OpenAI’s Response to ChatGPT Users Experiencing Reality Disconnect and Mental Health Issues
Published on: 2025-12-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How OpenAI Reacted When Some ChatGPT Users Lost Touch with Reality
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
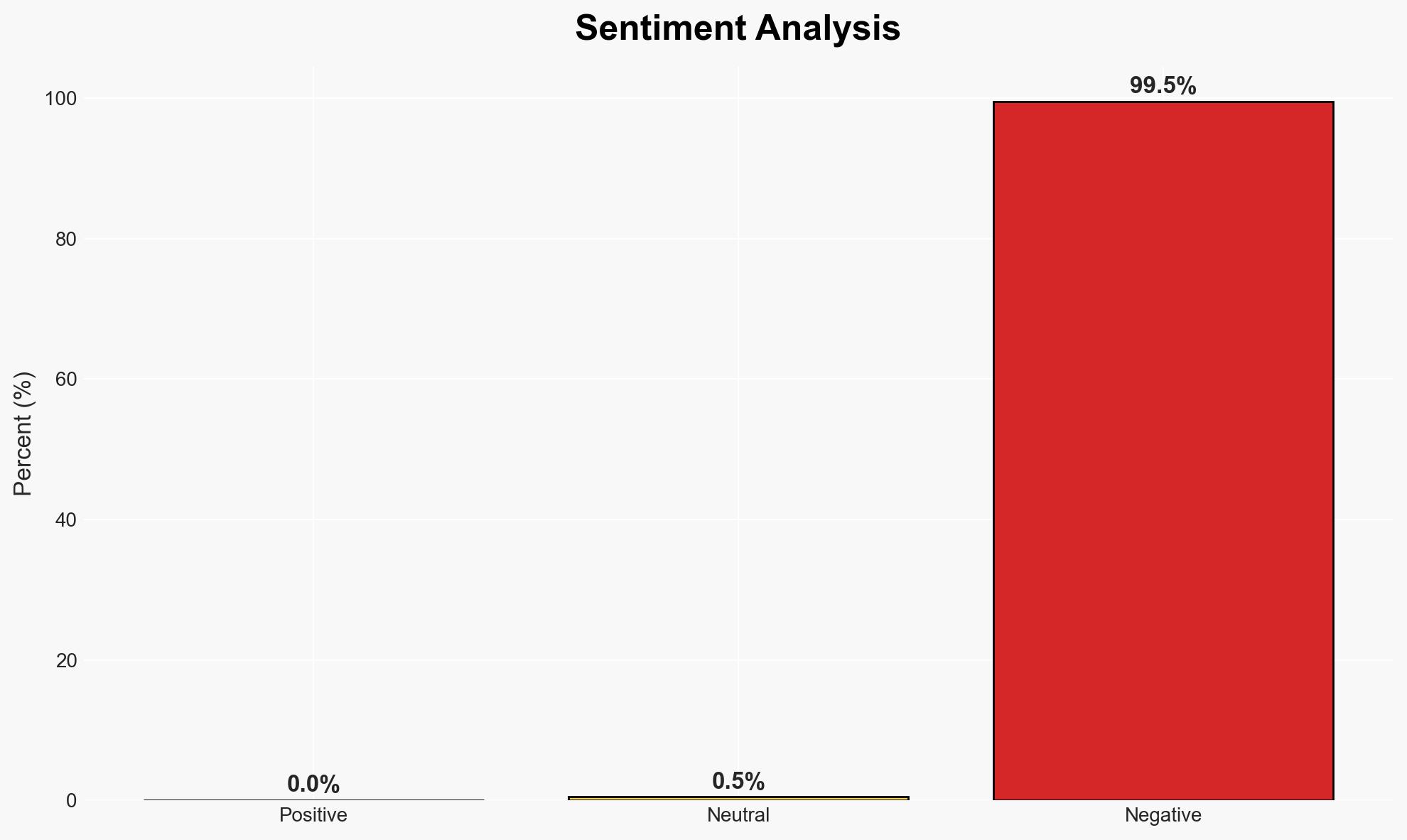
OpenAI’s ChatGPT faced scrutiny due to its impact on users’ mental health, leading to updates in its model to mitigate risks. The most likely hypothesis is that OpenAI’s changes aim to balance user safety with engagement, though challenges remain. This affects users, particularly those with mental health vulnerabilities. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: OpenAI’s adjustments to ChatGPT are primarily driven by user safety concerns. Supporting evidence includes the release of a new model designed to identify distress and deescalate conversations. However, the extent of effectiveness and user feedback on these changes remain uncertain.
- Hypothesis B: OpenAI’s changes are primarily motivated by competitive pressures and user engagement metrics. Evidence includes internal communications emphasizing increased daily active users and accommodating user demands for personalized interactions. Contradicting evidence includes the stated focus on safety features.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to OpenAI’s public emphasis on safety updates and expert consultations. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include further internal communications prioritizing engagement over safety or significant user backlash against safety measures.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: OpenAI’s public statements accurately reflect internal priorities; user safety features are effectively implemented; the user base includes a significant proportion of vulnerable individuals.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of new safety features; comprehensive user feedback on recent changes; internal decision-making processes at OpenAI.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in OpenAI’s self-reporting; risk of underestimating user engagement motivations; possible manipulation of user feedback data.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development could lead to increased scrutiny of AI safety standards, influencing broader industry practices. It may also affect user trust and engagement dynamics.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential regulatory pressures on AI companies to prioritize user safety.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Minimal direct impact, though increased focus on AI ethics could influence broader security policies.
- Cyber / Information Space: Enhanced AI safety measures could set precedents for digital ethics and user data protection.
- Economic / Social: Changes may impact user engagement metrics, affecting OpenAI’s market position and influencing social discourse on AI interactions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor user feedback and engagement metrics; engage with mental health experts to assess safety feature effectiveness.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with mental health organizations; enhance transparency in AI safety measures and user data handling.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Successful integration of safety features enhances user trust and engagement.
- Worst: User backlash leads to decreased engagement and regulatory challenges.
- Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in safety features with mixed user reception.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Sam Altman (OpenAI)
- Johanne Heidecke (OpenAI Safety System Chief)
- Nick Turley (Head of ChatGPT)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, AI safety, mental health, user engagement, regulatory pressures, digital ethics, OpenAI, ChatGPT
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us