The evolving CISO role bridging the gap between security and strategy – TechRadar
Published on: 2025-08-25
Intelligence Report: The evolving CISO role bridging the gap between security and strategy – TechRadar
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The role of the Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is evolving from a technical specialist to a strategic business leader, responsible for aligning cybersecurity initiatives with organizational goals. This shift is driven by complex threat landscapes, technological advancements, and increased regulatory pressures. The most supported hypothesis is that CISOs will increasingly integrate cybersecurity into broader business strategies, enhancing organizational resilience. Confidence Level: High. Recommended Action: Organizations should invest in training and resources to support CISOs in this expanded role, ensuring alignment between security and business objectives.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The CISO role will continue to evolve into a strategic leadership position, integrating cybersecurity with business strategy to enhance organizational resilience.
Hypothesis 2: The CISO role will remain primarily technical, with strategic integration limited by organizational resistance and resource constraints.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported due to the increasing complexity of cyber threats and regulatory demands that necessitate a strategic approach. The source text highlights the need for CISOs to engage with executive leadership and shape enterprise resilience, supporting the strategic integration hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions:
– Organizations will prioritize cybersecurity as a strategic component.
– CISOs have or will develop the necessary skills for strategic leadership.
Red Flags:
– Potential cognitive bias in assuming all organizations will adapt to this change.
– Lack of data on organizations resistant to integrating cybersecurity with business strategy.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration of cybersecurity into business strategy could lead to improved resilience against cyber threats, but failure to adapt may result in increased vulnerability. Economic implications include potential cost savings from streamlined security processes. Geopolitically, organizations that fail to adapt may face heightened risks from state-sponsored cyber threats. Psychologically, the shift may increase stress on CISOs as they take on more strategic responsibilities.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Organizations should invest in leadership training for CISOs to enhance strategic capabilities.
- Develop a clear framework for integrating cybersecurity into business strategy.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: CISOs successfully integrate cybersecurity into business strategy, enhancing resilience and reducing risk.
- Worst Case: Organizations fail to adapt, leading to increased vulnerability and potential regulatory penalties.
- Most Likely: Gradual integration with varying success across different organizations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
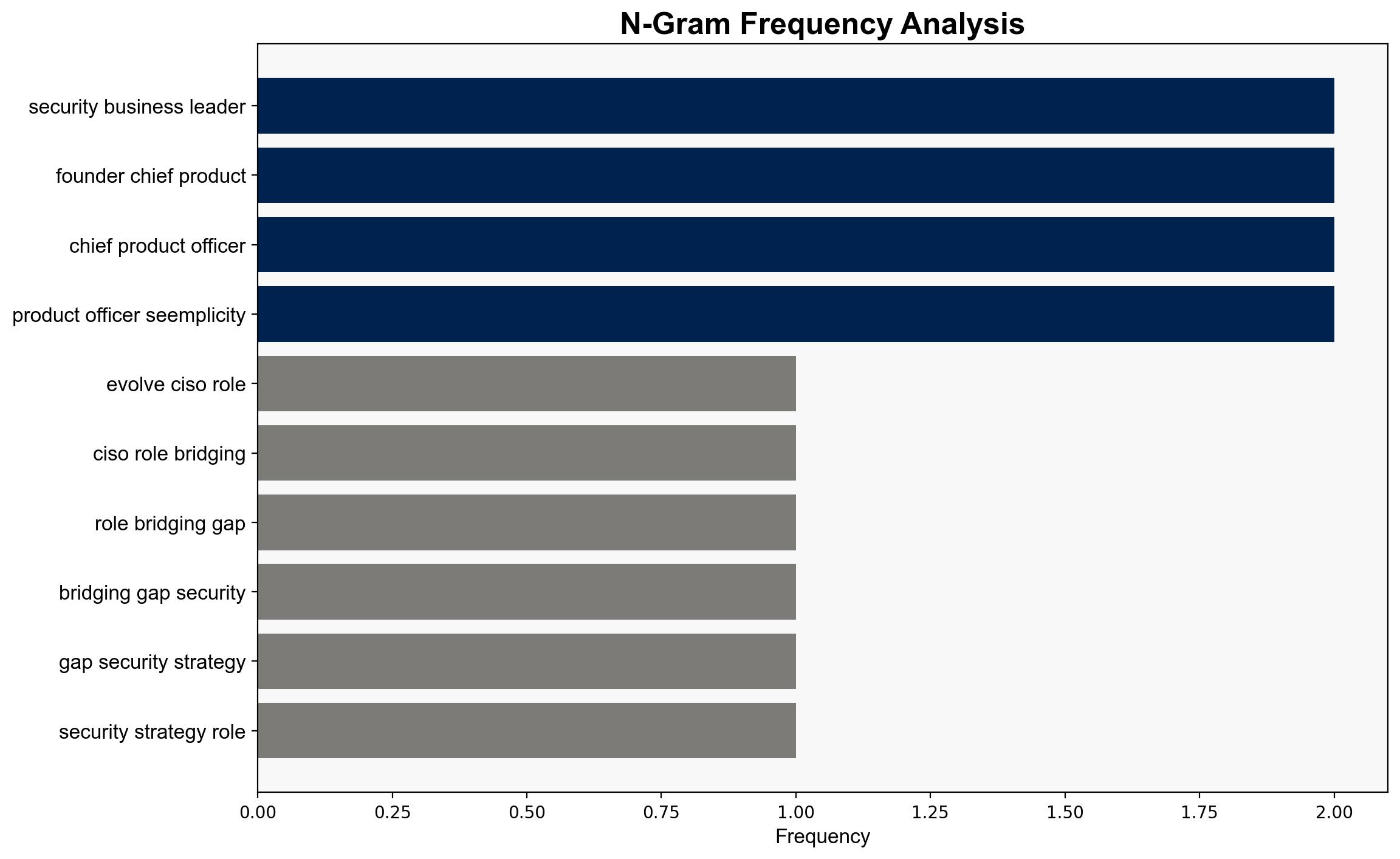
– Seemplicity (mentioned as a company involved in cybersecurity advancements)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus