2026 ThreatsDay Bulletin: Evolving Cybercrime Tactics and Emerging Patterns in macOS Attacks and Botnet Explo…
Published on: 2026-01-01
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: ThreatsDay Bulletin GhostAd Drain macOS Attacks Proxy Botnets Cloud Exploits and 12 Stories
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
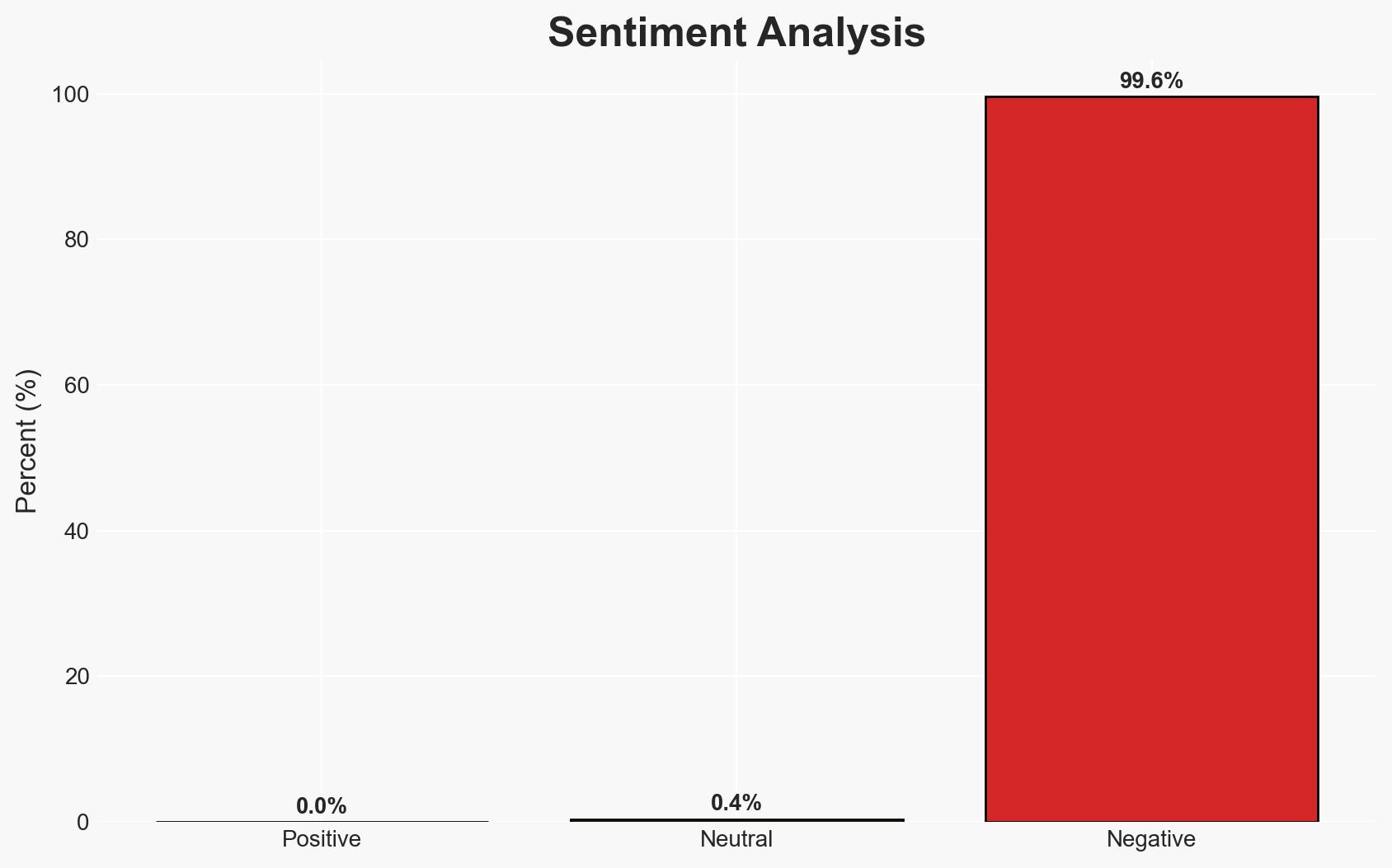
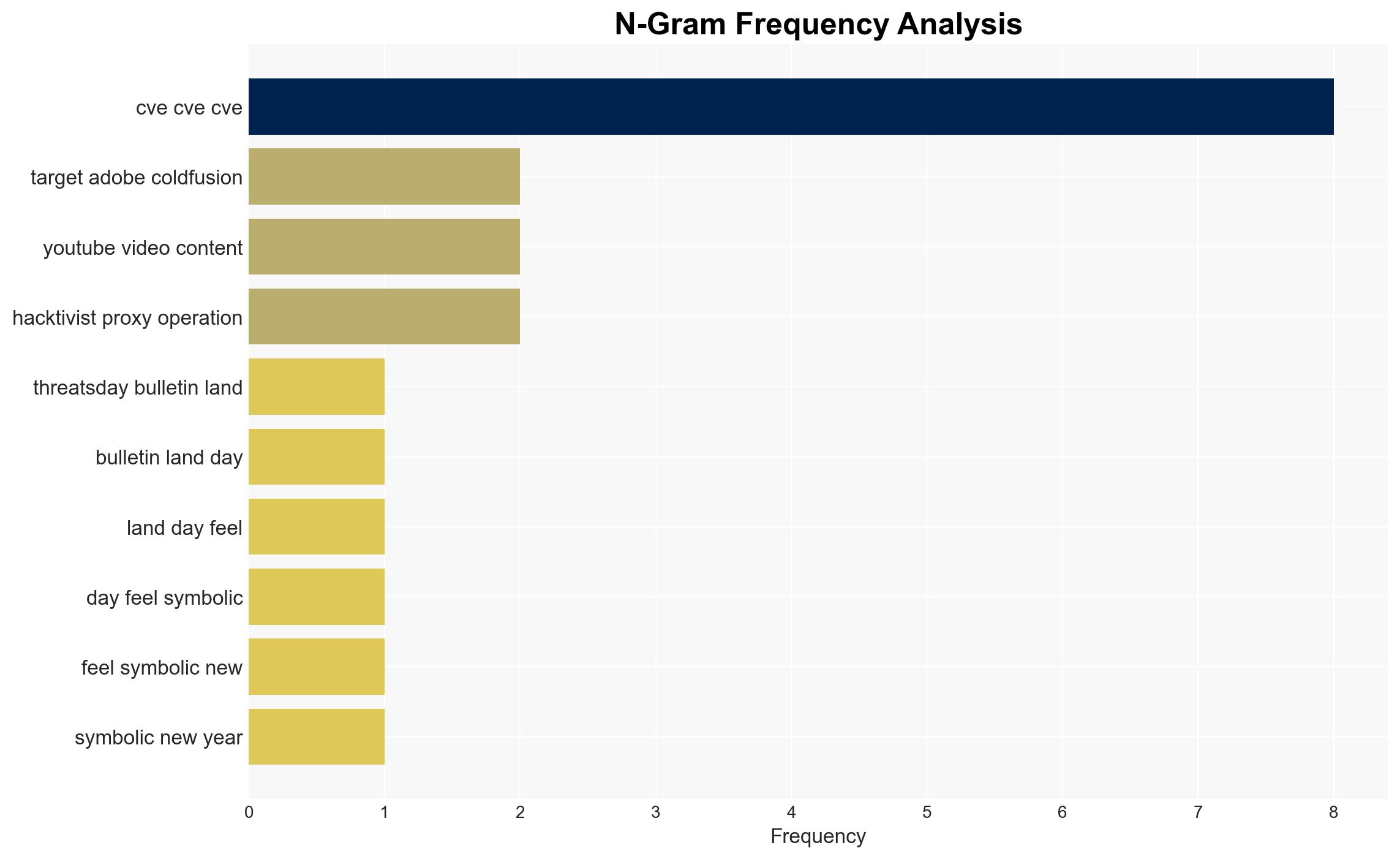
The latest ThreatsDay Bulletin highlights a trend towards more calculated and persistent cyber threats, with a focus on exploiting multiple small vulnerabilities rather than singular large-scale breaches. The arrest of a Lithuanian national for distributing malware disguised as KMSAuto and a coordinated attack on Adobe ColdFusion servers underscore the evolving threat landscape. This assessment is made with moderate confidence, as the data indicates a shift in tactics but lacks comprehensive attribution details.
2. Competing Hypotheses
- Hypothesis A: The increase in small-scale, calculated cyber attacks is primarily driven by independent cybercriminals leveraging existing vulnerabilities for financial gain. This is supported by the arrest of the Lithuanian national and the use of widely known CVEs in the ColdFusion attacks. However, the lack of detailed attribution to specific groups or state actors introduces uncertainty.
- Hypothesis B: These attacks are part of a coordinated effort by state-sponsored actors to test and refine cyber warfare tactics on a global scale. The use of infrastructure based in Japan and the targeting of multiple countries could indicate a broader strategic objective. Contradicting this is the absence of direct evidence linking these activities to state actors.
- Assessment: Hypothesis A is currently better supported due to the financial motivations evident in the KMSAuto scam and the opportunistic nature of exploiting known vulnerabilities. Key indicators that could shift this judgment include evidence of state sponsorship or a change in target selection towards more strategic assets.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
- Assumptions: Cybercriminals are primarily motivated by financial gain; the vulnerabilities exploited are widely known and accessible; the infrastructure used does not inherently indicate state sponsorship.
- Information Gaps: Detailed attribution of the ColdFusion attacks; motivations and affiliations of the Lithuanian suspect beyond financial gain; potential state involvement.
- Bias & Deception Risks: Confirmation bias towards financial motivations; potential source bias from cybersecurity firms; lack of independent verification of state involvement claims.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The observed cyber activities suggest an evolving threat landscape where attackers exploit small vulnerabilities with precision, potentially leading to increased difficulty in defending against such threats.
- Political / Geopolitical: Potential for increased tensions if state sponsorship is confirmed, especially if critical infrastructure is targeted.
- Security / Counter-Terrorism: Heightened alertness required for cybersecurity defenses, with a focus on patch management and incident response.
- Cyber / Information Space: Increased sophistication in cyber operations could lead to more complex information warfare tactics.
- Economic / Social: Potential economic impacts from successful cyber attacks on businesses and critical infrastructure, leading to social unrest.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Immediate Actions (0–30 days): Enhance monitoring of known vulnerabilities, particularly in widely used software; increase collaboration with international cybersecurity agencies.
- Medium-Term Posture (1–12 months): Develop resilience measures through regular security audits and employee training; strengthen public-private partnerships for threat intelligence sharing.
- Scenario Outlook:
- Best: Improved defenses reduce successful exploitations, leading to a decline in cyber incidents.
- Worst: State-sponsored actors escalate attacks, targeting critical infrastructure with significant geopolitical consequences.
- Most-Likely: Continued opportunistic attacks by financially motivated criminals, with occasional state-sponsored incidents.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
- Lithuanian national (arrested for KMSAuto malware distribution)
- CTG Server Limited (Japan-based infrastructure used in ColdFusion attacks)
- GreyNoise (cybersecurity firm reporting on ColdFusion attacks)
- Not clearly identifiable from open sources in this snippet for other actors.
7. Thematic Tags
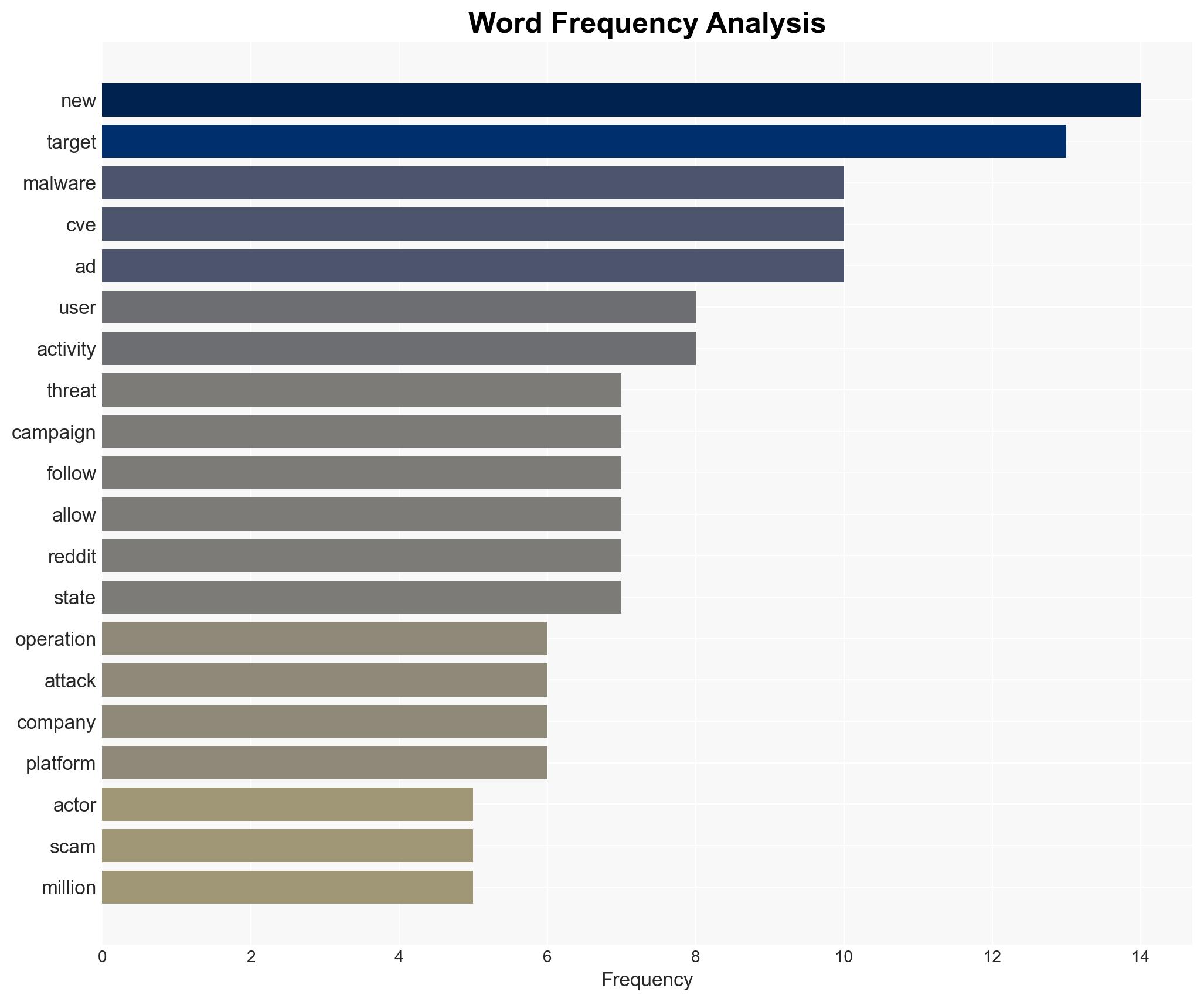
cybersecurity, malware, financial crime, state-sponsored attacks, vulnerability exploitation, international cooperation, cyber defense
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model hostile behavior to identify vulnerabilities.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us