Venezuela Suspends Operations of Six International Airlines Amid Rising US-Venezuela Tensions
Published on: 2025-11-28
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Why has Venezuela banned six international airlines amid US tensions
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
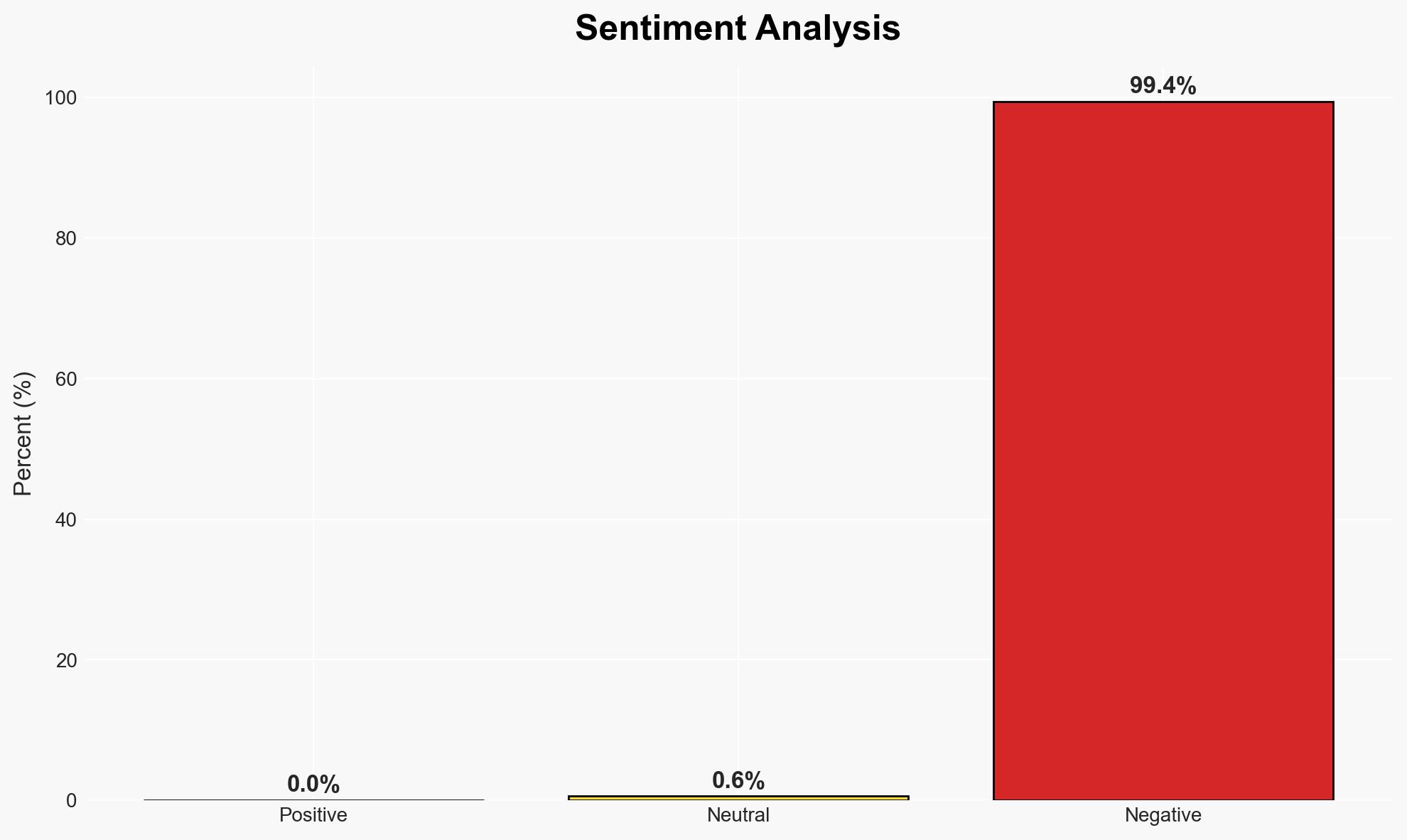
The Venezuelan government’s decision to ban six international airlines appears to be a strategic response to escalating tensions with the United States, particularly in light of recent US warnings about Venezuelan airspace. This action may serve as a signal of defiance against US influence and pressure. The most likely hypothesis is that this is a politically motivated move to consolidate internal power and resist external pressure. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate due to limited direct evidence of Venezuela’s strategic intentions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The ban on international airlines is a direct response to US pressure and warnings about Venezuelan airspace, aimed at asserting sovereignty and countering perceived US aggression. Supporting evidence includes the timing of the ban following US warnings and the historical context of US-Venezuela tensions. Contradicting evidence is the lack of explicit statements from Venezuela linking the ban to US actions.
- Hypothesis B: The ban is primarily driven by internal political considerations, such as consolidating power domestically and projecting strength to the Venezuelan populace. Supporting evidence includes the Venezuelan government’s narrative of resisting foreign intervention and the need to maintain internal control. Contradicting evidence is the potential economic harm from reduced international connectivity.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the alignment of the ban with recent US actions and warnings. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include explicit statements from Venezuelan officials linking the ban to domestic political strategies or evidence of internal dissent being a primary motivator.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: The Venezuelan government prioritizes sovereignty over economic impacts; US-Venezuela relations will remain strained; the ban is a calculated political maneuver.
- Information Gaps: Lack of direct statements from Venezuelan officials on the rationale behind the ban; limited visibility into internal Venezuelan political deliberations.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential for confirmation bias in interpreting actions as solely anti-US; risk of Venezuelan government using the ban as propaganda to mislead about internal stability.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The airline ban could exacerbate existing tensions between Venezuela and the US, potentially leading to further diplomatic or economic retaliations. It may also impact regional stability and economic conditions within Venezuela.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased diplomatic isolation of Venezuela; risk of retaliatory measures by affected countries.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened risk of military posturing or incidents in the region; potential for increased internal security measures by Venezuela.
- Cyber / Information Space: Possible increase in information warfare or propaganda efforts by Venezuela to justify the ban and rally domestic support.
- Economic / Social: Negative impact on Venezuela’s economy due to reduced tourism and business travel; potential for increased public dissatisfaction if economic conditions worsen.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor Venezuelan government communications for shifts in rhetoric; engage with regional partners to assess collective response options.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures to counter potential economic impacts; strengthen diplomatic channels to de-escalate tensions.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Diplomatic engagement leads to a reversal of the ban and improved relations.
- Worst: Escalation leads to military confrontations or further economic sanctions.
- Most-Likely: Continued diplomatic standoff with periodic escalations and de-escalations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Nicolas Maduro – President of Venezuela
- Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) – US aviation authority
- Marisela de Loaiza – President of the Airlines Association of Venezuela
- Paulo Rangel – Portuguese Foreign Minister
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
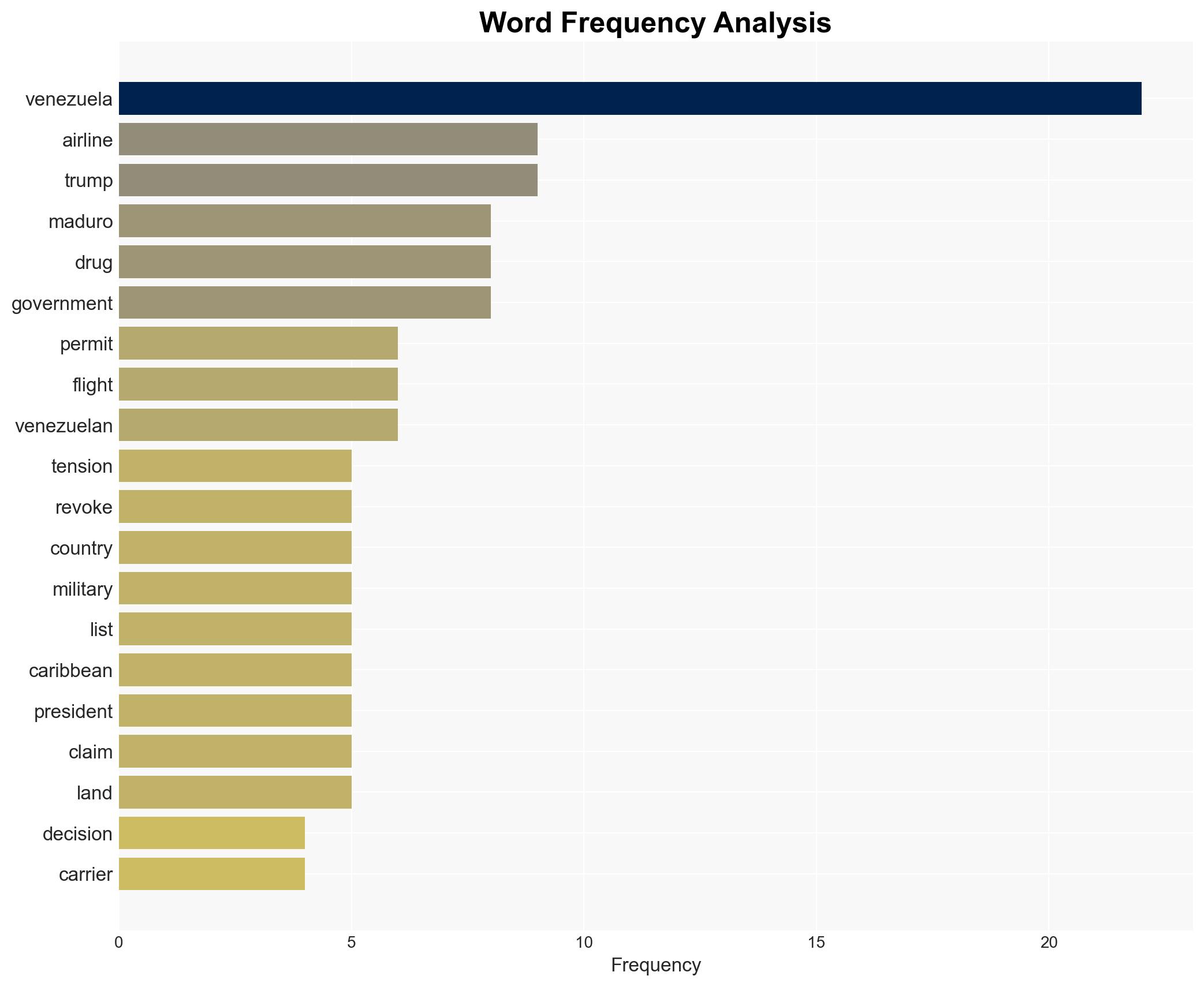
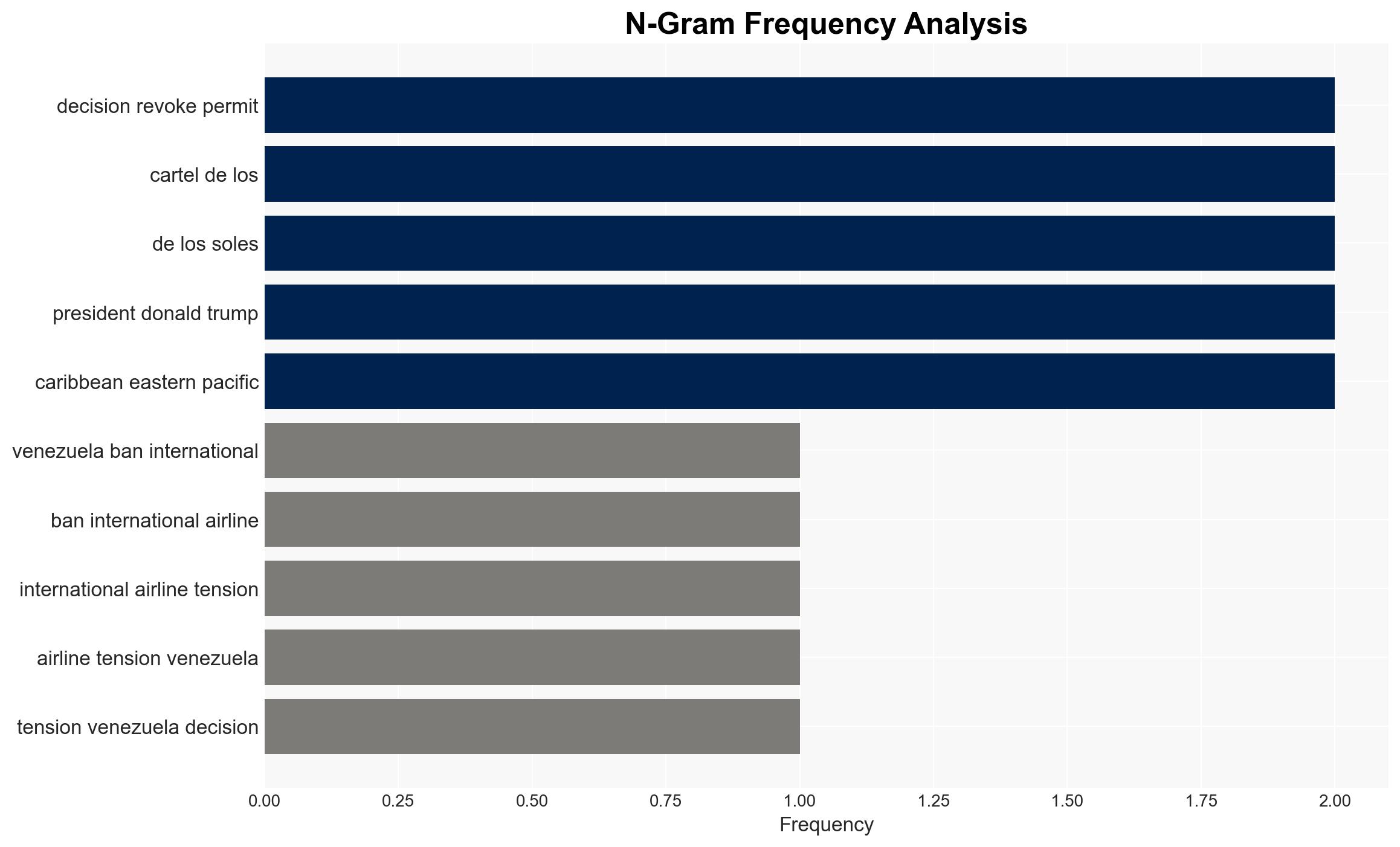
Counter-Terrorism, US-Venezuela relations, international aviation, geopolitical tensions, economic sanctions, airspace security, political strategy, regional stability
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- ACH 2.0: Reconstruct likely threat actor intentions via hypothesis testing and structured refutation.
- Indicators Development: Track radicalization signals and propaganda patterns to anticipate operational planning.
- Narrative Pattern Analysis: Analyze spread/adaptation of ideological narratives for recruitment/incitement signals.
Explore more:
Counter-Terrorism Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us