Haiti demands a new international force and reparations from France – Globalsecurity.org
Published on: 2025-09-29
Intelligence Report: Haiti demands a new international force and reparations from France – Globalsecurity.org
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
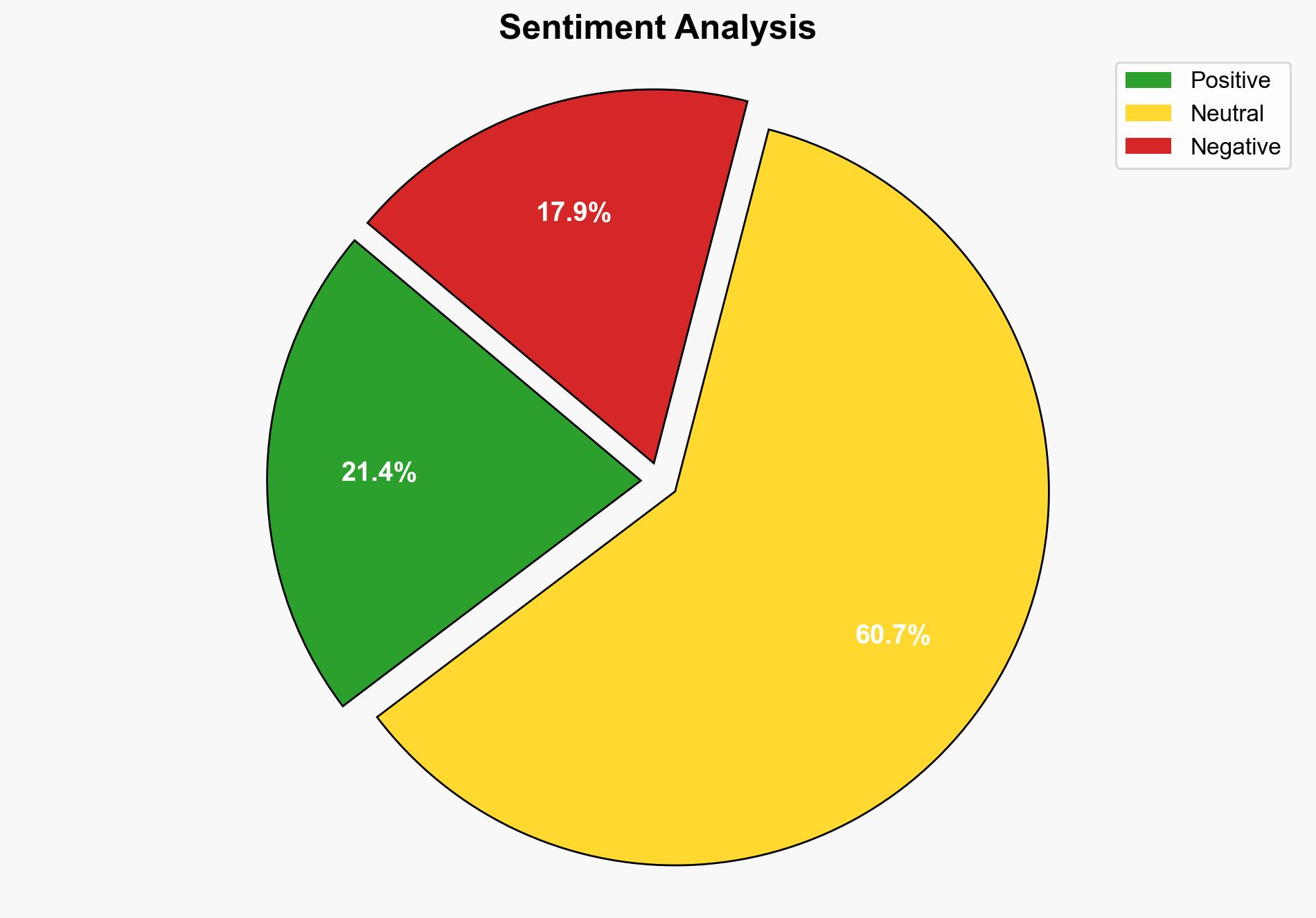
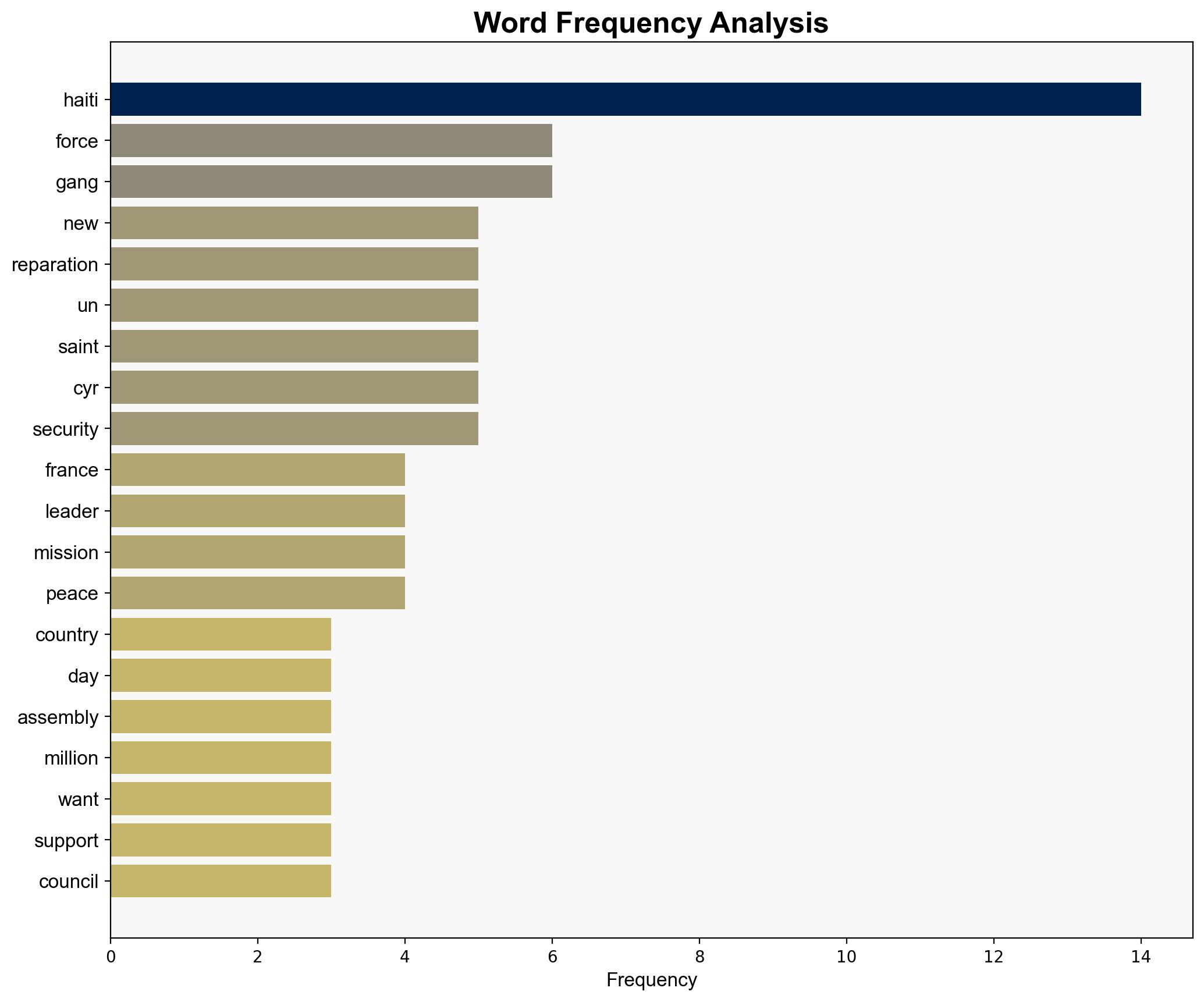
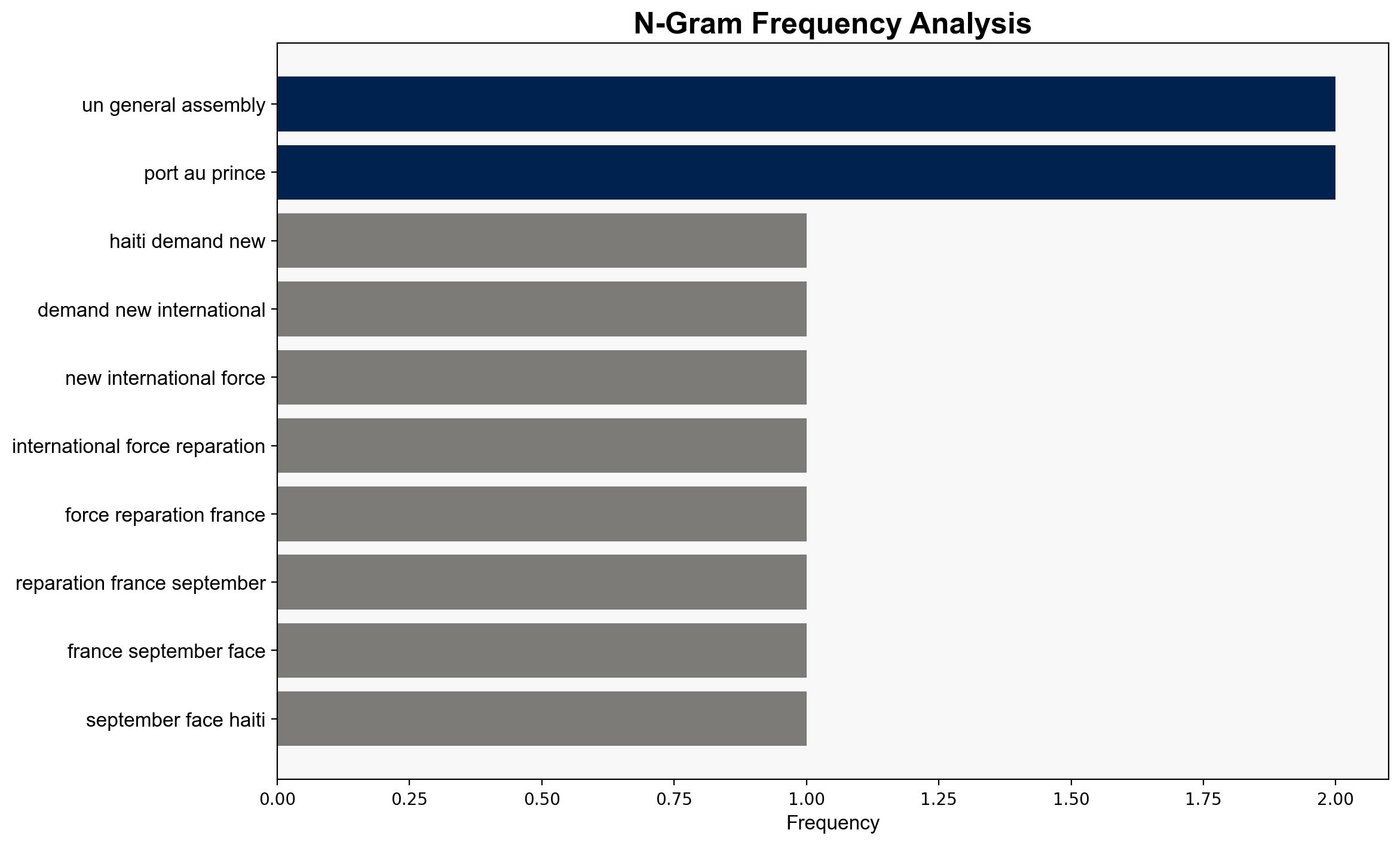
Haiti’s request for an international force and reparations from France highlights a complex interplay of security, historical grievances, and political instability. The most supported hypothesis suggests that Haiti’s demands are primarily driven by immediate security needs and historical justice, but there is also a strategic element aimed at gaining international leverage. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Support the establishment of a robust international security force under a clear mandate, while facilitating dialogue on historical grievances to prevent further destabilization.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Security-Driven Hypothesis**: Haiti’s primary motivation is to address the immediate security crisis caused by armed gangs and political instability. The demand for reparations is secondary, serving as a long-standing grievance that adds moral weight to their international appeal.
2. **Strategic Leverage Hypothesis**: Haiti is using the security crisis and historical grievances as leverage to gain broader international support and concessions, including financial aid and political backing, beyond immediate security needs.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: The assumption that international intervention will effectively stabilize Haiti may overlook the complexity of local dynamics and historical precedents of intervention failures.
– **Red Flags**: The reliance on voluntary contributions for the multinational security support mission (MSS) could lead to insufficient resources and commitment. The potential for political manipulation of the reparations demand could obscure genuine grievances.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Security Vacuum**: Failure to establish a new international force could lead to a security vacuum, exacerbating violence and instability.
– **Geopolitical Tensions**: The demand for reparations could strain Haiti-France relations and influence broader discussions on colonial reparations, potentially affecting international alliances.
– **Economic Impact**: Prolonged instability could deter investment and exacerbate economic decline, increasing humanitarian needs and migration pressures.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Support the creation of a well-funded and clearly mandated international security force to stabilize Haiti.
- Facilitate international dialogue on historical grievances to address reparations demands constructively.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Successful stabilization leads to credible elections and gradual economic recovery.
- Worst Case: Security vacuum leads to increased violence, humanitarian crisis, and regional instability.
- Most Likely: Partial stabilization with ongoing challenges in governance and economic recovery.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Laurent Saint-Cyr: Transitional leader of Haiti.
– United Nations Security Council
– Caribbean Community (CARICOM)
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, geopolitical stability, historical grievances, international intervention