US Navy Faces Recruitment Challenges for Warship Construction Amid Competitive Job Market
Published on: 2025-11-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: The US Navy Can’t Find Workers To Build Warships And It’s Pretty Clear Why
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
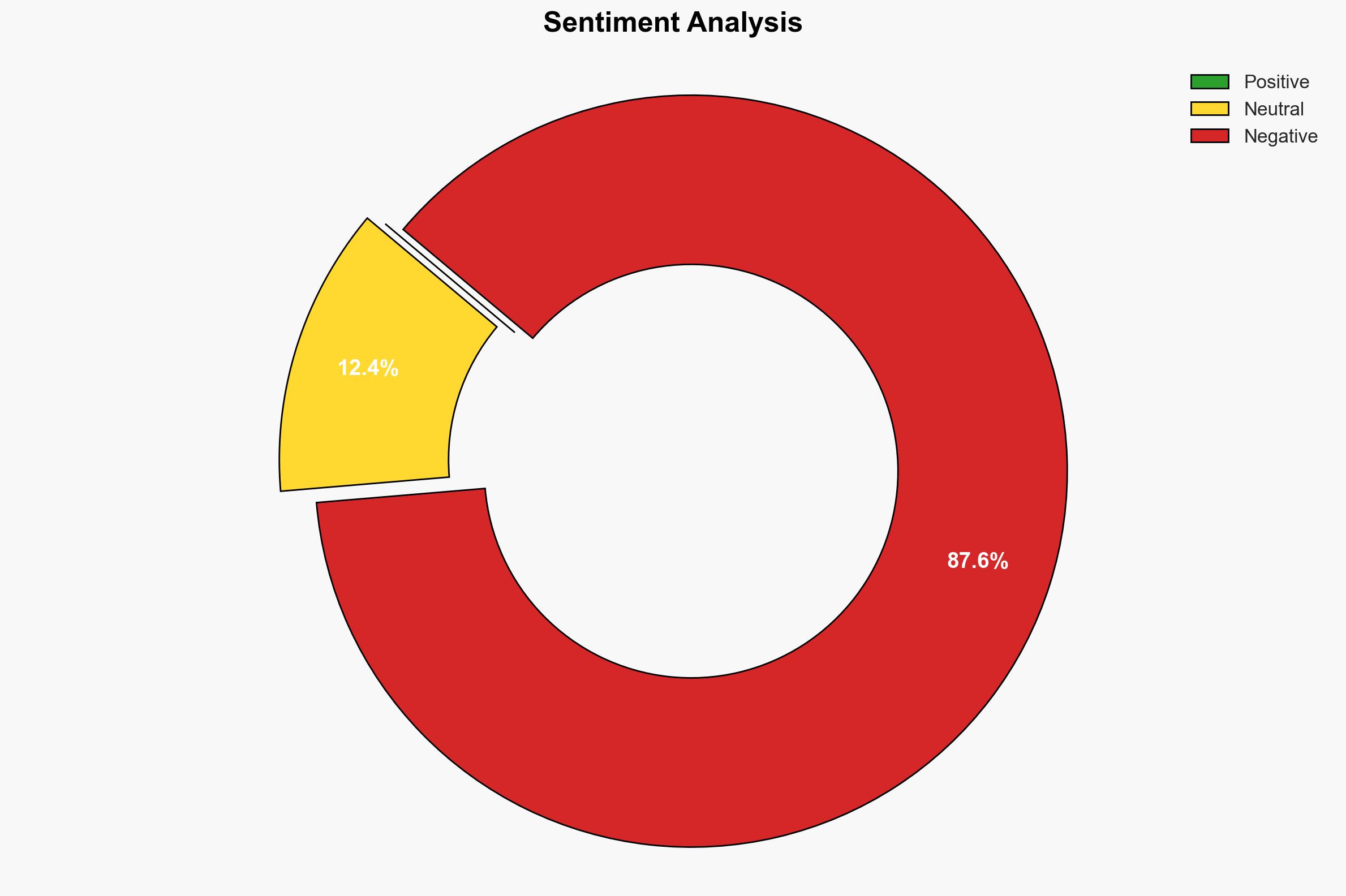
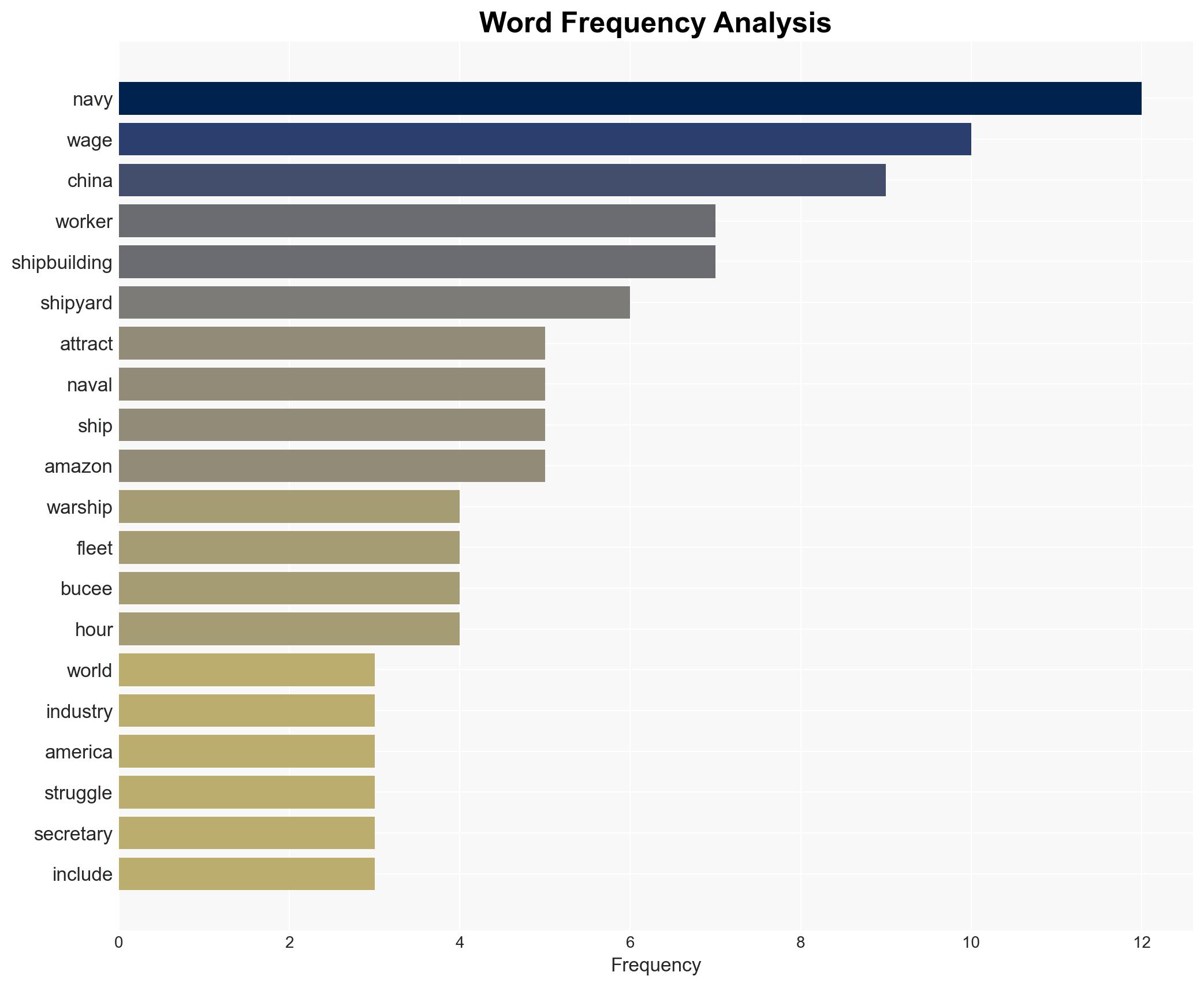
The U.S. Navy is experiencing significant workforce shortages in shipbuilding, impacting its ability to maintain fleet strength amid China’s naval expansion. The primary issue appears to be uncompetitive wages and challenging working conditions compared to other industries. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, given the available evidence and existing uncertainties.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The primary reason for the workforce shortage is uncompetitive wages and poor working conditions in shipyards compared to other industries like retail and logistics. Evidence includes wage comparisons and job conditions, but uncertainties remain about the full scope of non-wage factors affecting recruitment.
- Hypothesis B: The shortage is primarily due to a lack of skilled labor and inadequate training programs, rather than wage issues alone. This is supported by the technical demands of shipyard work and the long apprenticeship periods required, though evidence on training program availability is limited.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to clear evidence of wage disparities and challenging working conditions. However, improvements in training and working conditions could shift this judgment if they prove more influential than wage adjustments alone.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Navy’s workforce issues are primarily driven by economic factors; China’s naval expansion continues at its current pace; U.S. shipbuilding capacity is static without significant policy intervention.
- Information Gaps: Detailed data on the effectiveness of current training programs and the specific impact of non-wage factors on workforce retention.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in wage data comparisons; risk of underestimating the impact of non-economic factors such as job satisfaction and career development opportunities.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The workforce shortage in U.S. naval shipbuilding could lead to a strategic imbalance with China, affecting global naval power dynamics. This development may necessitate policy adjustments to bolster U.S. shipbuilding capabilities.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased geopolitical tension as the U.S. seeks to counterbalance China’s naval expansion.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Reduced naval readiness could impact U.S. ability to project power and respond to global threats.
- Cyber / Information Space: Limited direct impact; however, information operations could exploit perceived weaknesses in U.S. naval capabilities.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impact on regions dependent on shipbuilding; social implications of workforce shifts to other industries.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Conduct a comprehensive wage and working conditions review; initiate targeted recruitment campaigns.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with technical schools to enhance training programs; explore policy incentives for shipyard employment.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Successful workforce revitalization leads to increased shipbuilding capacity. Worst: Continued workforce shortages exacerbate naval capability gaps. Most-Likely: Incremental improvements in workforce conditions stabilize but do not fully resolve shortages.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- John Phelan – Navy Secretary
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us