Data breach exposes 273 lakh bank records – The Times of India
Published on: 2025-09-27
Intelligence Report: Data breach exposes 273 lakh bank records – The Times of India
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The data breach involving 273 lakh bank records, primarily affecting Aye Finance, suggests a significant cybersecurity lapse. The most supported hypothesis is that the breach resulted from a misconfiguration in the cloud server management by Aye Finance or its vendors. The recommended action is to enhance cybersecurity protocols and conduct a comprehensive audit of cloud configurations. Confidence level: Moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The breach was due to a misconfiguration in Aye Finance’s cloud server management, leading to the exposure of sensitive data.
Hypothesis 2: The breach was orchestrated by a malicious insider or external actor exploiting vulnerabilities within the National Automated Clearing House (NACH) system or its integration partners.
Using Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported due to the evidence of misconfiguration and delayed response by Aye Finance. Hypothesis 2 lacks direct evidence of malicious intent or exploitation by an insider or external actor.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
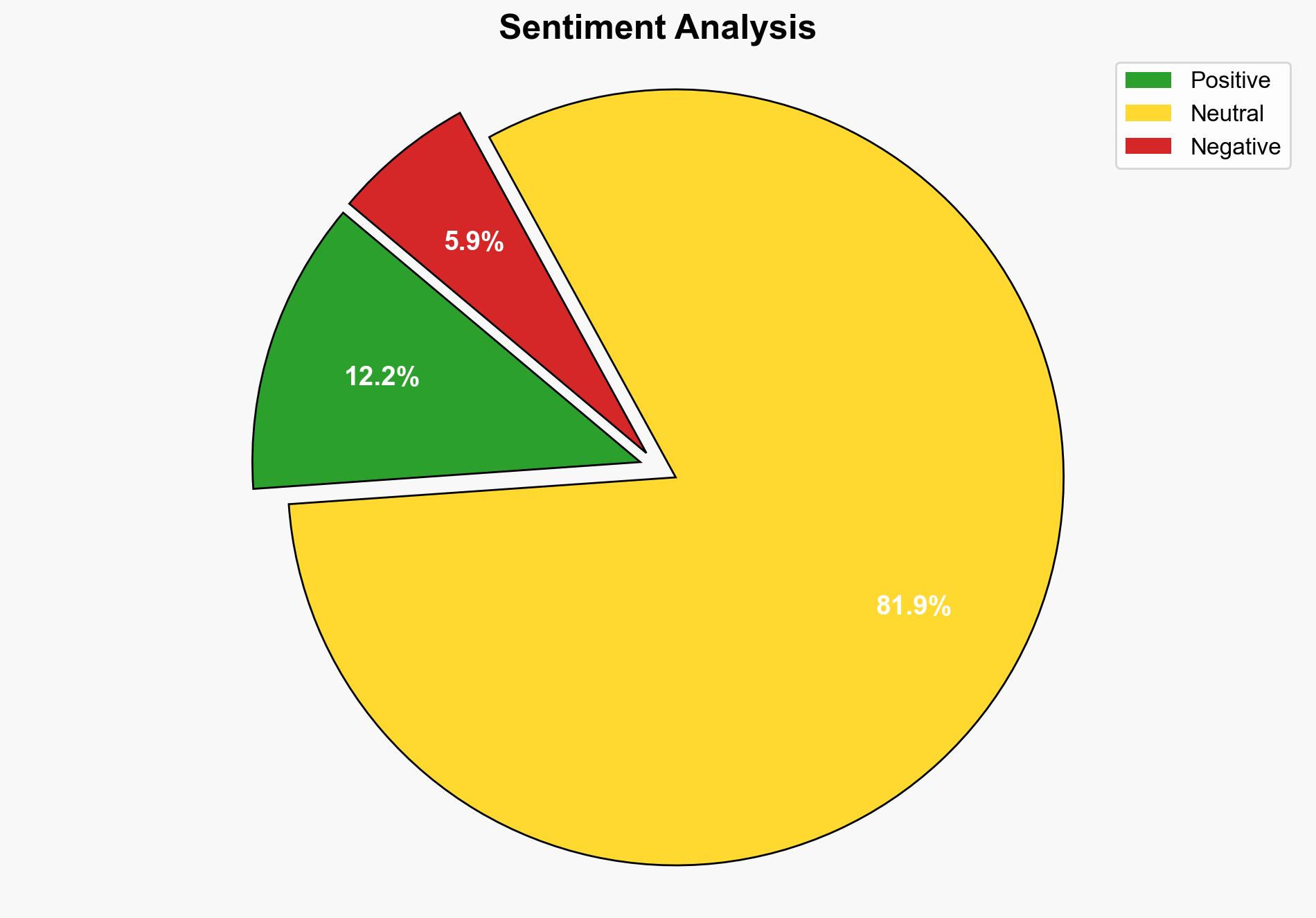
Assumptions include the belief that Aye Finance’s cloud management practices were inadequate and that the NACH system is secure. Red flags include the delayed response to the breach and the potential underreporting of other affected entities. The lack of immediate action by CERT-IN raises concerns about the responsiveness of national cybersecurity measures.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The breach poses significant risks to financial institutions’ reputations and consumer trust. It highlights vulnerabilities in cloud-based data management, potentially leading to stricter regulatory scrutiny. Economically, affected entities may face financial penalties and increased operational costs. Cybersecurity risks could escalate if similar vulnerabilities are exploited by malicious actors.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Conduct a thorough audit of cloud configurations and security protocols across all affected entities.
- Enhance collaboration between financial institutions and cybersecurity agencies to improve incident response times.
- Scenario-based projections:
- Best Case: Rapid containment and resolution of the breach, leading to improved cybersecurity measures.
- Worst Case: Further exploitation of vulnerabilities, resulting in additional breaches and financial losses.
- Most Likely: Gradual implementation of improved security protocols with moderate regulatory intervention.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Aye Finance
– UpGuard
– National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI)
– CERT-IN
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, cybersecurity, financial sector vulnerabilities, data protection