EU Member States agree to extend sanctions against Russia – Globalsecurity.org
Published on: 2025-09-13
Intelligence Report: EU Member States agree to extend sanctions against Russia – Globalsecurity.org
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The EU’s decision to extend sanctions against Russia reflects a continued commitment to a unified stance on Ukraine’s sovereignty. The most supported hypothesis suggests that the EU aims to maintain pressure on Russia while managing internal political dynamics. Confidence in this assessment is moderate due to potential internal EU disagreements and external geopolitical pressures. Recommended action includes reinforcing diplomatic efforts to ensure EU unity and preparing for potential Russian countermeasures.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The EU’s extension of sanctions is primarily driven by a genuine commitment to Ukraine’s territorial integrity and a strategic effort to deter Russian aggression.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The extension of sanctions is influenced by internal EU political dynamics, with member states using the sanctions as leverage for other political negotiations within the EU framework.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis A is better supported by the unanimous decision and the alignment with Latvia’s strong advocacy for sanctions. However, Hypothesis B cannot be dismissed due to the complexity of EU internal politics and the need for consensus.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that all EU member states are equally committed to the sanctions based on shared values rather than political expediency.
– **Red Flags**: The unanimity requirement could mask underlying dissent among member states. The lack of specific mention of dissenting voices or alternative proposals suggests potential suppression of internal disagreements.
– **Blind Spots**: The potential impact of external pressures, such as economic dependencies on Russia, is not addressed in the source text.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The extension of sanctions could lead to several strategic risks:
– **Economic**: Potential retaliatory measures by Russia affecting EU economies, particularly energy supplies.
– **Geopolitical**: Escalation of tensions between the EU and Russia, potentially impacting global diplomatic relations.
– **Cyber**: Increased likelihood of cyberattacks from Russian entities targeting EU infrastructure.
– **Psychological**: Heightened public concern within EU states about energy security and economic stability.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance diplomatic engagement with EU member states to ensure continued consensus and address any underlying dissent.
- Prepare contingency plans for potential Russian economic retaliation, particularly in the energy sector.
- Strengthen cybersecurity measures across the EU to mitigate potential Russian cyber threats.
- Scenario Projections:
- **Best Case**: Continued EU unity leads to successful deterrence of Russian aggression.
- **Worst Case**: Internal EU disagreements weaken the sanctions regime, emboldening Russia.
- **Most Likely**: Sanctions remain in place with periodic reviews and adjustments, maintaining a status quo of tension.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Russian President
– Russian Prime Minister
– Members of the Russian government and military
– Latvian Ministry of Foreign Affairs
7. Thematic Tags
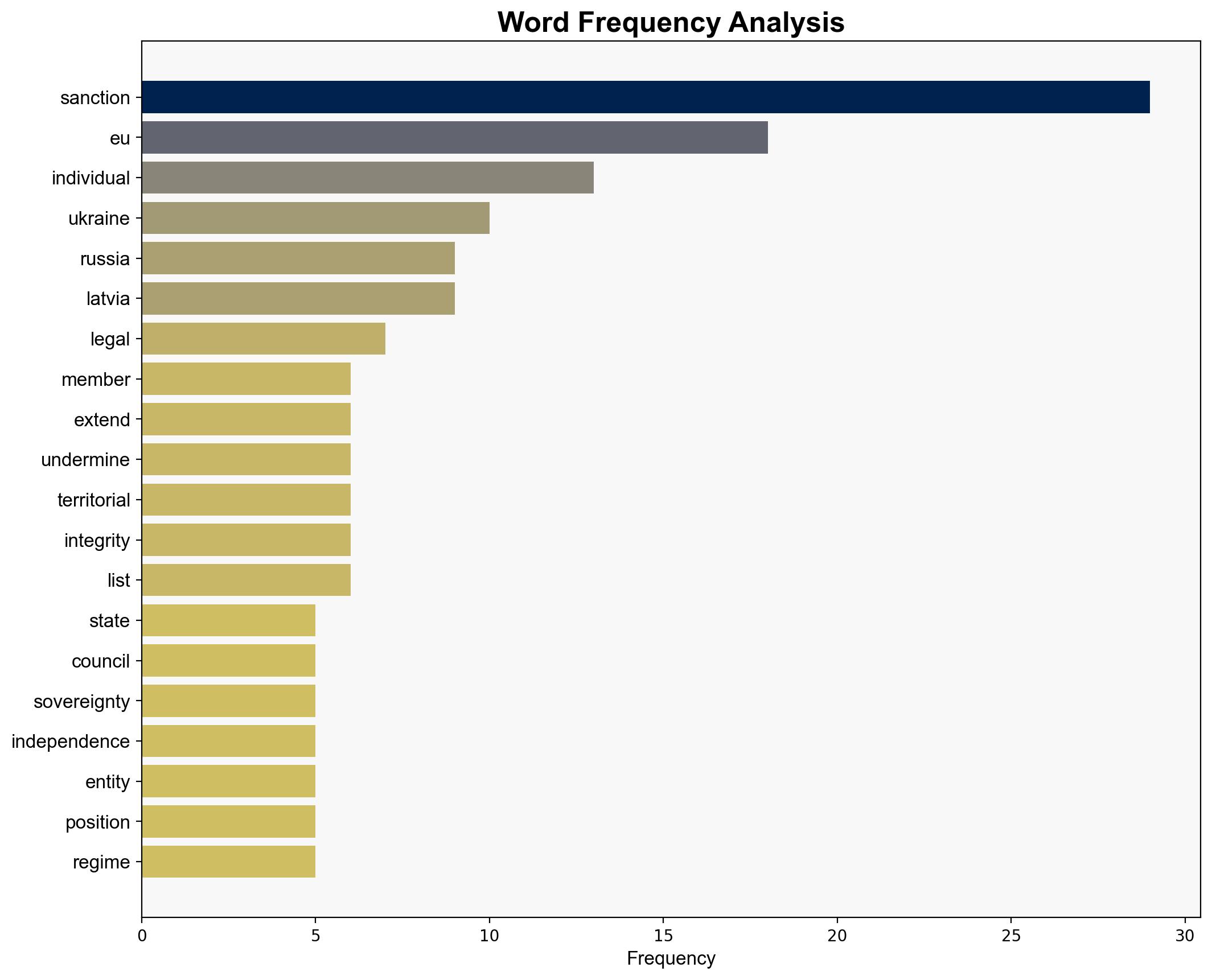
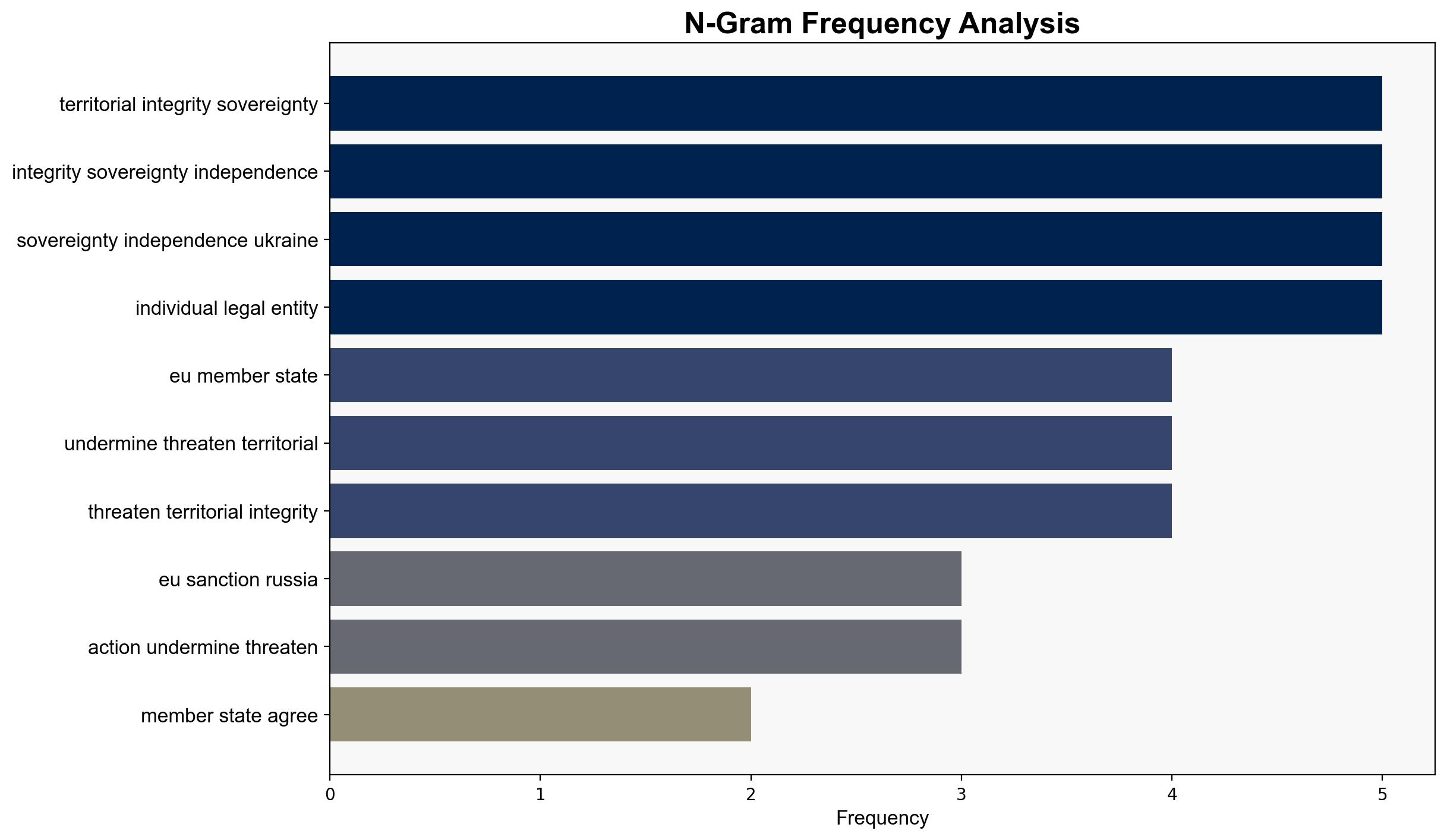
national security threats, geopolitical strategy, EU-Russia relations, sanctions policy