2024 saw a record-breaking number of dangerously humid days – New Scientist
Published on: 2025-08-14
Intelligence Report: 2024 saw a record-breaking number of dangerously humid days – New Scientist
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
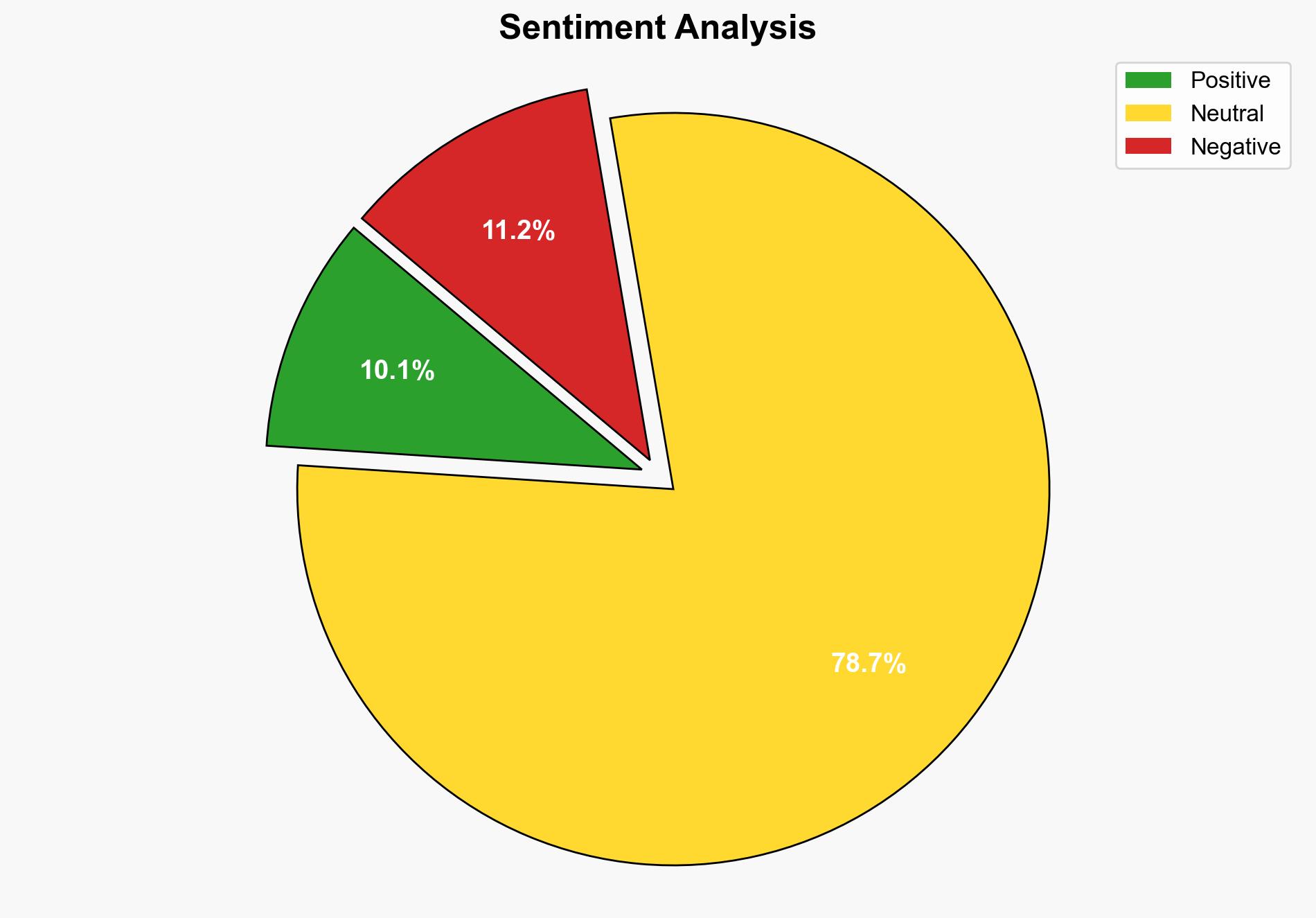
The analysis suggests that the increase in dangerously humid days is primarily driven by climate change, with a high confidence level. This hypothesis is better supported by the data, which aligns with established climate models predicting increased humidity due to global warming. Immediate strategic action is recommended to enhance adaptive measures and mitigate health risks associated with extreme humidity.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis 1**: The record-breaking number of dangerously humid days is a direct consequence of climate change, leading to increased global humidity levels.
2. **Hypothesis 2**: The increase in humid days is due to a combination of natural climate variability and anthropogenic factors unrelated to climate change, such as urbanization and deforestation.
Using the Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is more strongly supported by the data. The correlation between rising temperatures and increased humidity aligns with climate change models. Hypothesis 2 lacks comprehensive evidence linking urbanization or deforestation directly to the observed global humidity trends.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that the data accurately reflects global trends and that climate models are reliable predictors of future conditions.
– **Red Flags**: Potential bias in attributing all changes to climate change without considering regional variations or other contributing factors. The absence of data on urban heat islands or localized weather patterns could skew interpretations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The increase in dangerously humid days poses significant health risks, particularly in vulnerable regions like the Middle East and Southeast Asia. This could lead to increased mortality rates, economic disruptions, and potential migration pressures. Geopolitically, countries may face internal unrest due to resource scarcity and health crises. The psychological impact on populations could also exacerbate tensions and reduce resilience.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance public health infrastructure to manage heat-related illnesses effectively.
- Invest in climate adaptation strategies, such as improved urban planning and green spaces to mitigate heat effects.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Global cooperation leads to effective climate action, reducing future humidity levels.
- Worst Case: Continued inaction exacerbates health crises and economic instability.
- Most Likely: Incremental improvements in adaptation, with ongoing challenges in high-risk regions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Kate Willett is noted for her contributions to the report, providing insights into the health impacts of increased humidity.
7. Thematic Tags
climate change, public health, global security, environmental policy