Opinion Rice Can Feed The World – Even With Fewer Farmers – Ndtvprofit.com
Published on: 2025-08-27
Intelligence Report: Opinion Rice Can Feed The World – Even With Fewer Farmers – Ndtvprofit.com
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
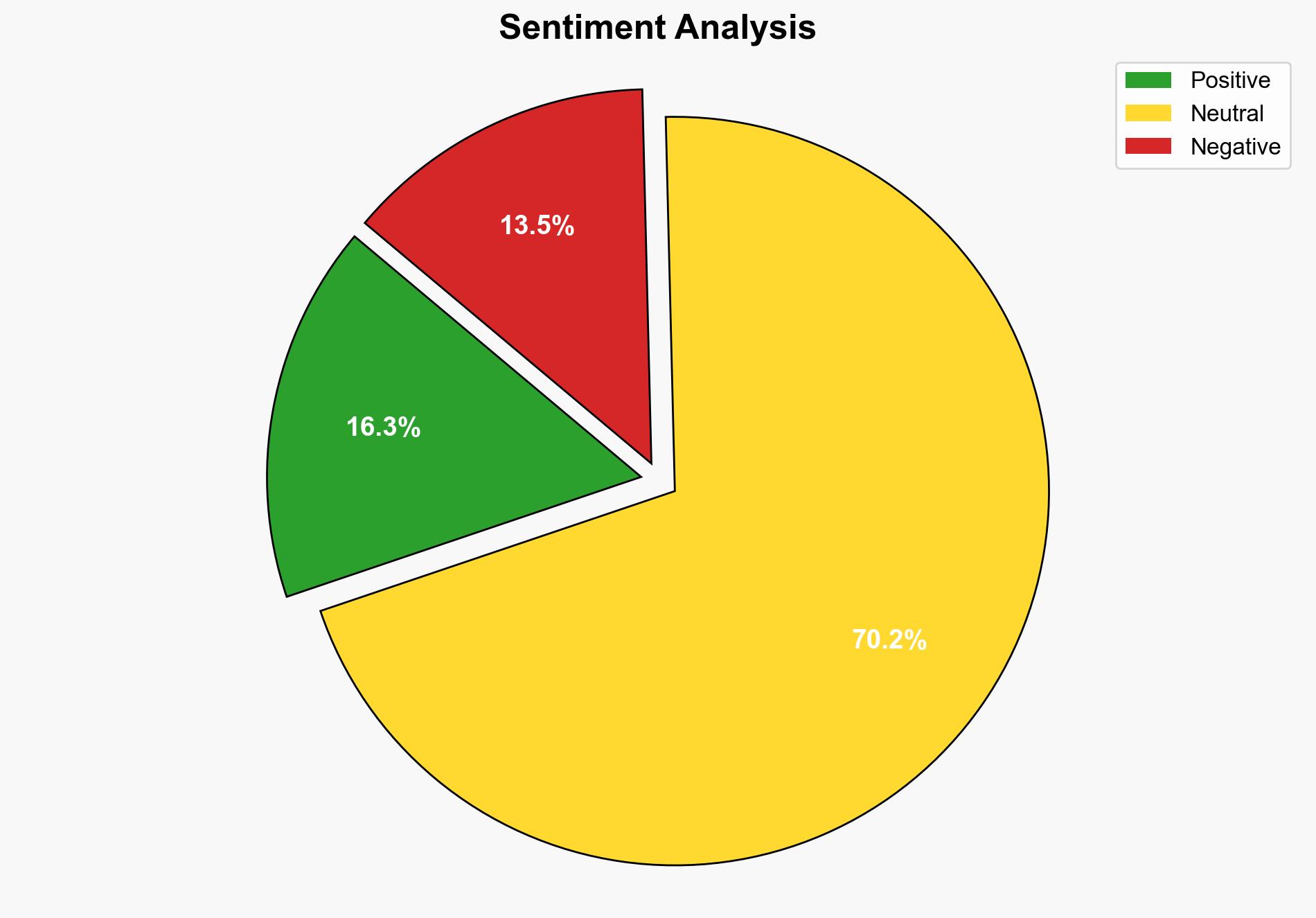
The most supported hypothesis is that modern agricultural methods and technological advances can significantly enhance rice production, potentially alleviating food shortages despite a reduction in the number of farmers. Confidence level: Moderate. The recommended action is to promote investment in agricultural technology and infrastructure to sustain and increase rice yields globally.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis 1**: Technological advancements and modern farming methods will enable rice production to meet global food demands, even with fewer farmers. This is supported by evidence of increased yields due to improved agricultural practices and technology.
2. **Hypothesis 2**: Despite technological advancements, climate change and socio-political factors will hinder rice production, leading to persistent food shortages. This hypothesis considers the impact of climate variability and political instability on agricultural productivity.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**:
– Technological innovations will continue to be accessible and affordable for farmers.
– Governments will support and invest in modern agricultural practices.
– **Red Flags**:
– Potential overreliance on technology without addressing environmental impacts.
– Political resistance to genetically modified organisms (GMOs) could limit technological adoption.
– Climate change effects may be underestimated in their impact on agricultural productivity.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Economic**: Increased rice production could stabilize food prices, reducing hunger and poverty in vulnerable regions.
– **Geopolitical**: Nations heavily reliant on rice imports may experience reduced dependency, altering trade dynamics.
– **Environmental**: Overuse of technology and GMOs might lead to ecological imbalances if not managed sustainably.
– **Socio-political**: Resistance to modern agricultural methods could lead to social unrest, especially if food security is threatened.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Encourage public and private investment in agricultural technology and infrastructure.
- Promote international cooperation to address climate change impacts on agriculture.
- Develop educational programs for farmers on sustainable practices and technology adoption.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best: Global rice production meets demand, stabilizing food prices.
- Worst: Climate change and political instability severely disrupt production, leading to food crises.
- Most Likely: Moderate improvements in production with regional disparities due to varying adoption rates of technology.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– No specific individuals mentioned. Entities include governments, agricultural technology firms, and international organizations focused on food security.
7. Thematic Tags
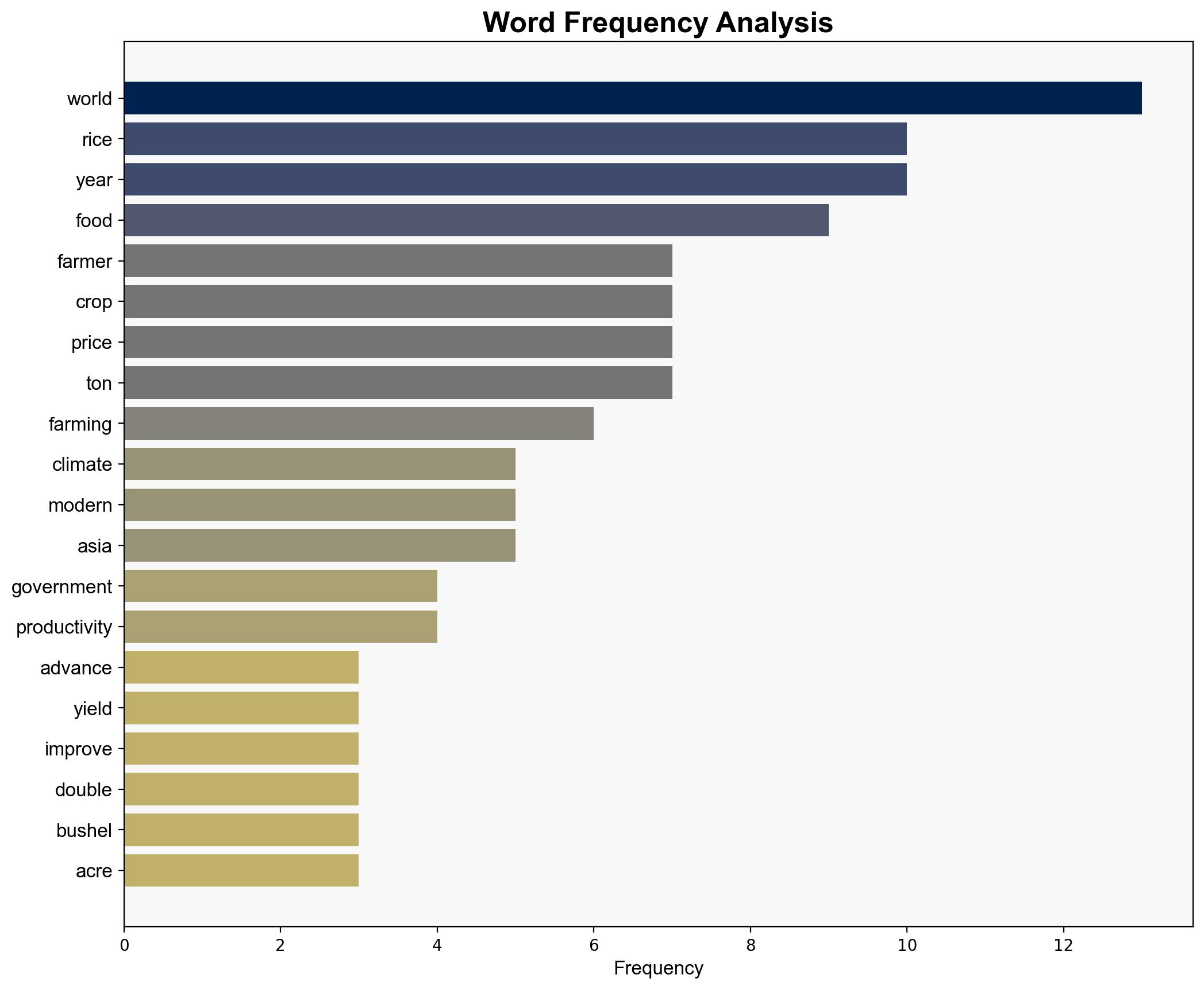
food security, agricultural technology, climate change, geopolitical stability