Worlds adaptation financing falls dangerously short warns UNEP report – BusinessLine
Published on: 2025-11-12
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Worlds adaptation financing falls dangerously short warns UNEP report – BusinessLine
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
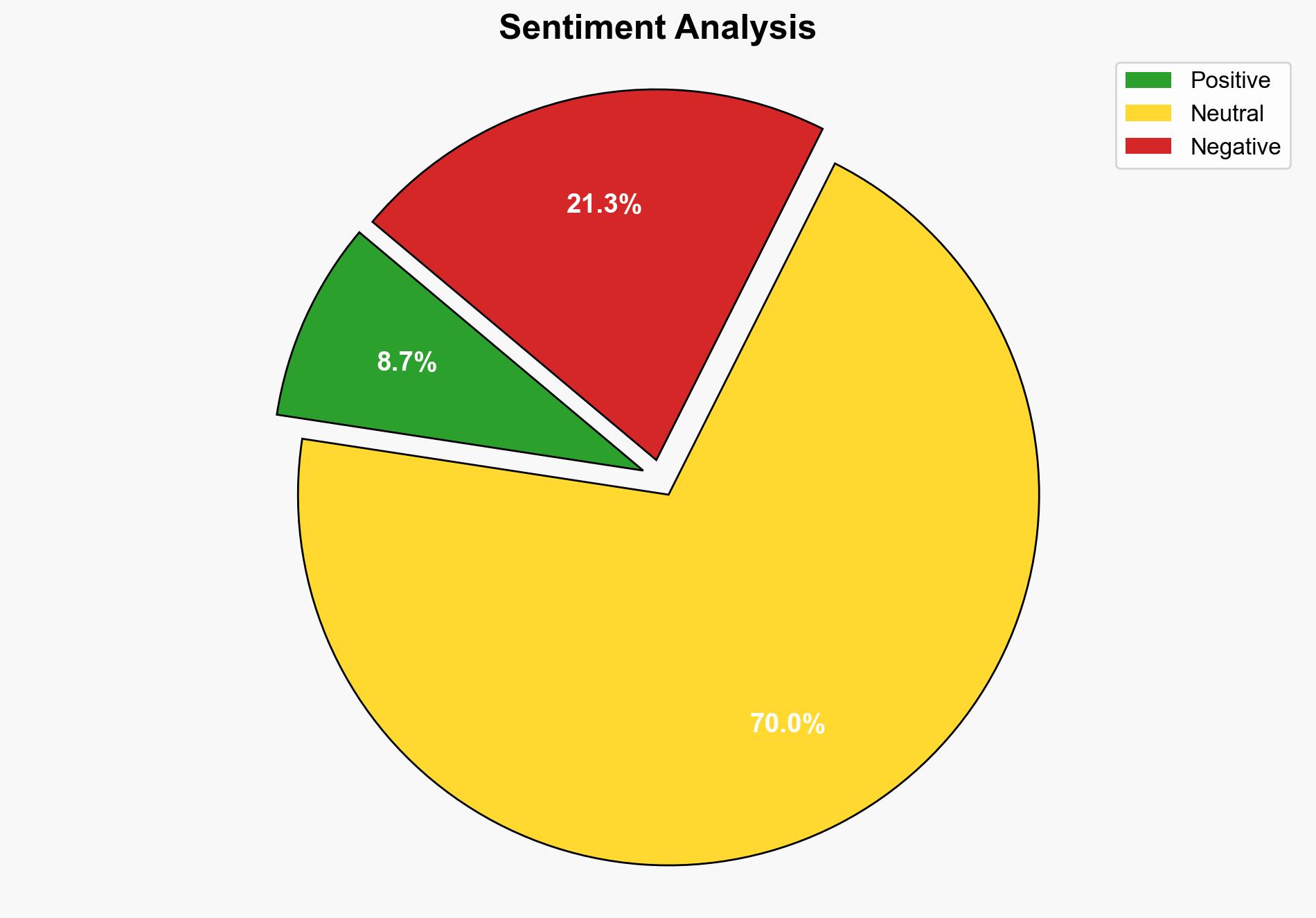
The UNEP report highlights a critical shortfall in global adaptation financing, posing significant risks to vulnerable populations and economies. The most supported hypothesis is that the lack of adequate funding will exacerbate humanitarian and economic losses, particularly in regions like India facing extreme climate threats. Confidence Level: High. Recommended action includes prioritizing international collaboration to increase adaptation funding and integrating local resilience initiatives.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The funding gap will lead to increased humanitarian and economic losses due to inadequate adaptation measures.
Hypothesis 2: Despite current funding shortfalls, technological advancements and local initiatives will mitigate the worst impacts of climate change.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the current scale of the funding gap and the immediate threats posed by climate change, particularly in vulnerable regions. Hypothesis 2 assumes rapid technological and local innovation, which may not be feasible without significant financial support.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include the belief that current funding levels are insufficient and that climate threats will continue to escalate. A red flag is the potential underestimation of local adaptation capabilities and innovations. There is also a risk of bias in assuming that international funding is the sole solution, neglecting local and private sector contributions.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The funding shortfall could lead to cascading threats, including increased humanitarian crises, economic instability, and political unrest in affected regions. There is a risk of cyber and informational threats as entities may exploit vulnerabilities in disaster response systems. Economically, productivity losses could lead to broader market instability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable steps include enhancing international financial collaboration, promoting public-private partnerships, and investing in local resilience initiatives.
- Best Scenario: Increased funding and effective local initiatives significantly mitigate climate impacts.
- Worst Scenario: Continued funding shortfalls lead to severe humanitarian and economic crises.
- Most-likely Scenario: Incremental improvements in funding and local initiatives provide some relief but fall short of comprehensive adaptation needs.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Sanjay Srivastava, Radhakrishnan, UNEP, NIAS, Indian Institute of Science, UN ESCAP, International Labour Organisation, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal Academy of Higher Education.
7. Thematic Tags
Climate Change, Adaptation Financing, Humanitarian Risk, Economic Stability, International Collaboration
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology