US probes malware email targeting trade talks with China Report – The Times of India
Published on: 2025-09-08
Intelligence Report: US probes malware email targeting trade talks with China Report – The Times of India
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
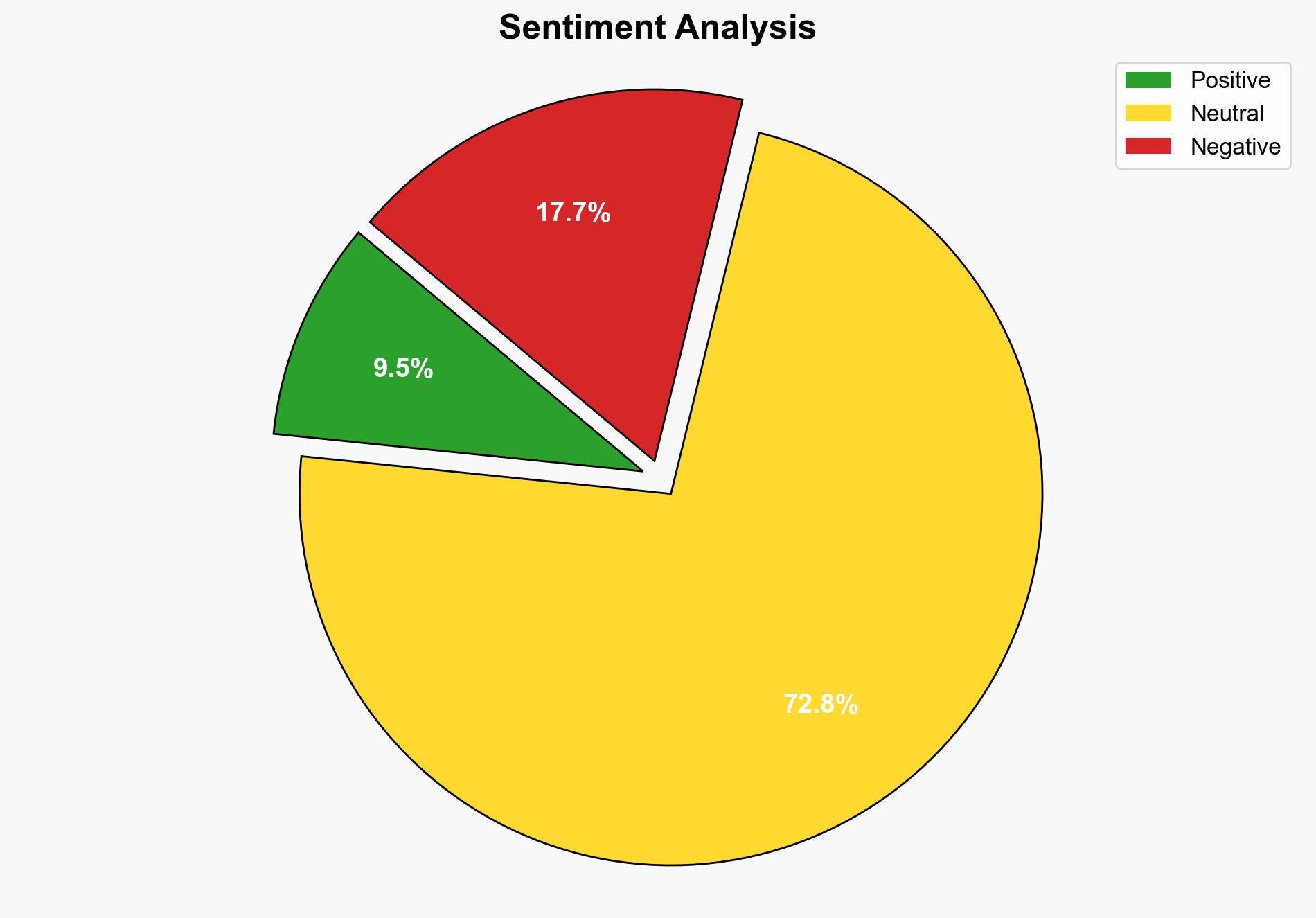
The investigation into malware-laden emails allegedly linked to Chinese intelligence aims to gain insights into US-China trade talks. The most supported hypothesis is that this is a state-sponsored cyber espionage effort by China, given the strategic importance of the trade discussions. Confidence level is moderate due to the complexity of attribution in cyber operations. Recommended action includes enhancing cybersecurity protocols and diplomatic engagement to address cyber threats.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **State-Sponsored Espionage Hypothesis**: The malware email campaign is a deliberate effort by Chinese intelligence to gather information on US trade strategies and recommendations, leveraging cyber capabilities to gain a strategic advantage in ongoing trade negotiations.
2. **False Flag Operation Hypothesis**: The operation could be a false flag by another actor aiming to frame China, thereby exacerbating US-China tensions and diverting attention from their own activities.
Using Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH), the state-sponsored espionage hypothesis is better supported due to the alignment of the operation’s objectives with China’s strategic interests and past behavior patterns in cyber activities.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that the malware’s sophistication and target selection are indicative of state sponsorship. Another assumption is that the timing aligns with strategic interests in trade negotiations.
– **Red Flags**: The difficulty in attributing cyber operations definitively to a state actor is a significant red flag. The possibility of misattribution due to sophisticated obfuscation techniques should be considered.
– **Blind Spots**: Lack of concrete evidence linking the operation directly to Chinese state entities remains a blind spot.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Economic Implications**: Successful espionage could undermine US negotiating positions, affecting trade outcomes and economic stability.
– **Cybersecurity Risks**: This incident highlights vulnerabilities in communication channels used by policymakers and trade negotiators.
– **Geopolitical Risks**: Escalation of cyber tensions could lead to broader geopolitical conflicts, affecting international relations and alliances.
– **Psychological Impact**: The perception of vulnerability may erode trust in digital communications, impacting decision-making processes.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance cybersecurity measures for government and associated entities, focusing on email security and threat detection capabilities.
- Engage in diplomatic dialogues with China to address cyber espionage concerns and establish norms for state behavior in cyberspace.
- Scenario Projections:
- **Best Case**: Improved cybersecurity deters future attacks, and diplomatic efforts lead to a reduction in cyber tensions.
- **Worst Case**: Continued cyber operations exacerbate US-China tensions, leading to retaliatory actions and economic disruptions.
- **Most Likely**: Incremental improvements in cybersecurity with ongoing low-level cyber skirmishes between the US and China.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– John Moolenaar
– FBI
– Chinese Embassy in Washington
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, counter-terrorism, regional focus