Invasive parasitic wasp spotted in the US for the first time – Popular Science
Published on: 2025-08-25
Intelligence Report: Invasive parasitic wasp spotted in the US for the first time – Popular Science
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
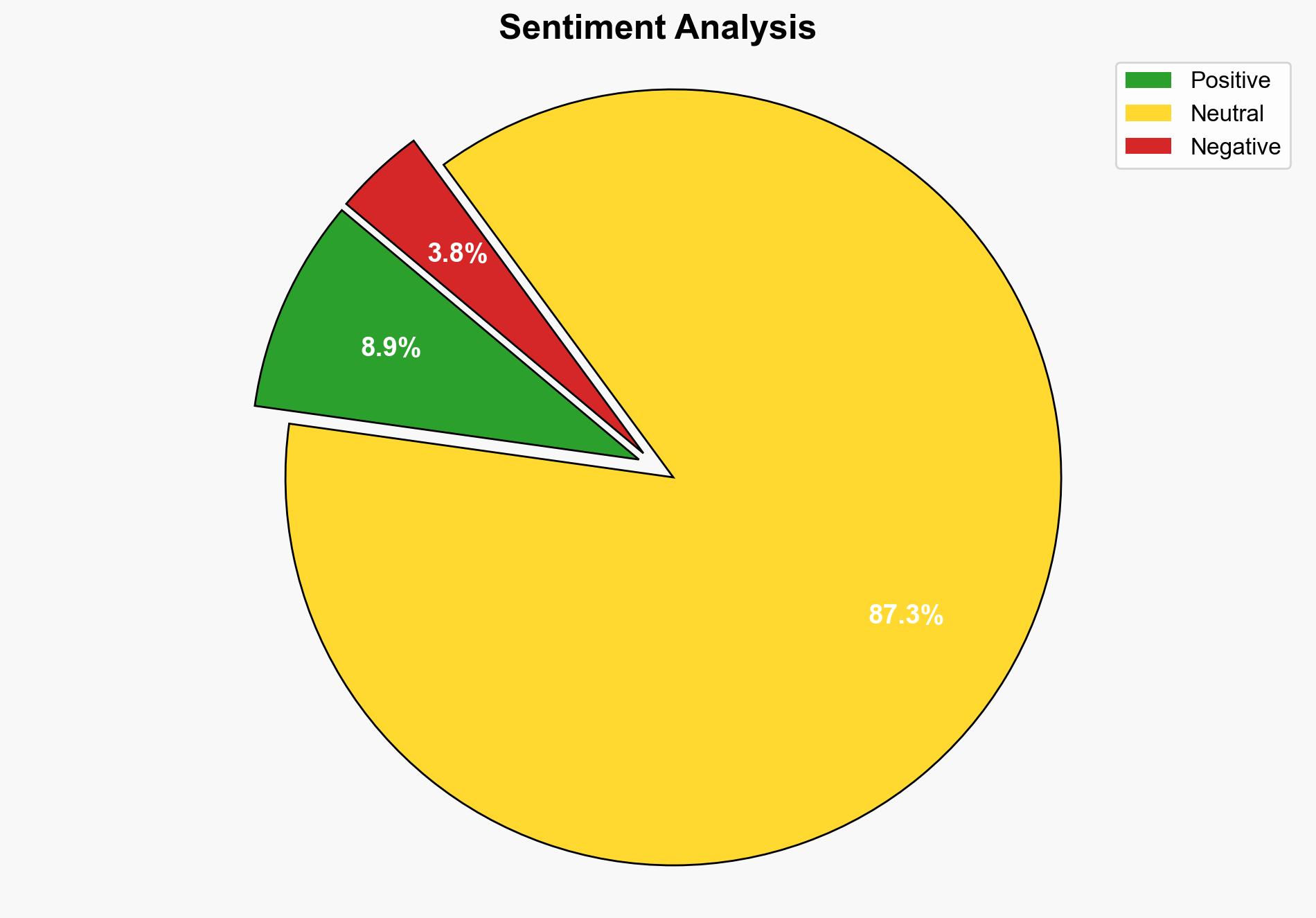
The introduction of the parasitic wasp Bootanomyia dorsalis to North America is confirmed, with potential ecological impacts on native oak gall wasp populations. The most supported hypothesis suggests that the wasp was introduced through human activity, possibly linked to historical plant imports. Confidence in this hypothesis is moderate due to genetic evidence and historical context. Recommended action includes monitoring and research to understand ecological impacts and prevent further introductions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: Bootanomyia dorsalis was introduced to North America through human activity, such as the importation of non-native oak species by European colonists or recent global trade.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The wasp naturally expanded its range to North America due to environmental changes or other natural migration factors.
Using Bayesian Scenario Modeling, Hypothesis A is better supported due to genetic evidence indicating multiple introductions and historical records of plant imports. Hypothesis B lacks direct evidence and is less consistent with the genetic diversity observed.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: Hypothesis A assumes historical plant trade routes facilitated the introduction. Hypothesis B assumes environmental factors could naturally lead to range expansion.
– **Red Flags**: Lack of comprehensive historical data on plant imports and potential biases in genetic sampling. The genetic diversity observed might not fully represent the entire population.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The introduction of B. dorsalis poses ecological risks, potentially disrupting native oak gall wasp populations and their ecological roles. This could lead to broader ecosystem impacts, affecting biodiversity and forest health. If not monitored, it may also set a precedent for other invasive species introductions, increasing ecological vulnerability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Conduct detailed ecological impact assessments to understand the effects on native species and ecosystems.
- Enhance monitoring programs using citizen science platforms like iNaturalist to track the wasp’s spread.
- Develop preventive measures for future introductions, including stricter controls on plant imports.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Effective monitoring and control measures limit ecological impact.
- Worst Case: Unchecked spread leads to significant biodiversity loss and ecosystem disruption.
- Most Likely: Moderate ecological impact with manageable spread through targeted interventions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Kirsten Prior
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, ecological impact, invasive species, biodiversity, environmental monitoring