Rice prices experience slight increase, but surplus supply may lead to downward pressure soon.
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Global rice prices rise a tad but trend may change soon on surplus supplies
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
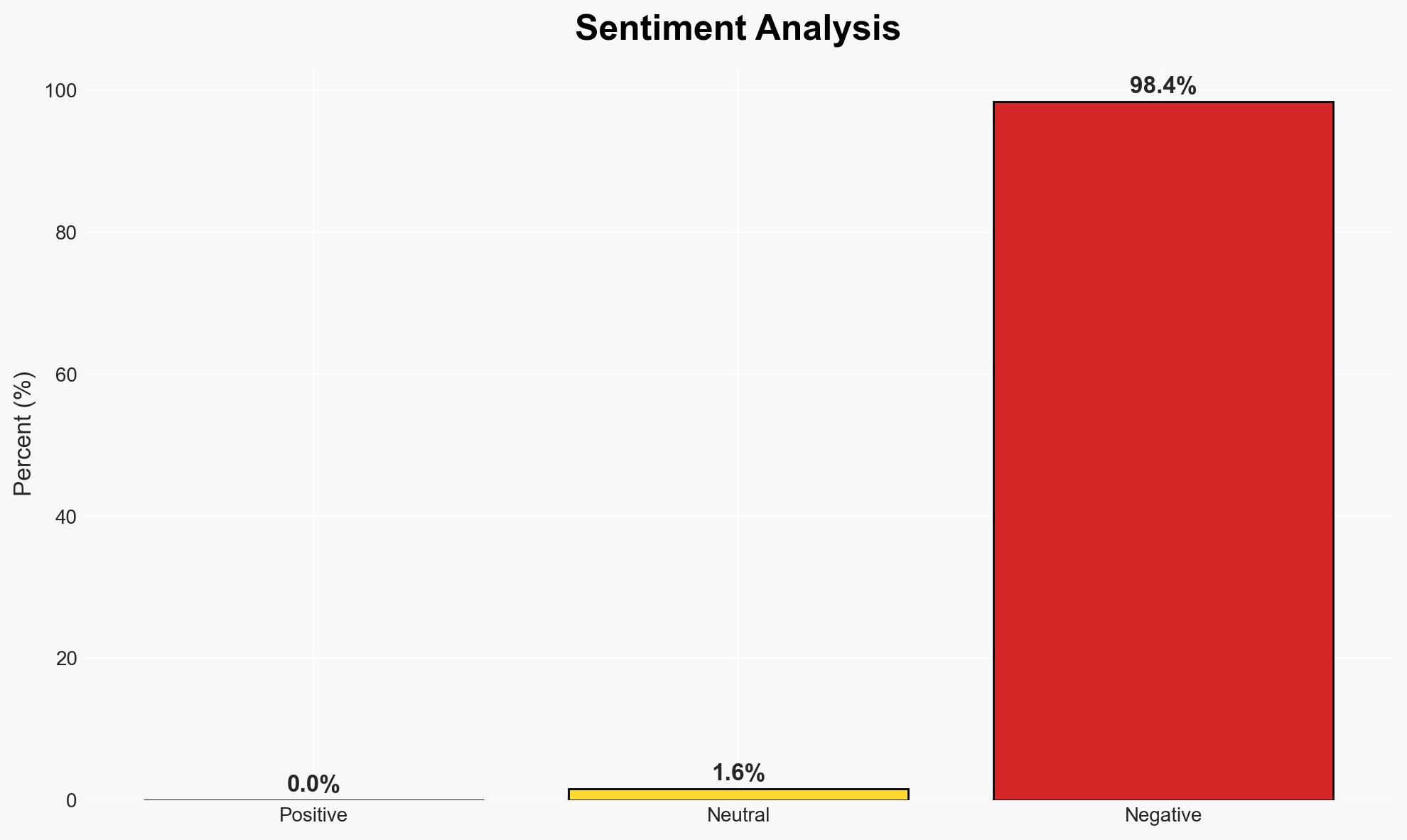
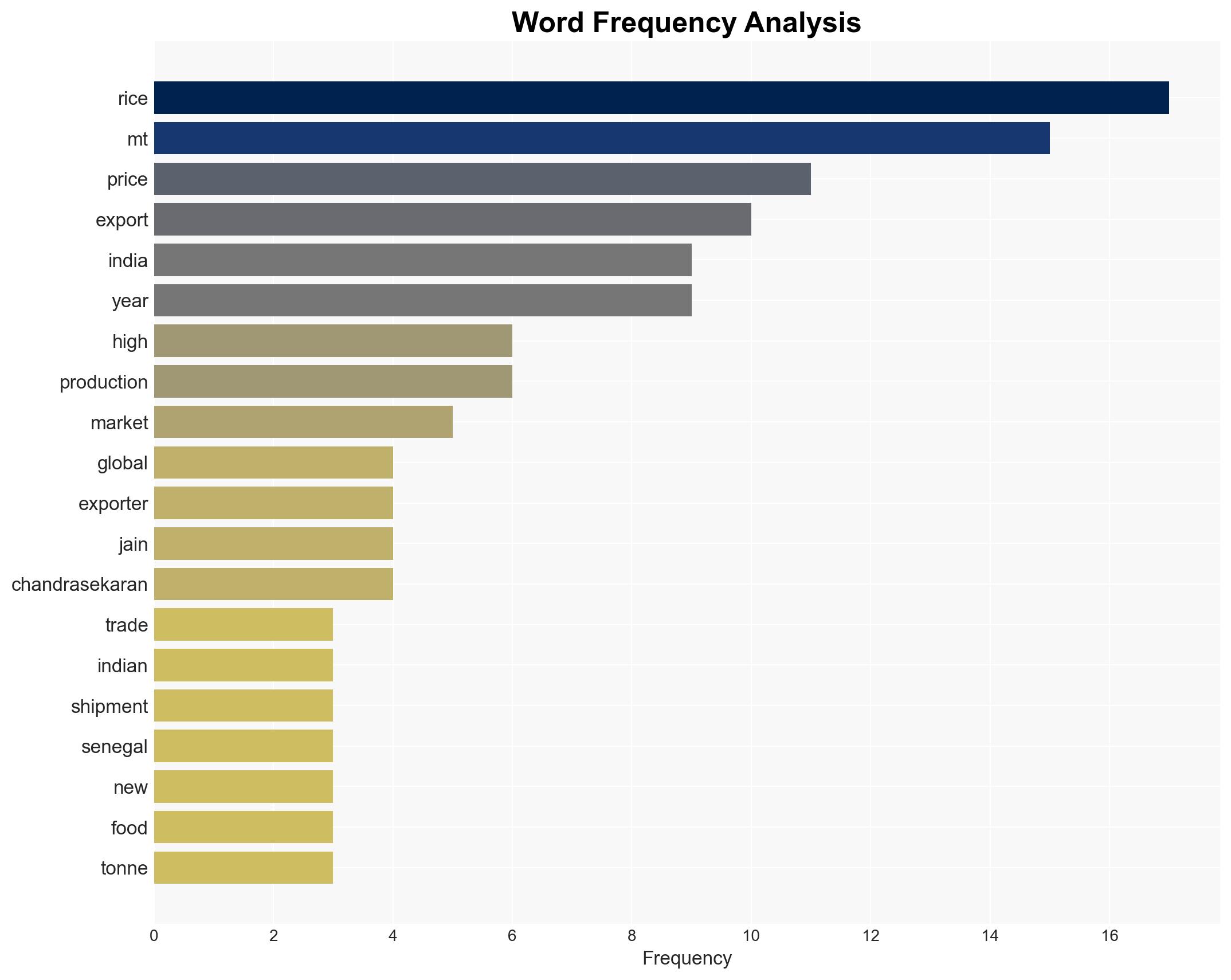
Global rice prices have increased slightly, but this trend is unlikely to continue due to anticipated surplus supplies from India. The situation primarily affects rice exporters and importers, particularly in Africa and Asia. Current assessment indicates moderate confidence that prices will stabilize or decrease in the near term.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The recent rise in rice prices is a temporary fluctuation due to short-term disruptions in Indian shipments and expiring import licenses in Senegal. Supporting evidence includes reports of large inventories in India and expected record-high production. However, uncertainties remain regarding the impact of potential climatic events like La Niña.
- Hypothesis B: The price increase is indicative of a longer-term trend driven by broader global supply chain issues and potential export restrictions. This is contradicted by the expected surplus from India and the lifting of some export bans, suggesting that current price pressures are not sustainable.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the anticipated surplus and policy adjustments in India. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include unexpected climatic impacts or changes in export policies by major rice-producing countries.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: India will maintain or increase its rice production; current export policies will remain stable; climatic conditions will not severely disrupt production.
- Information Gaps: Precise data on the impact of climatic conditions on rice production in Southeast Asia; detailed export policy changes in other major rice-producing countries.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in reports from Indian exporters seeking to influence market perceptions; risk of underestimating climatic impacts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The development could lead to a stabilization or decrease in global rice prices, affecting international trade dynamics and food security strategies.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased diplomatic engagement between rice-exporting and importing nations to secure stable supply chains.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Limited direct impact; however, food price stability can contribute to broader regional stability.
- Cyber / Information Space: Minimal direct impact; potential for misinformation campaigns around food security issues.
- Economic / Social: Stabilized rice prices could alleviate inflationary pressures in importing countries, supporting economic stability and social cohesion.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor climatic developments and policy changes in major rice-producing countries; engage with key exporters to confirm supply chain stability.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures for potential supply disruptions; strengthen partnerships with alternative suppliers.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Surplus leads to price stabilization, enhancing food security (trigger: sustained high production levels).
- Worst: Climatic events disrupt production, causing price spikes (trigger: severe weather patterns).
- Most-Likely: Prices stabilize with minor fluctuations (trigger: successful policy adjustments and surplus realization).
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Rajesh Paharia Jain, New Delhi-based exporter
- Chandrasekaran, Managing Director, Svastha Ecoharvest
- Madan Prakash, Director, Rajathi Group
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us