Clorox sues Cognizant for giving away passwords which led to major breach – TechRadar
Published on: 2025-07-24
Intelligence Report: Clorox sues Cognizant for giving away passwords which led to major breach – TechRadar
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
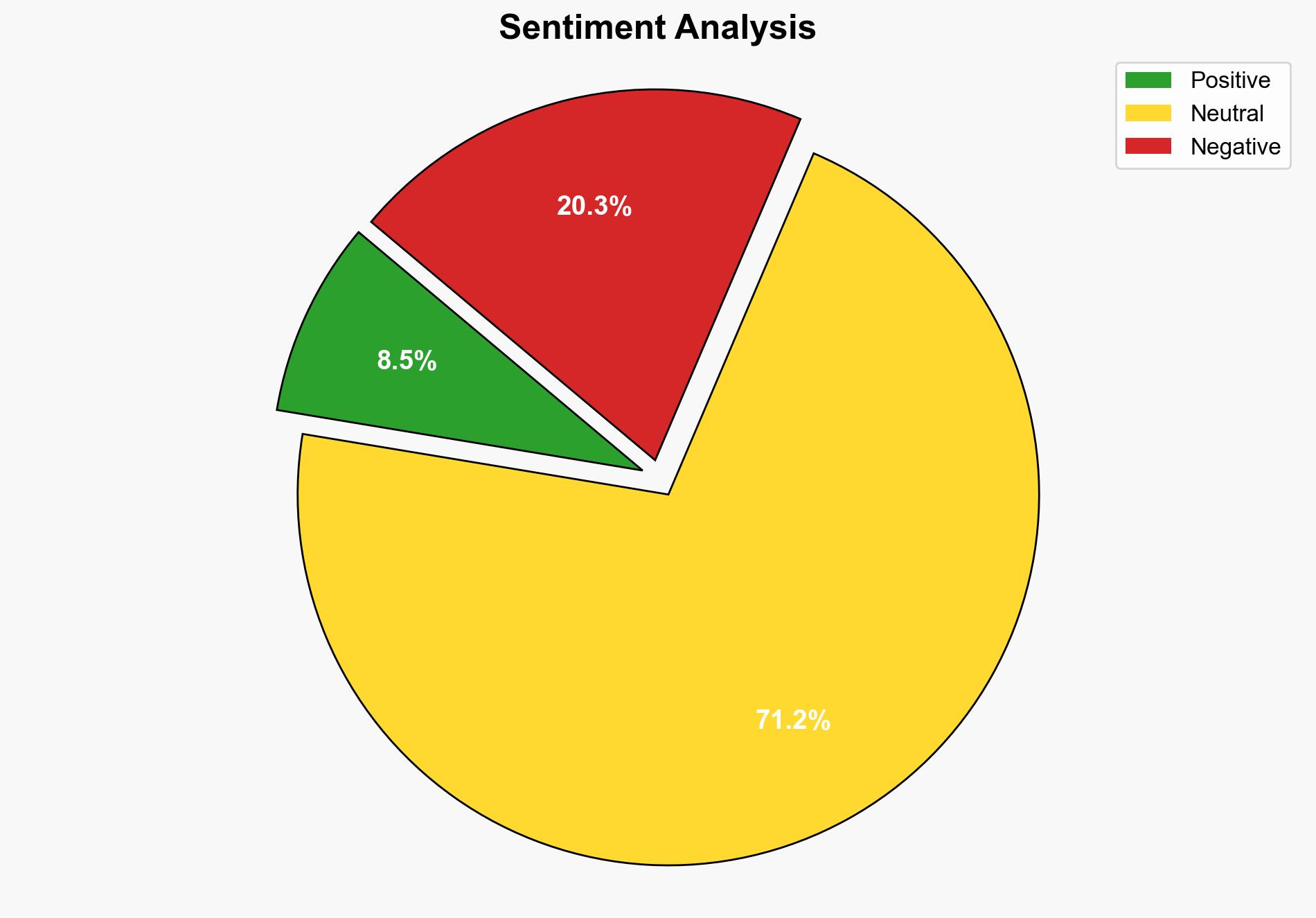
The most supported hypothesis is that Cognizant’s failure to adhere to standard identity verification procedures led to the breach, resulting in significant operational and financial damage to Clorox. Confidence level: Moderate. It is recommended that Clorox enhance its internal cybersecurity protocols and consider renegotiating service contracts to include comprehensive cybersecurity responsibilities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The breach was primarily due to Cognizant’s negligence in following established identity verification procedures, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Hypothesis 2: The breach resulted from Clorox’s inadequate internal cybersecurity measures, with Cognizant’s role being limited to a narrow scope of help desk services, not encompassing broader cybersecurity responsibilities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions:
– Hypothesis 1 assumes that Cognizant had clear procedures in place that were not followed.
– Hypothesis 2 assumes Clorox’s internal cybersecurity was insufficient to prevent or mitigate the breach.
Red Flags:
– Lack of detailed evidence on the specific procedures Cognizant allegedly failed to follow.
– Potential bias in Clorox’s claims, possibly deflecting blame from internal shortcomings.
– Cognizant’s defense highlights a possible misalignment of service expectations.
Blind Spots:
– Insufficient information on Clorox’s internal cybersecurity measures.
– Limited insight into the contractual obligations and scope of Cognizant’s services.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The breach exposes Clorox to significant reputational damage and financial loss, potentially affecting market confidence and customer trust. The incident underscores the risk of relying on third-party service providers for critical cybersecurity functions without clear accountability. There is a potential for similar breaches if systemic vulnerabilities are not addressed, which could lead to further economic and operational disruptions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Mitigation: Clorox should conduct a comprehensive review of its cybersecurity protocols and service provider contracts to ensure clear delineation of responsibilities.
- Opportunities: Invest in advanced cybersecurity training for employees and enhance multi-factor authentication processes.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Clorox strengthens its cybersecurity posture, preventing future breaches and restoring stakeholder confidence.
- Worst Case: Continued vulnerabilities lead to additional breaches, exacerbating financial and reputational damage.
- Most Likely: Incremental improvements in cybersecurity, with ongoing legal proceedings impacting Clorox’s public image.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Clorox
– Cognizant
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, corporate governance, risk management