US-Israeli Strategy to Fragment Gaza Faces Resistance Amid Rising Palestinian Casualties and Destruction
Published on: 2025-12-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
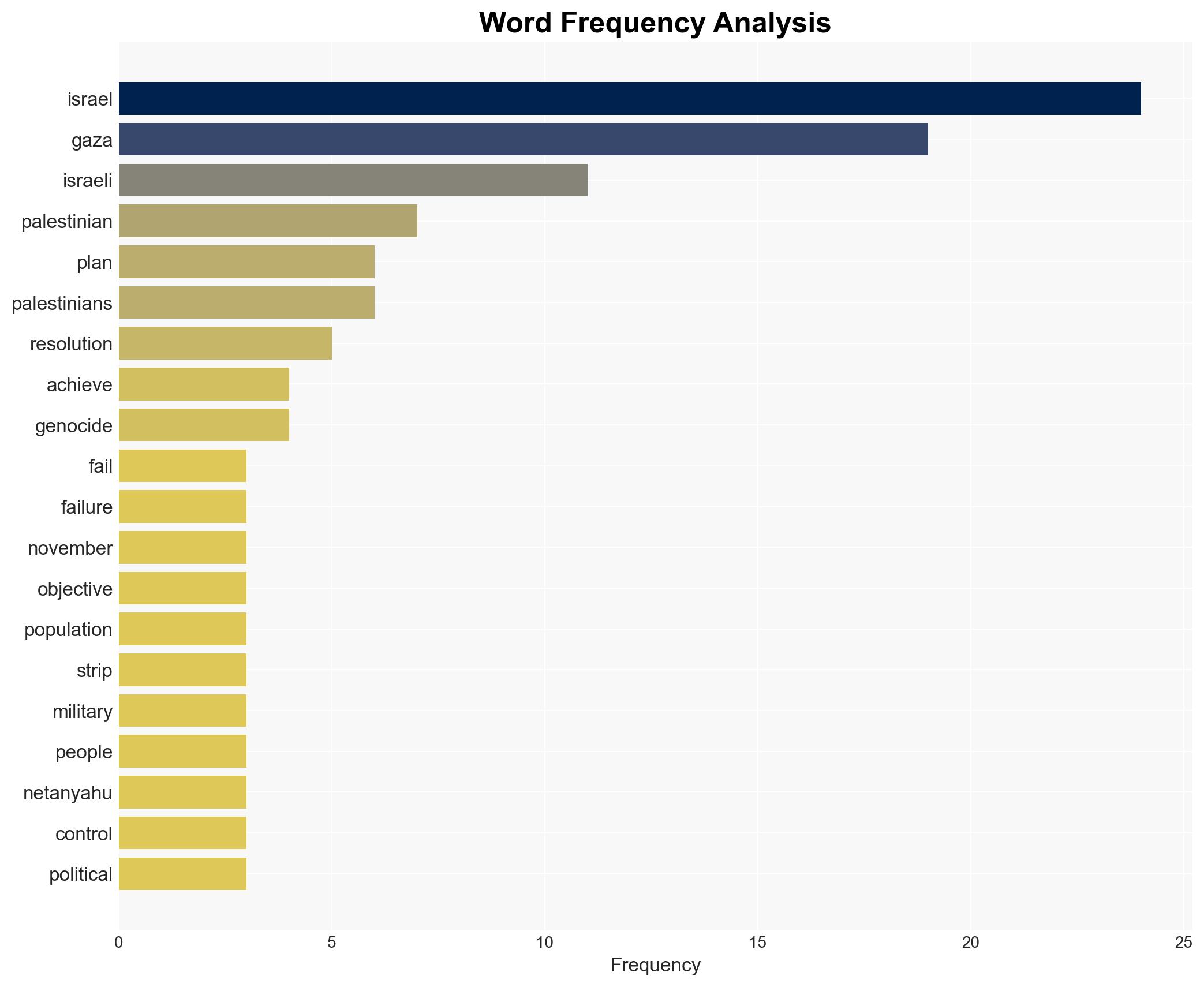
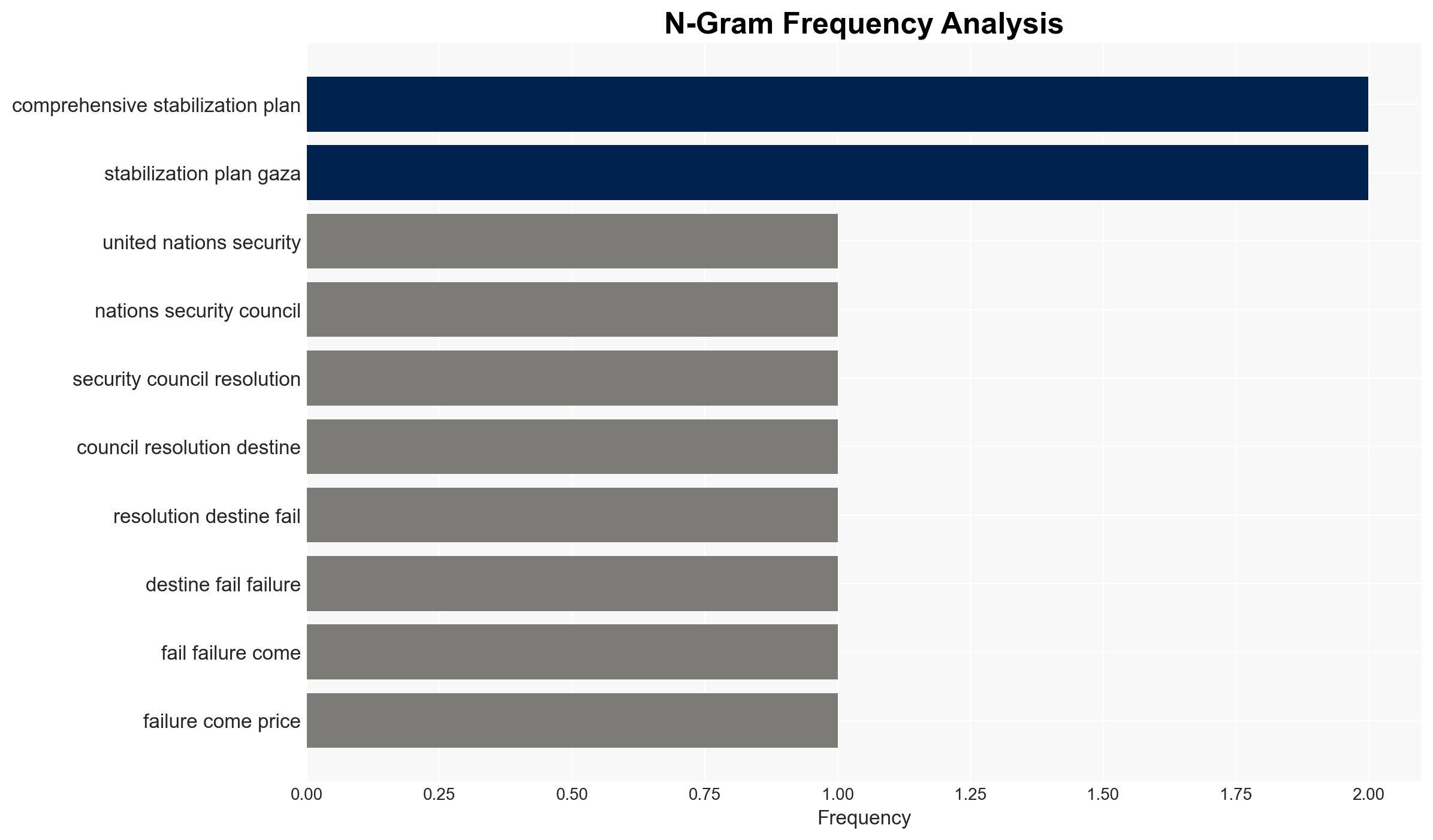
Intelligence Report: UNSC 2803 The US-Israeli Scheme To Partition Gaza and Break Palestinian Will
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
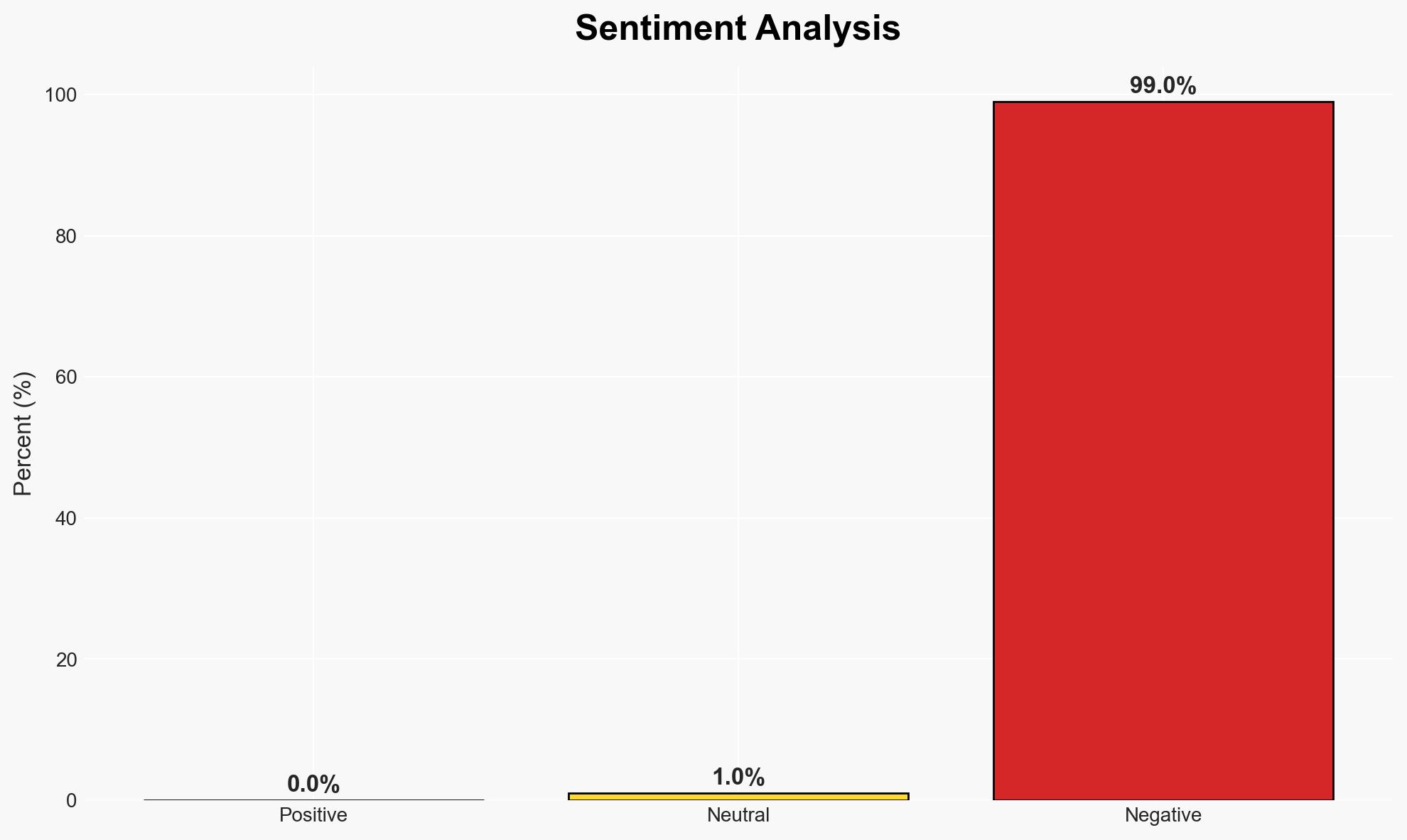
The UNSC resolution appears to be part of a broader strategy by the US and Israel to exert control over Gaza, potentially leading to increased violence and instability in the region. The plan’s success is uncertain, with significant opposition and potential for humanitarian crises. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The resolution is a genuine attempt to stabilize Gaza and facilitate a peaceful transition. Supporting evidence includes the formal adoption of the resolution and international backing. Contradicting evidence includes ongoing violence and Israel’s historical actions in the region.
- Hypothesis B: The resolution is a strategic maneuver by Israel and the US to consolidate control over Gaza, under the guise of stabilization. Supporting evidence includes the exclusion of Palestinian authorities from the transitional administration and continued Israeli military actions. Contradicting evidence could include any genuine efforts to improve humanitarian conditions.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the exclusion of Palestinian authorities and ongoing military actions, which align with historical patterns of Israeli strategy. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include genuine improvements in humanitarian conditions or increased Palestinian involvement in governance.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Israel aims to maintain long-term control over Gaza; the US supports Israeli objectives in the region; Palestinian groups will resist disarmament.
- Information Gaps: Details on the operational plans of the international stabilization force and the specific terms of the ceasefire agreement.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in sources favoring Israeli or US perspectives; risk of manipulated narratives to justify military actions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The resolution’s implementation could exacerbate tensions and lead to further violence, impacting regional stability and international relations.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased regional isolation of Israel and strained relations with Arab states.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of insurgency and retaliatory attacks by Palestinian groups.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in cyber operations targeting Israeli and US interests, as well as propaganda campaigns.
- Economic / Social: Deterioration of economic conditions in Gaza, leading to humanitarian crises and social unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Increase intelligence monitoring of military activities in Gaza; engage with international partners to assess humanitarian needs.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to counter potential insurgency; strengthen diplomatic channels with regional actors.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Genuine stabilization and improved conditions in Gaza. Worst: Escalation of violence and humanitarian crisis. Most-Likely: Continued instability with intermittent conflict.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu
- US President Donald Trump (at the time of the plan’s initiation)
- Palestinian Authority (excluded from the transitional administration)
- International Stabilization Force (ISF)
7. Thematic Tags
National Security Threats, Middle East conflict, Israeli-Palestinian relations, UNSC resolutions, military strategy, humanitarian crisis, geopolitical strategy, international diplomacy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Expose and correct potential biases in assessments through red-teaming and structured challenge.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Use probabilistic forecasting for conflict trajectories or escalation likelihood.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map relationships between state and non-state actors for impact estimation.
Explore more:
National Security Threats Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us