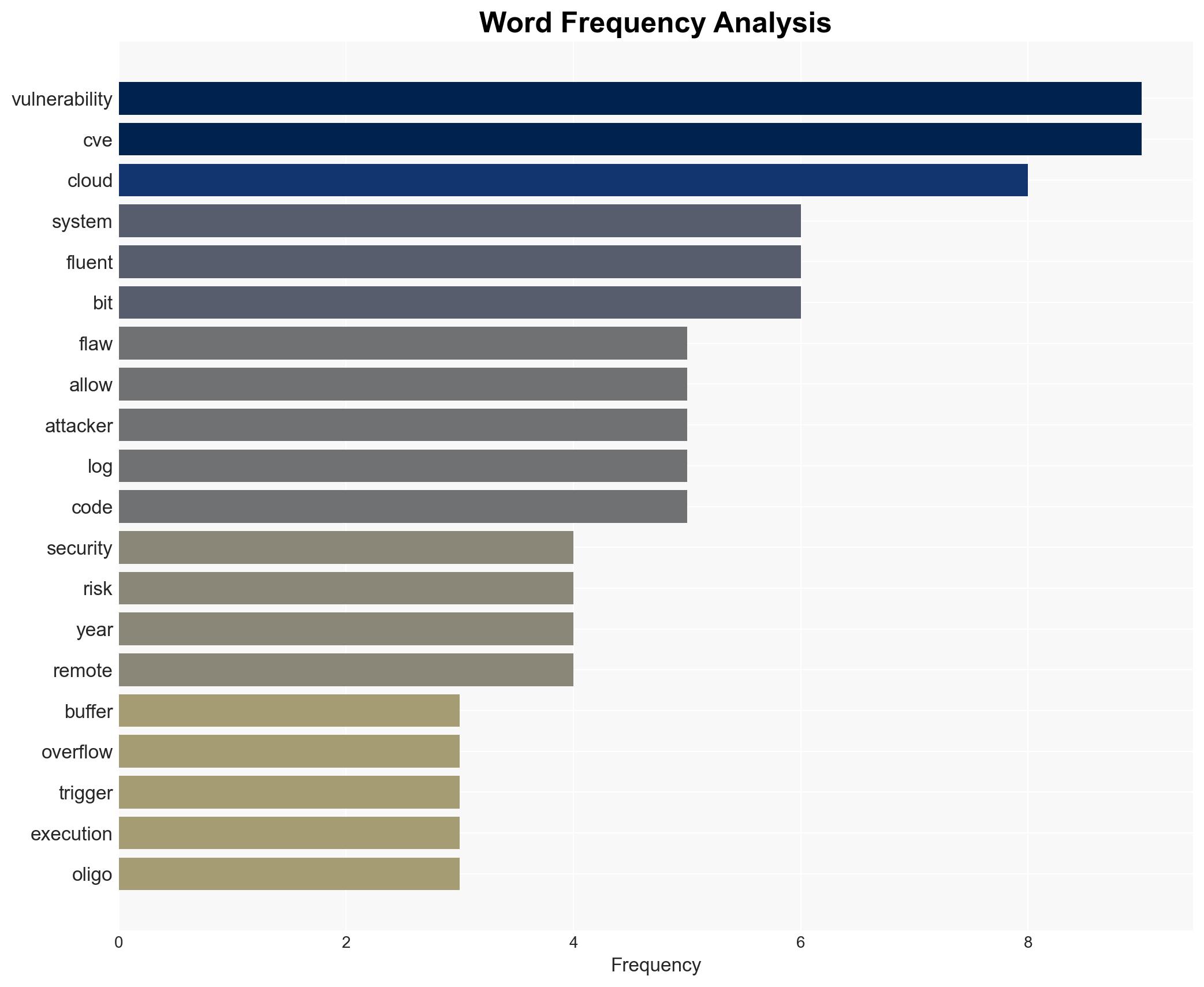
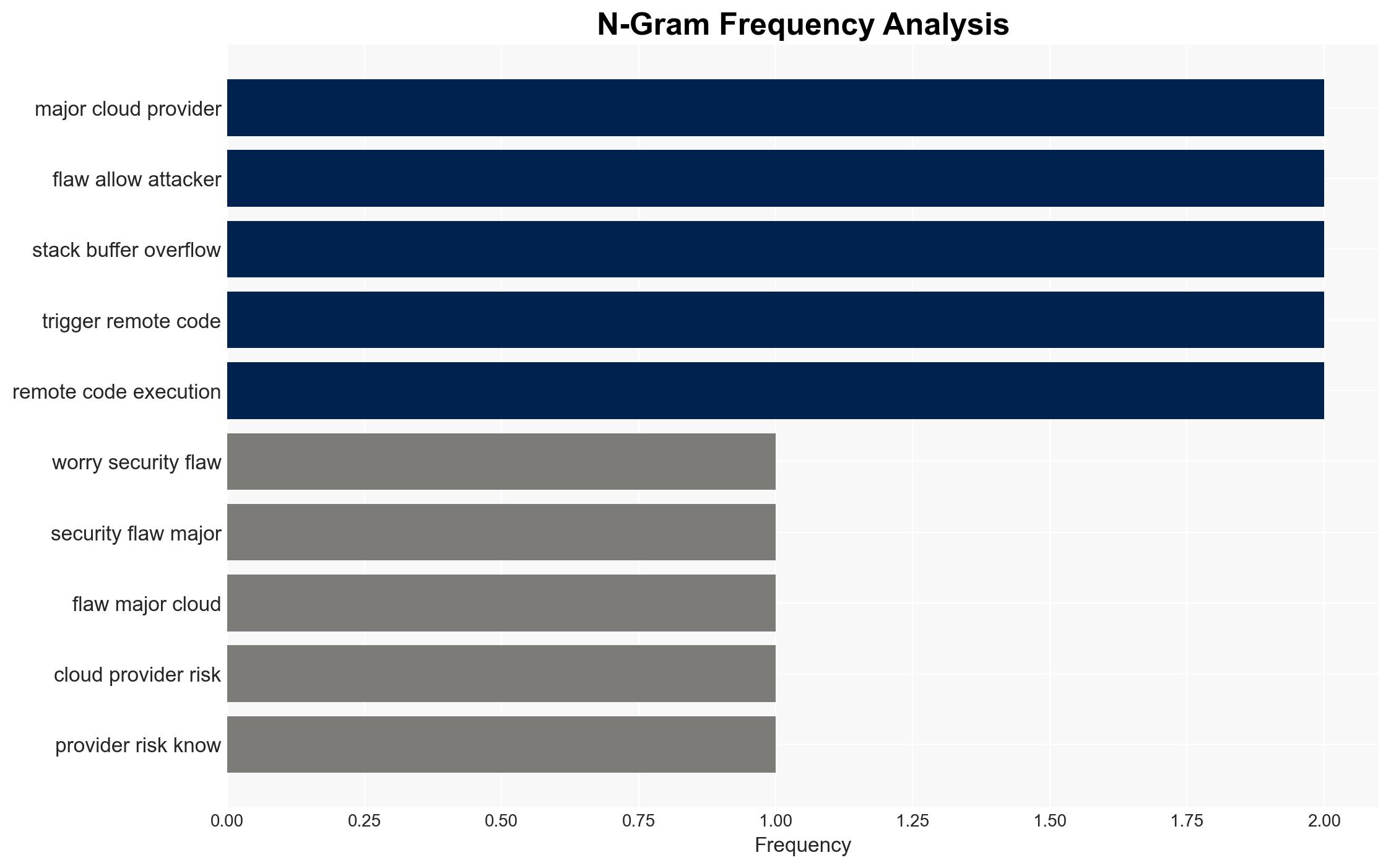
Recent vulnerabilities in the Fluent Bit log processing tool pose significant risks to major cloud providers, including AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. These vulnerabilities could allow attackers to manipulate logs and execute remote code, potentially compromising cloud infrastructure. The most likely hypothesis is that these vulnerabilities will be exploited by cybercriminals targeting high-value sectors such as banking and AI. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the ongoing nature of the threat and the industry’s response.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The vulnerabilities in Fluent Bit will lead to widespread exploitation by cybercriminals, resulting in significant disruptions to cloud services. This is supported by the critical nature of the flaws and the extensive deployment of Fluent Bit across industries. However, the rapid response by cloud providers to patch these vulnerabilities could mitigate this risk.
- Hypothesis B: Cloud providers will successfully mitigate the vulnerabilities with minimal disruption, due to their robust security protocols and the swift patching efforts already underway. This is contradicted by the potential for residual risks due to the widespread use of the vulnerable software and the low technical barrier to exploitation.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the critical nature of the vulnerabilities and the potential for exploitation before patches are fully implemented. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include the speed and effectiveness of patch deployment and any emerging reports of successful exploitations.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Cloud providers will prioritize patching these vulnerabilities; attackers have the capability and intent to exploit these flaws; the vulnerabilities are not already widely exploited.
- Information Gaps: The current extent of exploitation in the wild; specific details on the effectiveness of the patches deployed by cloud providers.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reporting from security researchers with vested interests; possible underreporting by affected companies to protect reputations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development of these vulnerabilities could lead to increased cyber threats against critical infrastructure sectors, affecting both operational continuity and data integrity.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation in cyber tensions between state and non-state actors exploiting these vulnerabilities.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased risk of cyber-attacks on critical infrastructure, potentially disrupting national security operations.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for misinformation campaigns leveraging compromised cloud data to undermine trust in digital services.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic losses for businesses reliant on cloud services, leading to broader economic instability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of cloud environments for signs of exploitation; ensure all systems are updated with the latest patches; conduct security audits on cloud deployments.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms for threat intelligence sharing; invest in advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Rapid patching and no significant exploitations occur, maintaining cloud service integrity.
- Worst: Widespread exploitation leads to major disruptions in cloud services, affecting critical sectors.
- Most-Likely: Some exploitation occurs, but effective mitigation limits the impact to isolated incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Oligo Security Research Team
- Uri Katz, Oligo Security Researcher
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud
- Microsoft Azure
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, cloud security, cyber vulnerabilities, remote code execution, patch management, critical infrastructure
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us