Global Reactions to China’s Expanding Export Power: Balancing Trade, Security, and Innovation Concerns
Published on: 2025-12-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Dani Rodrik How should the world respond to China’s growing export dominance
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
China’s increasing export dominance poses significant challenges and opportunities for global markets, particularly in sectors like manufacturing and renewable energy. The most likely hypothesis is that nations will adopt a mix of protectionist and strategic industrial policies to mitigate risks associated with China’s export growth. This affects global trade dynamics and national security considerations, with moderate confidence in this assessment.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Nations will primarily respond to China’s export dominance by erecting trade barriers and reshoring manufacturing to protect domestic industries. This is supported by current trends in national security policies and industrial strategies but is contradicted by potential economic inefficiencies and global trade norms.
- Hypothesis B: Countries will engage in strategic cooperation with China, leveraging its manufacturing prowess to enhance innovation and climate benefits. This hypothesis is supported by the potential for mutual economic gains but is contradicted by geopolitical tensions and national security concerns.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the prevailing geopolitical climate and national security imperatives. Indicators such as increased trade barriers and strategic industrial policies could further validate this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Global trade norms will continue to influence national policies; China’s export growth will persist; geopolitical tensions will remain a significant factor in policy decisions.
- Information Gaps: Specific data on the impact of Chinese exports on innovation and employment in importing countries is lacking.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in interpreting China’s economic strategies as purely adversarial; risk of overestimating the effectiveness of protectionist measures.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The response to China’s export dominance will shape global economic and security landscapes, potentially leading to increased protectionism and geopolitical tensions.
- Political / Geopolitical: Escalation of trade tensions and realignment of international alliances.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Increased focus on protecting critical supply chains and sensitive technologies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Potential for cyber operations targeting trade and industrial sectors.
- Economic / Social: Economic instability in regions heavily reliant on manufacturing; potential social unrest due to job losses.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor trade policy changes and geopolitical developments; enhance intelligence sharing on supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for critical industries; foster international partnerships to balance trade and security interests.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Strategic cooperation leads to mutual economic benefits and innovation growth.
- Worst: Heightened trade wars and geopolitical conflicts disrupt global markets.
- Most-Likely: A mixed approach with selective protectionism and strategic partnerships.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Jake Sullivan, National Security Advisor to President Joe Biden
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
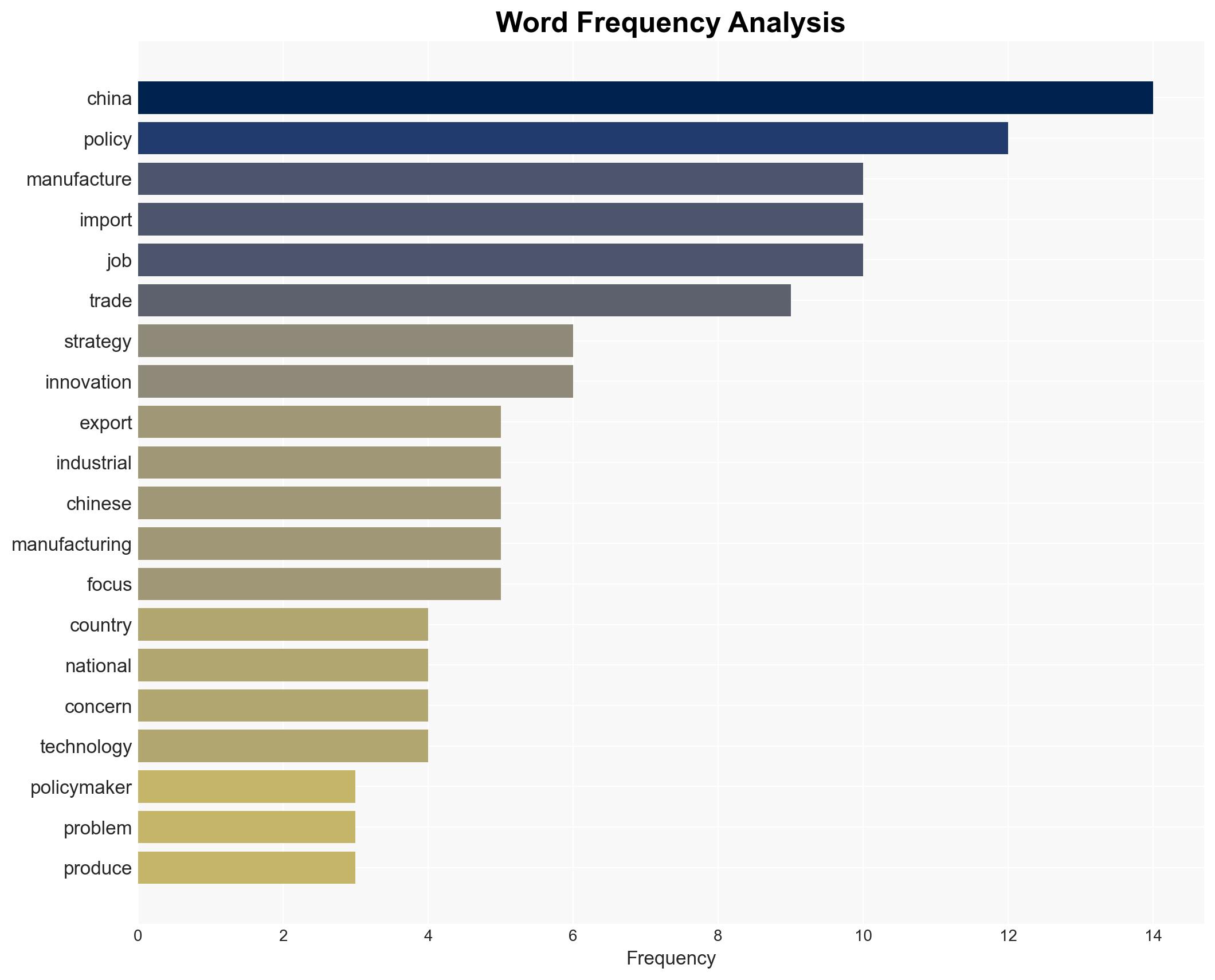
National Security Threats, trade policy, national security, industrial strategy, geopolitical tensions, innovation, manufacturing, economic resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us