25 billion Gmail users at risk after Google database hack – PCWorld
Published on: 2025-08-20
Intelligence Report: 25 billion Gmail users at risk after Google database hack – PCWorld
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
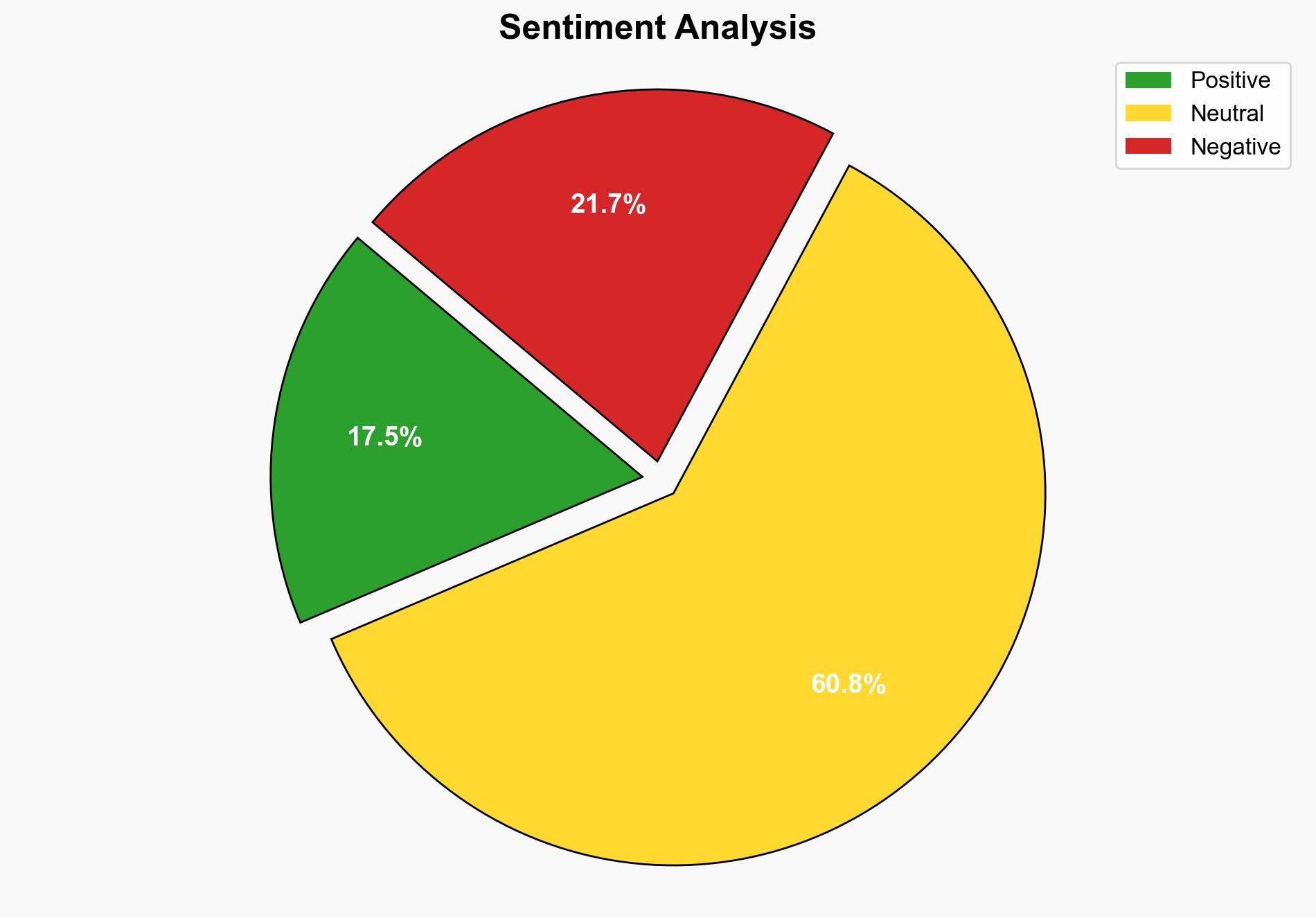
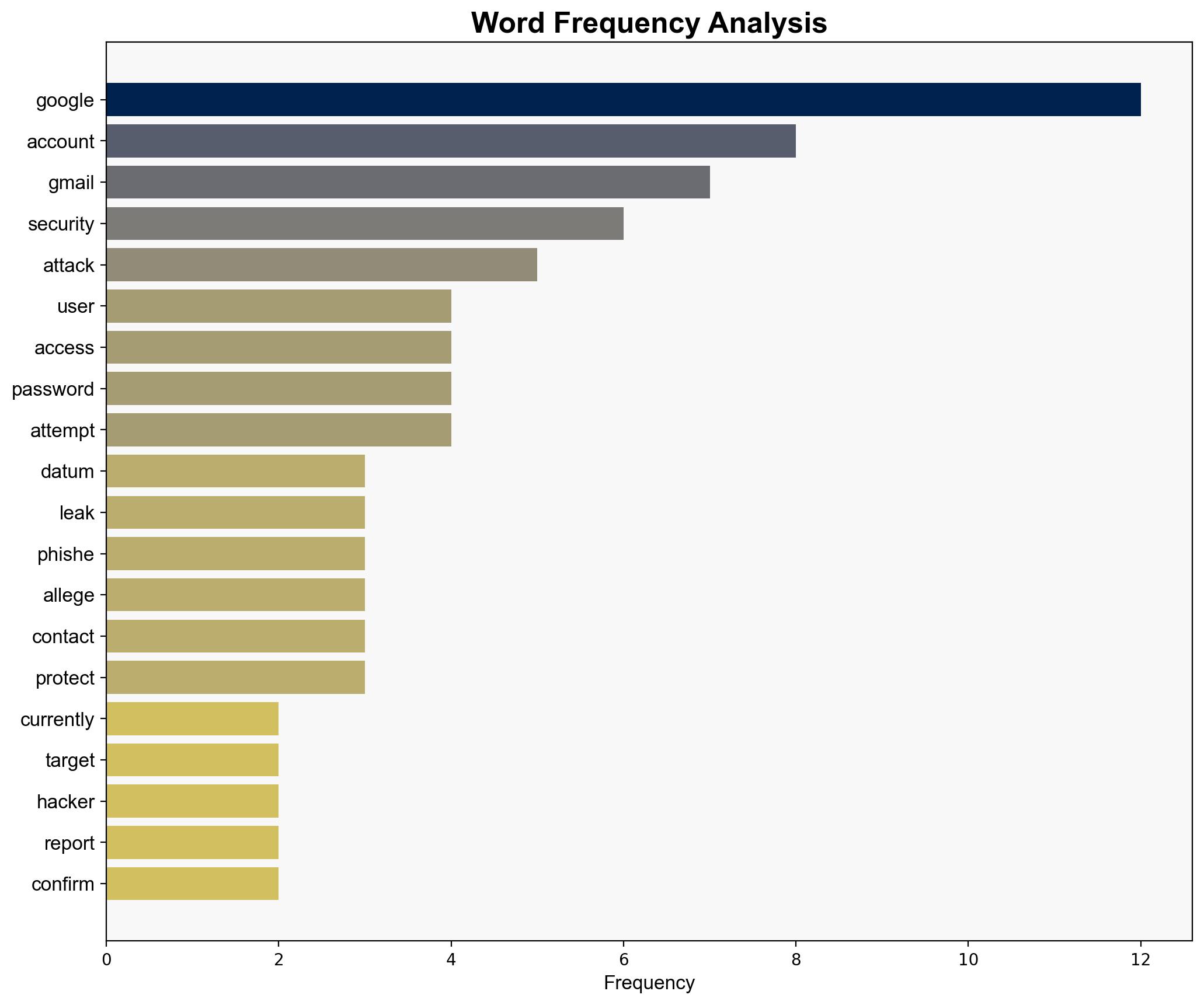
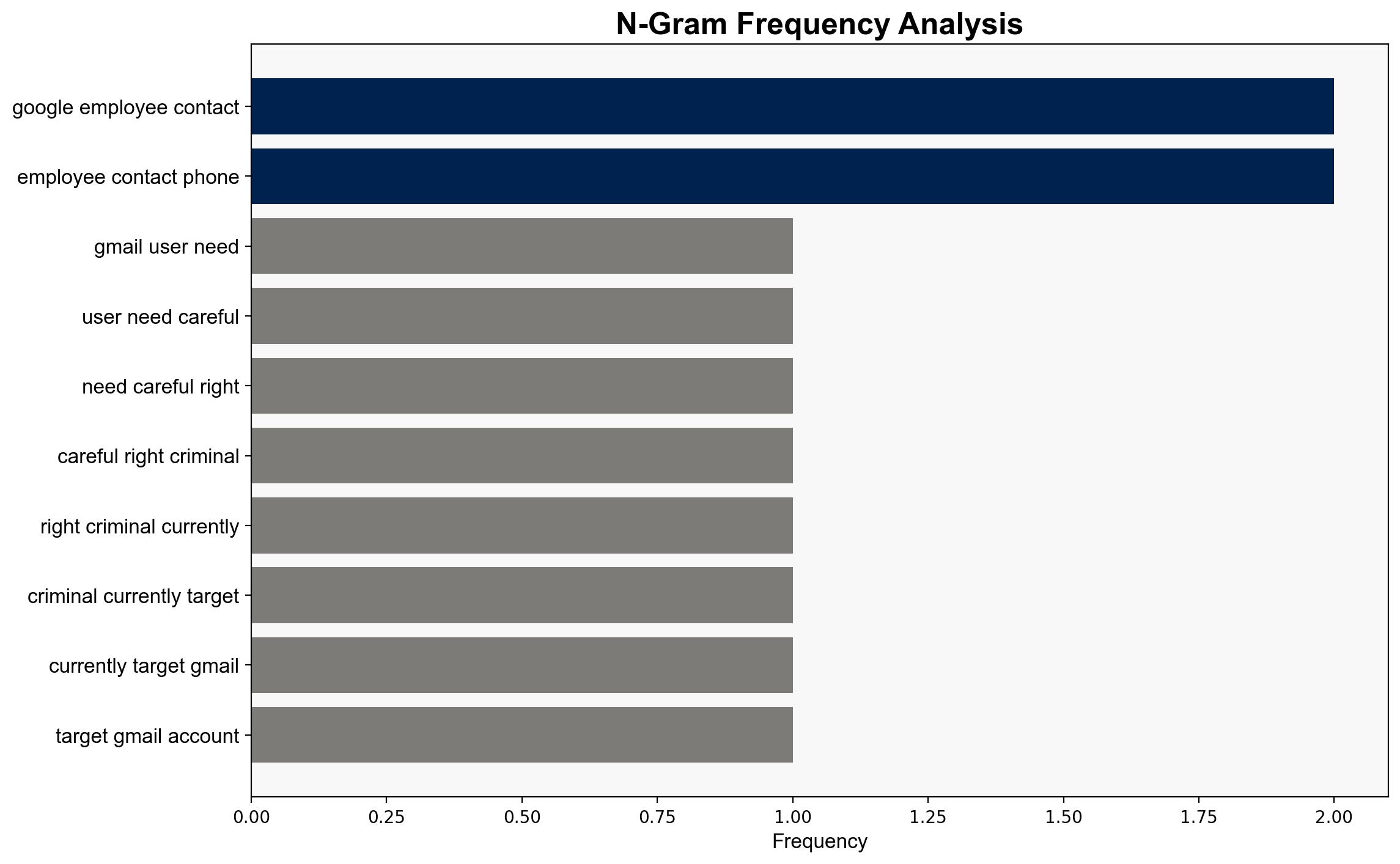
The analysis suggests a moderate confidence level in the hypothesis that the reported breach is a targeted attack by the hacker group “ShinyHunter” aimed at exploiting Google users for financial gain through phishing and malware. Immediate action is recommended to enhance user awareness and strengthen security protocols. The alternative hypothesis, that the breach is exaggerated or misreported, is less supported by current evidence.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The breach is a genuine and significant security incident orchestrated by “ShinyHunter,” targeting Google users for phishing and malware attacks.
Hypothesis 2: The breach is exaggerated or misreported, possibly due to miscommunication or misinformation, with no substantial threat to users.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported due to Google’s confirmation of the attack and the detailed description of the methods used by attackers. Hypothesis 2 lacks corroborative evidence and relies on assumptions of misinformation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions:
– Hypothesis 1 assumes the credibility of Google’s confirmation and the technical feasibility of the reported attack methods.
– Hypothesis 2 assumes potential exaggeration by media or miscommunication from Google.
Red Flags:
– Lack of detailed technical information on the breach.
– Absence of independent verification of the breach’s scale.
– Potential bias in media reporting.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The breach poses significant risks, including:
– Economic: Potential financial losses from phishing attacks.
– Cybersecurity: Increased vulnerability of Google services.
– Psychological: Erosion of trust in Google’s security measures.
– Geopolitical: Potential exploitation by state-sponsored actors.
Escalation scenarios include widespread phishing campaigns and increased sophistication in malware deployment targeting Google services.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance user education on phishing and security practices.
- Implement additional security measures, such as two-factor authentication and regular security audits.
- Best Case: Swift containment of the breach with minimal user impact.
- Worst Case: Large-scale phishing attacks leading to significant financial and data losses.
- Most Likely: Continued attempts at phishing with moderate user impact.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– “ShinyHunter” (hacker group)
– Google (affected entity)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus