Petroleum prices reacted to economic and geopolitical uncertainty in the second quarter – Eia.gov
Published on: 2025-08-06
Intelligence Report: Petroleum prices reacted to economic and geopolitical uncertainty in the second quarter – Eia.gov
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
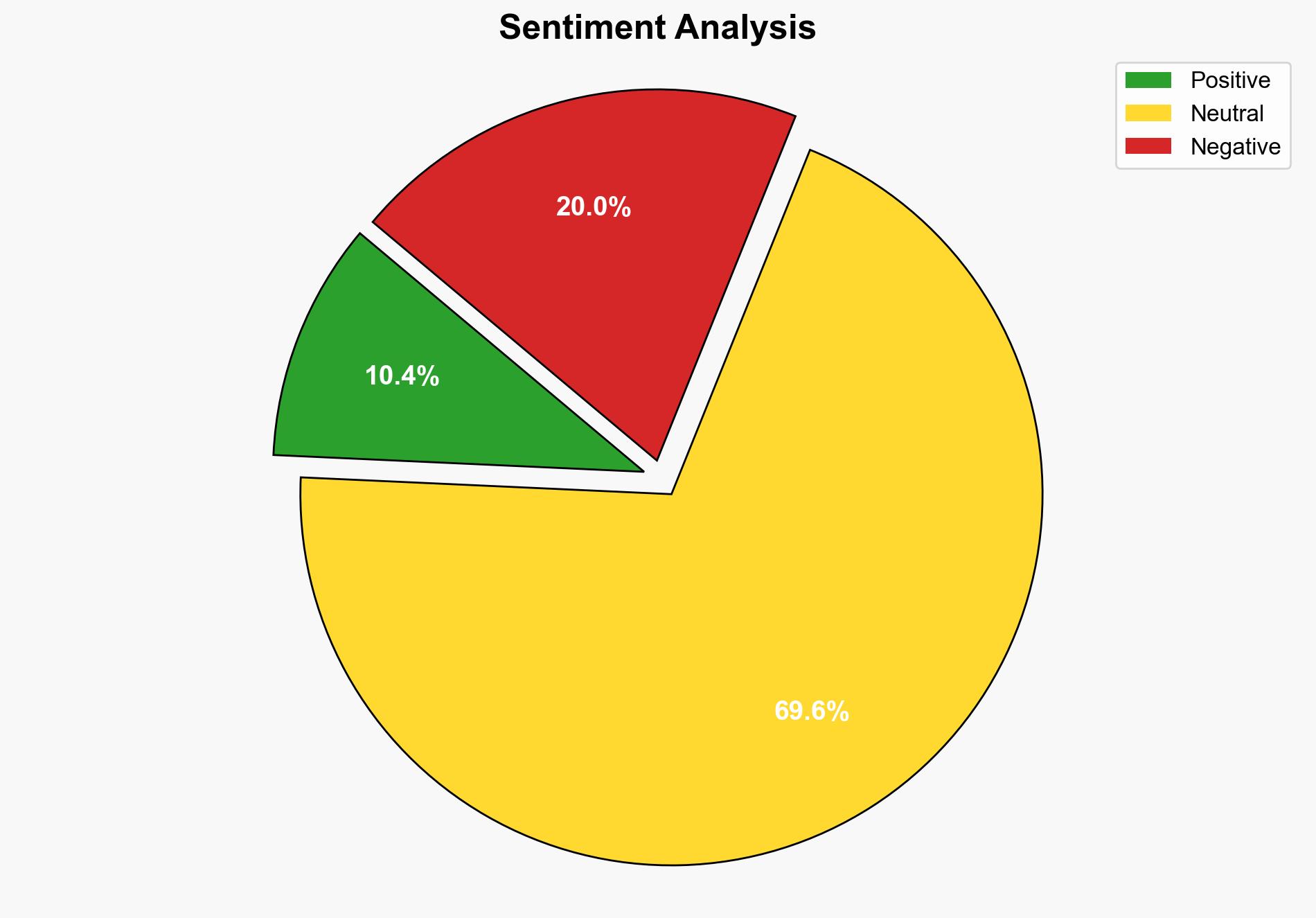
The analysis suggests that geopolitical tensions in the Middle East and economic uncertainties, such as trade disputes, significantly influenced petroleum price volatility in the second quarter. The hypothesis that geopolitical factors, particularly the Iran-Israel conflict, played a more dominant role is better supported. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Enhance monitoring of geopolitical developments in the Middle East and adjust strategic reserves and trade policies accordingly.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Geopolitical Dominance Hypothesis**: The primary driver of petroleum price volatility was geopolitical tensions, especially the Iran-Israel conflict, which heightened fears of supply disruptions.
2. **Economic Influence Hypothesis**: Economic factors, including global trade uncertainties and changes in government policies affecting biofuel compliance, were the main contributors to price fluctuations.
Using ACH 2.0, the geopolitical dominance hypothesis is more supported due to the timing of price spikes aligning with geopolitical events, such as the Israeli strike on Iran and subsequent ceasefire. Economic indicators, while influential, show less direct correlation with immediate price changes.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that geopolitical events have a more immediate impact on oil prices than economic policies. Another assumption is that refinery margins and biofuel compliance credits are secondary factors.
– **Red Flags**: Potential bias in attributing price changes solely to geopolitical events without considering the cumulative effect of economic policies. Lack of detailed data on the impact of small refinery exemptions and RFS policy changes.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The interplay of geopolitical tensions and economic policies could lead to sustained volatility in petroleum markets. A significant risk is the potential for escalation in the Middle East, which could disrupt global oil supply chains. Economic policies, particularly those related to biofuels, could further complicate market dynamics if not aligned with geopolitical realities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance intelligence gathering on Middle Eastern geopolitical developments to anticipate potential supply disruptions.
- Review and potentially adjust strategic petroleum reserves to buffer against sudden supply shocks.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Stabilization of Middle Eastern tensions and resolution of trade disputes lead to price stabilization.
- Worst Case: Escalation of conflicts in the Middle East causes significant supply disruptions and price spikes.
- Most Likely: Continued volatility with periodic spikes due to unresolved geopolitical tensions and economic policy shifts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are mentioned in the source text. Key entities include the governments of Israel and Iran, and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regarding biofuel compliance policies.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, geopolitical tensions, energy markets, Middle East conflict, economic policy impact