NANOG 95
Published on: 2025-11-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: NANOG 95
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The NANOG 95 meeting highlighted significant advancements and challenges in network technologies, particularly in mobile and Wi-Fi sectors. The ongoing evolution of these technologies suggests a shift towards higher capacity and efficiency, though economic and infrastructural challenges persist. The most likely hypothesis is that mobile and Wi-Fi technologies will continue to evolve with incremental improvements, but market saturation and high infrastructure costs may limit rapid expansion. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: Mobile and Wi-Fi technologies will continue to evolve with incremental improvements, driven by advancements in digital signal processing and increased spectrum availability. This is supported by reported increases in capacity and efficiency, though market saturation and infrastructure costs are key uncertainties.
- Hypothesis B: The evolution of mobile and Wi-Fi technologies will stagnate due to market saturation and the high costs associated with new infrastructure deployment. While there is evidence of market saturation, ongoing technological advancements contradict this hypothesis.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to ongoing technological advancements and the historical trend of continuous improvement in network capacities. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include significant economic downturns or breakthroughs in alternative technologies.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The market will continue to demand higher network capacities; technological advancements will proceed at a steady pace; infrastructure investments will remain economically viable.
- Information Gaps: Detailed economic models for infrastructure deployment costs; precise data on market saturation levels; potential regulatory changes affecting spectrum allocation.
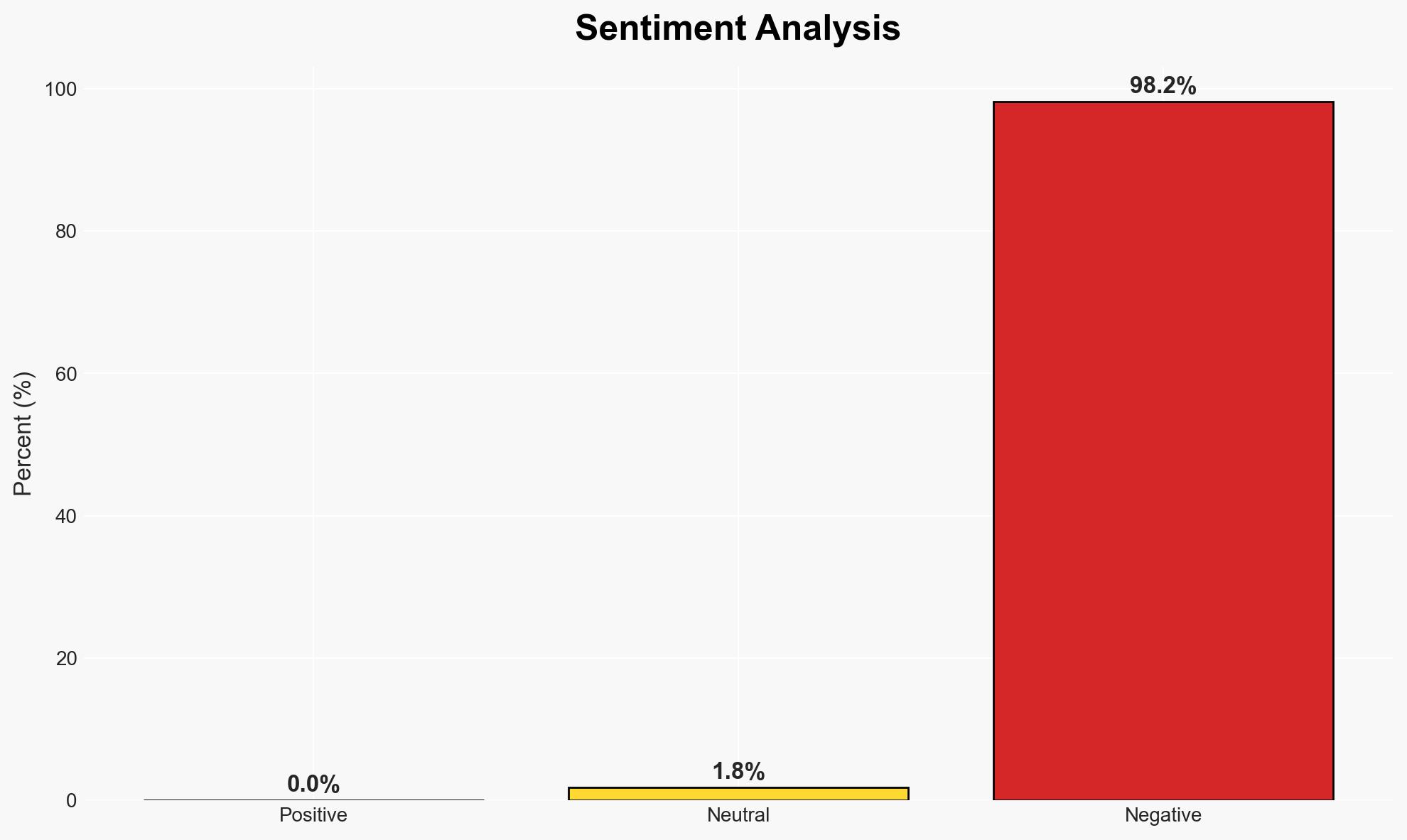
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias from industry stakeholders promoting optimistic technological forecasts; lack of independent verification of reported technological advancements.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued evolution of network technologies could lead to significant changes in global communication infrastructure, with potential impacts across various domains.
- Political / Geopolitical: Increased competition for spectrum resources could lead to geopolitical tensions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Enhanced network capabilities may improve surveillance and intelligence operations but also increase vulnerabilities to cyber threats.
- Cyber / Information Space: Greater network capacities could facilitate more sophisticated cyber operations and information dissemination.
- Economic / Social: Market saturation could lead to economic instability in the telecommunications sector, impacting social connectivity and access to information.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor technological advancements and market trends; assess regulatory environments for spectrum allocation.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with key technology developers; invest in research for alternative communication technologies.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Continued technological advancements lead to enhanced global connectivity. Worst: Economic downturns and regulatory barriers stall technological progress. Most-Likely: Incremental improvements continue, moderated by economic and regulatory challenges.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Geoff Huston, North American Network Operator Group (NANOG)
- Len Bosack, XKL
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
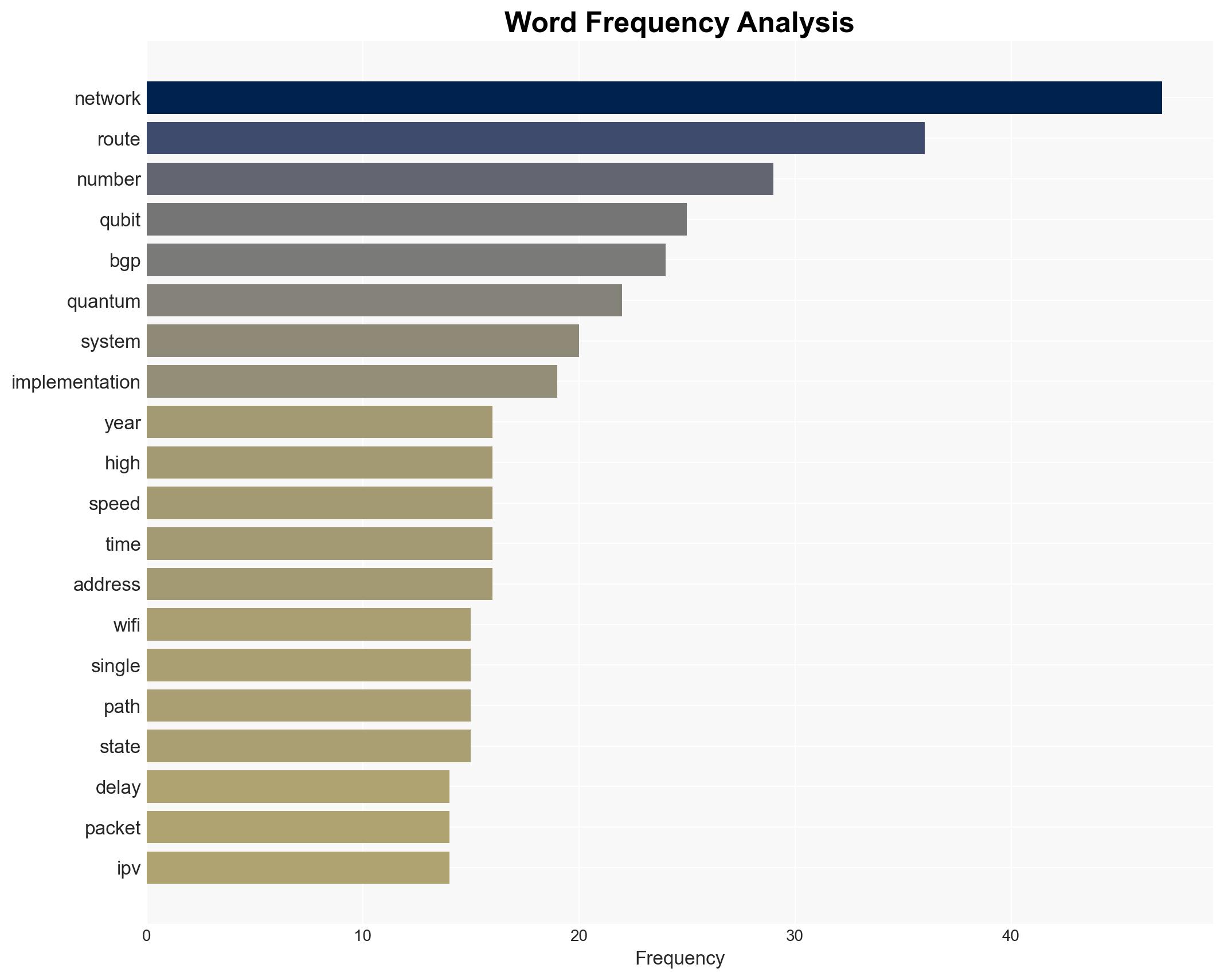
Cybersecurity, network technology, mobile evolution, Wi-Fi advancements, market saturation, infrastructure costs, spectrum allocation, digital signal processing
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us