1Password Introduces Anti-Phishing Feature to Combat Rising Credential Theft Risks
Published on: 2026-01-27
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: 1Password’s new anti-phishing feature targets your most inescapable vulnerability – here’s how
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
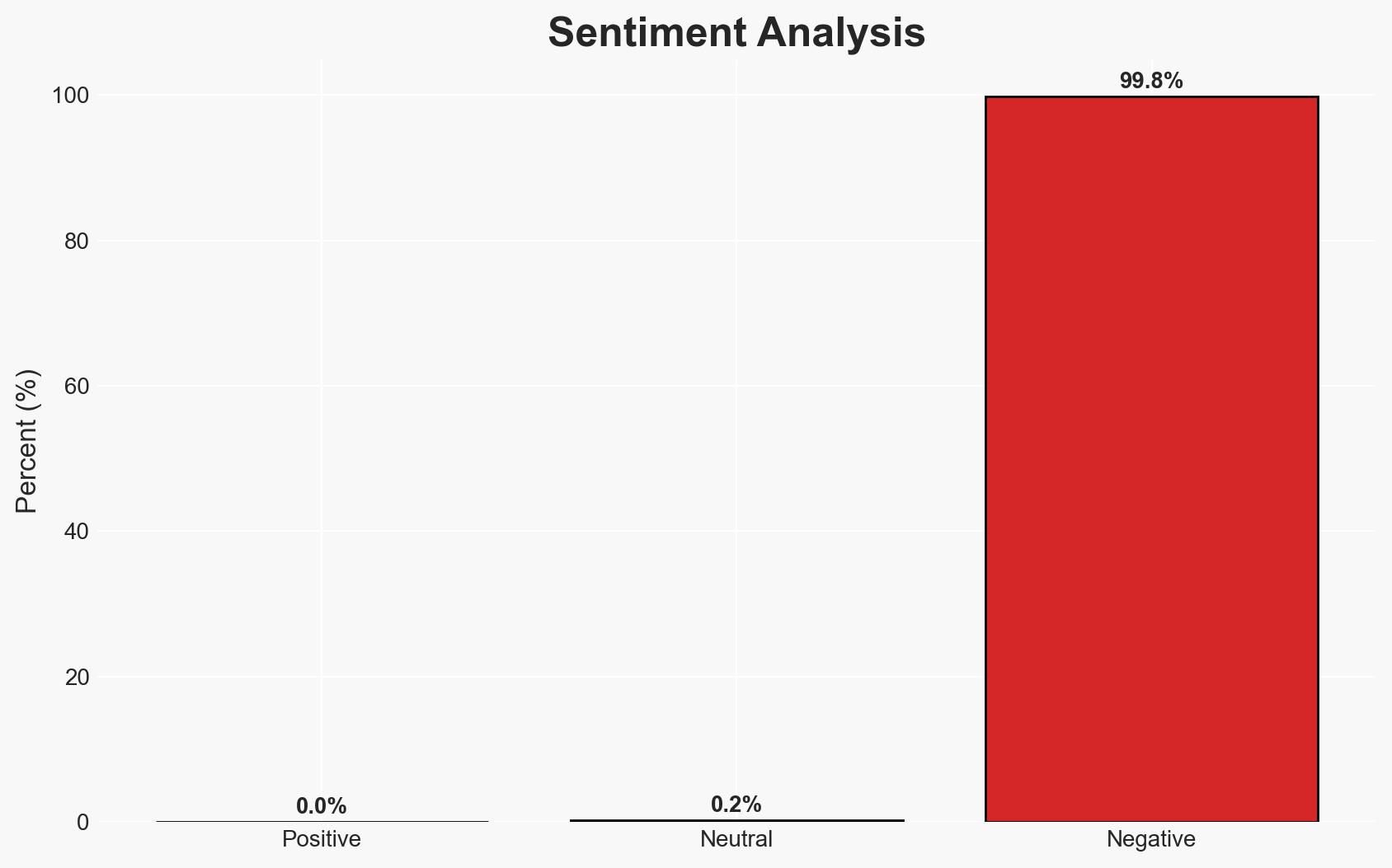
1Password has introduced a new anti-phishing feature to enhance user security against increasingly sophisticated phishing attacks, which are often facilitated by AI tools. The feature aims to prevent users from inadvertently providing credentials to fraudulent websites. This development is particularly relevant for businesses and individuals frequently targeted by phishing schemes. Overall confidence in this assessment is moderate, given the reliance on survey data and potential biases.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The new anti-phishing feature by 1Password will significantly reduce successful phishing attacks. This is supported by the feature’s design to introduce an additional verification step, potentially preventing users from submitting credentials to fake sites. However, the effectiveness is uncertain due to potential user misunderstanding of the feature.
- Hypothesis B: The feature will have limited impact on reducing phishing attacks due to user complacency and the sophistication of phishing tactics. This is supported by the high percentage of users who have already fallen victim to phishing scams, indicating a persistent vulnerability that may not be fully mitigated by the new feature.
- Assessment: Hypothesis B is currently better supported due to the high prevalence of phishing success rates and the potential for users to bypass security features. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include user adoption rates of the feature and any reported decreases in phishing incidents.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Users will correctly utilize the new feature; phishing tactics will not rapidly evolve to circumvent the feature; survey data accurately reflects broader user behavior.
- Information Gaps: Detailed metrics on the feature’s effectiveness post-implementation; comprehensive data on phishing attack evolution in response to such security features.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Potential bias in survey data due to self-reporting; possible underestimation of phishing sophistication by security developers.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The introduction of enhanced anti-phishing features could lead to a temporary decrease in successful phishing attacks, but may also drive attackers to develop more advanced techniques. This dynamic could influence broader cybersecurity strategies and user education efforts.
- Political / Geopolitical: Minimal direct impact, though increased cybersecurity measures could influence international cyber policy discussions.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Potential reduction in phishing-related breaches could lower risks of data theft and subsequent exploitation by malicious actors.
- Cyber / Information Space: May prompt a shift in phishing tactics, leading to more sophisticated cyber threats.
- Economic / Social: Improved security could enhance user trust in digital platforms, but persistent phishing threats may continue to undermine confidence.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Monitor user feedback and incident reports to assess the feature’s impact; enhance user education on recognizing phishing attempts.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop partnerships with cybersecurity firms to share threat intelligence; invest in adaptive security technologies to counter evolving phishing tactics.
- Scenario Outlook: Best: Significant reduction in phishing incidents; Worst: Attackers develop bypass methods, maintaining current threat levels; Most-Likely: Gradual improvement in security with ongoing adaptation by attackers.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- 1Password (Developer of the anti-phishing feature)
- StripeOLT (Documented a related phishing attack)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, phishing, AI tools, user education, digital security, threat mitigation, cyber threats
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us