Hackers Wipe Out Ksh159 Billion From Kenyan Banks In 2024 – Thekenyatimes.com
Published on: 2025-09-10
Intelligence Report: Hackers Wipe Out Ksh159 Billion From Kenyan Banks In 2024 – Thekenyatimes.com
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
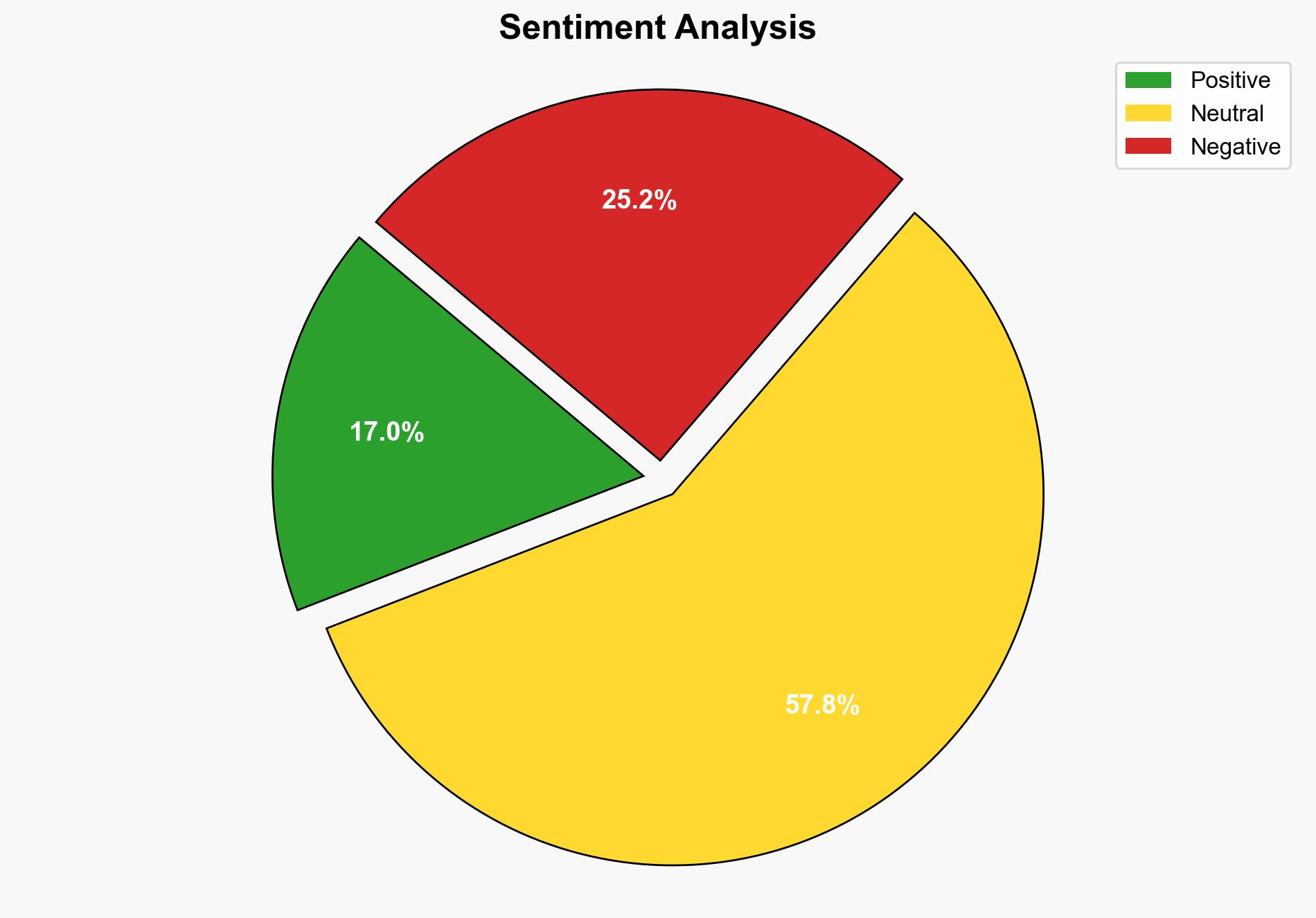
The most supported hypothesis is that the significant financial loss experienced by Kenyan banks is primarily due to increased sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks, exacerbated by inadequate cybersecurity measures within the financial sector. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action includes enhancing cybersecurity protocols and adopting advanced threat detection technologies.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The financial losses are primarily due to a significant increase in the sophistication and frequency of cyberattacks targeting Kenyan banks, exploiting existing vulnerabilities in their cybersecurity infrastructure.
Hypothesis 2: The reported losses are exaggerated or misreported, possibly due to internal mismanagement or fraudulent activities within the banks, rather than external cyber threats.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions:
– Hypothesis 1 assumes that the cyberattacks are indeed sophisticated and that banks have not adequately updated their cybersecurity measures.
– Hypothesis 2 assumes potential internal collusion or misreporting of financial data.
Red Flags:
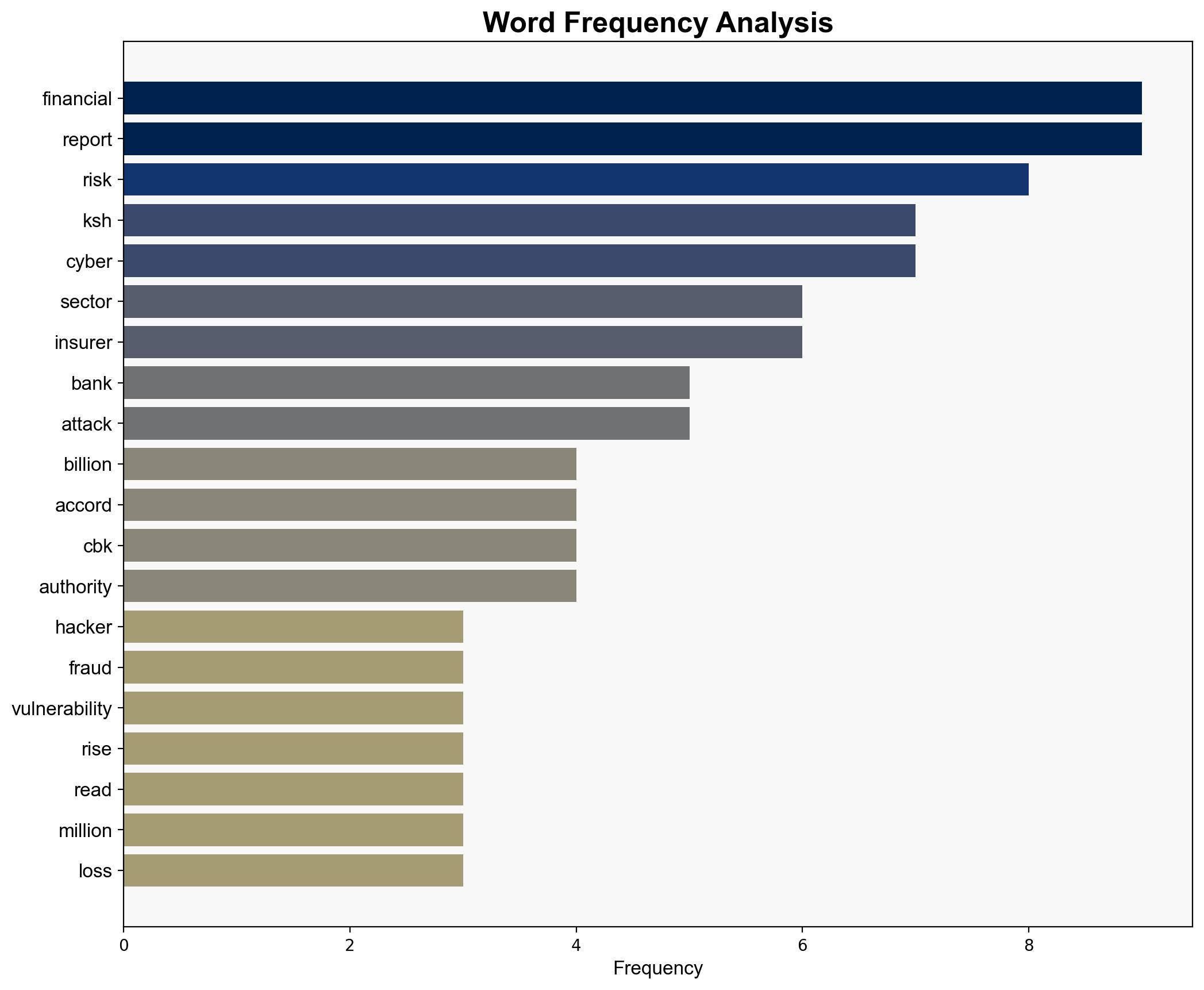
– Lack of detailed evidence on the specific nature of the cyberattacks.
– Absence of independent verification of the reported financial losses.
– Potential bias in the source report, which may sensationalize the issue.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued vulnerability of Kenyan banks to cyberattacks could lead to further financial instability, loss of investor confidence, and potential economic repercussions. If internal mismanagement is a factor, it could indicate systemic issues within the banking sector, requiring regulatory intervention. The geopolitical risk includes potential exploitation by hostile actors to destabilize the region.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance cybersecurity frameworks by adopting AI-driven analytics and regular vulnerability assessments.
- Implement mandatory cybersecurity training for bank employees to mitigate human error.
- Conduct independent audits to verify the accuracy of reported losses and identify internal weaknesses.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Rapid implementation of advanced cybersecurity measures reduces future losses.
- Worst Case: Continued cyberattacks lead to further financial instability and loss of public trust.
- Most Likely: Gradual improvement in cybersecurity reduces the frequency of successful attacks, but some vulnerabilities remain.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Central Bank of Kenya (CBK)
– Capital Market Authority
– Insurance Regulatory Authority
– Retirement Benefit Authority
– Sacco Society Regulatory Authority
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, financial stability, regional focus