Intel QAT Accelerators Being Demoted On Linux By FSCRYPT Bug Prone Slow – Phoronix
Published on: 2025-07-28
Intelligence Report: Intel QAT Accelerators Being Demoted On Linux By FSCRYPT Bug Prone Slow – Phoronix
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
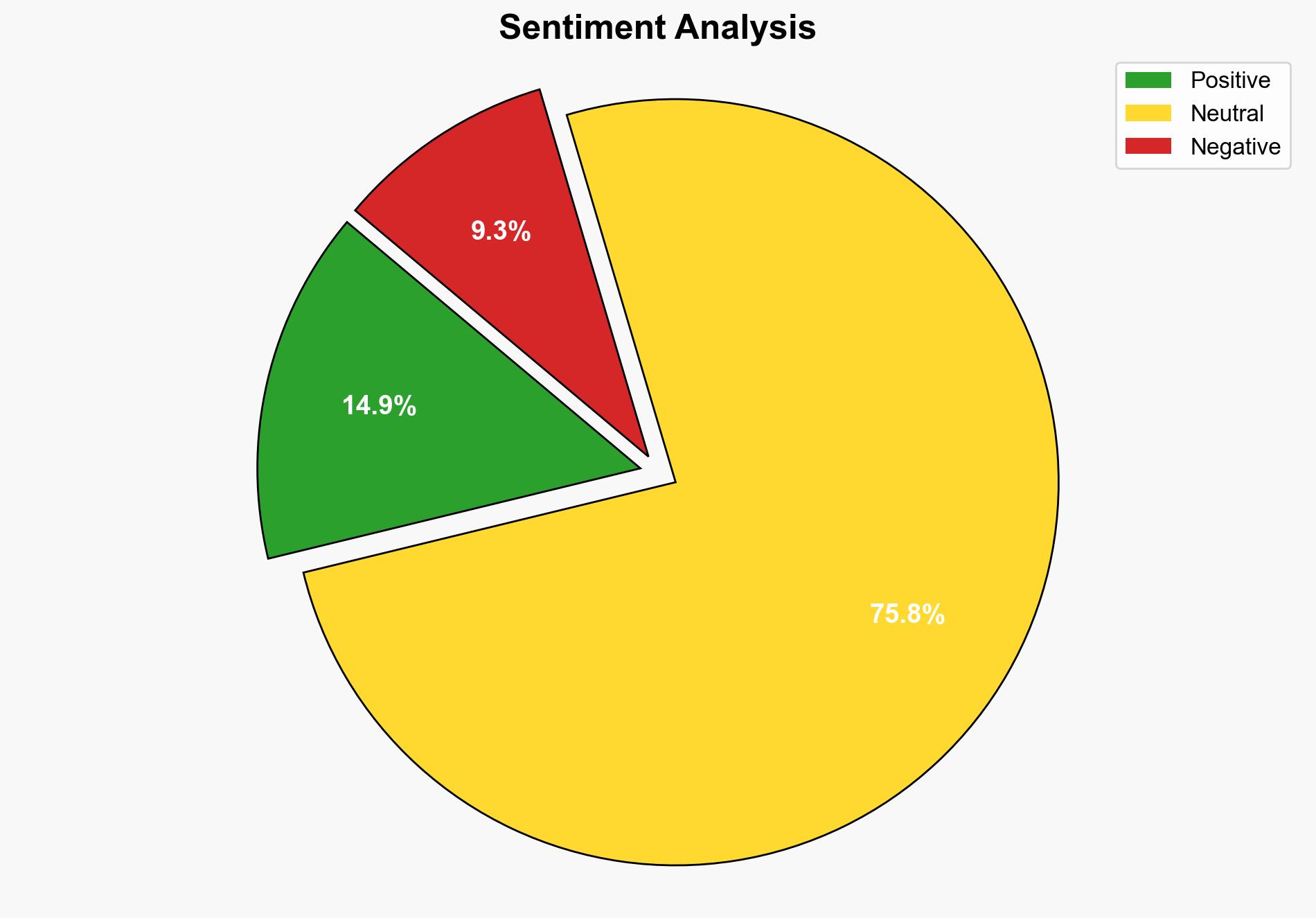
The demotion of Intel QAT accelerators in the Linux kernel due to performance issues and bug-prone behavior suggests a significant setback for Intel’s efforts to optimize its hardware for cryptographic tasks. The most supported hypothesis is that the current software support and driver issues are the primary cause of performance degradation. A strategic recommendation is to prioritize software optimization and driver stability to enhance the performance of Intel QAT accelerators. Confidence Level: Moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A:** The performance issues with Intel QAT accelerators are primarily due to inadequate software support and buggy drivers, leading to their demotion in the Linux kernel.
2. **Hypothesis B:** The performance issues are inherent to the hardware design of Intel QAT accelerators, which cannot compete with CPU-based cryptographic optimizations such as AVX and VAES.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported by the evidence of driver bugs and the need for software patches, as highlighted by Eric Biggers’ findings. Hypothesis B lacks direct evidence of hardware limitations, as the issues seem to stem from software inefficiencies rather than hardware constraints.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions:** It is assumed that software optimization can significantly improve QAT performance. It is also assumed that the demotion is purely performance-related and not influenced by external factors such as market competition.
– **Red Flags:** The reliance on anecdotal evidence from specific engineers without broader testing data could introduce bias. The absence of detailed performance metrics for QAT accelerators compared to other solutions is a blind spot.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The demotion of Intel QAT accelerators could lead to reduced adoption in environments relying on Linux for secure data processing, potentially impacting Intel’s market share in the server and enterprise sectors. This situation may also encourage competitors to capitalize on Intel’s software shortcomings. There is a risk of cascading effects if other hardware components face similar issues, leading to broader trust issues in Intel’s hardware solutions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- **Mitigation:** Accelerate the development and deployment of robust software patches to address driver issues. Engage with the Linux community to ensure timely integration of fixes.
- **Opportunities:** Leverage this challenge to improve collaboration with open-source communities, potentially enhancing Intel’s reputation and product reliability.
- **Projections:**
– **Best Case:** Successful software optimizations lead to restored confidence and increased adoption of Intel QAT accelerators.
– **Worst Case:** Continued performance issues result in long-term damage to Intel’s reputation and market position.
– **Most Likely:** Incremental improvements in software support lead to gradual recovery of performance and adoption rates.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Eric Biggers, who identified the performance issues and contributed to the AVX optimization.
– Intel, as the primary entity affected by the demotion of its QAT accelerators.
– The Linux kernel development community, which plays a crucial role in integrating patches and updates.
7. Thematic Tags
cybersecurity, software optimization, hardware performance, open-source collaboration