Chinas Commerce Ministry to Trump Rare-Earth Export Curbs Are Not Bans – CoinDesk
Published on: 2025-10-12
Intelligence Report: China’s Commerce Ministry to Trump Rare-Earth Export Curbs Are Not Bans – CoinDesk
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
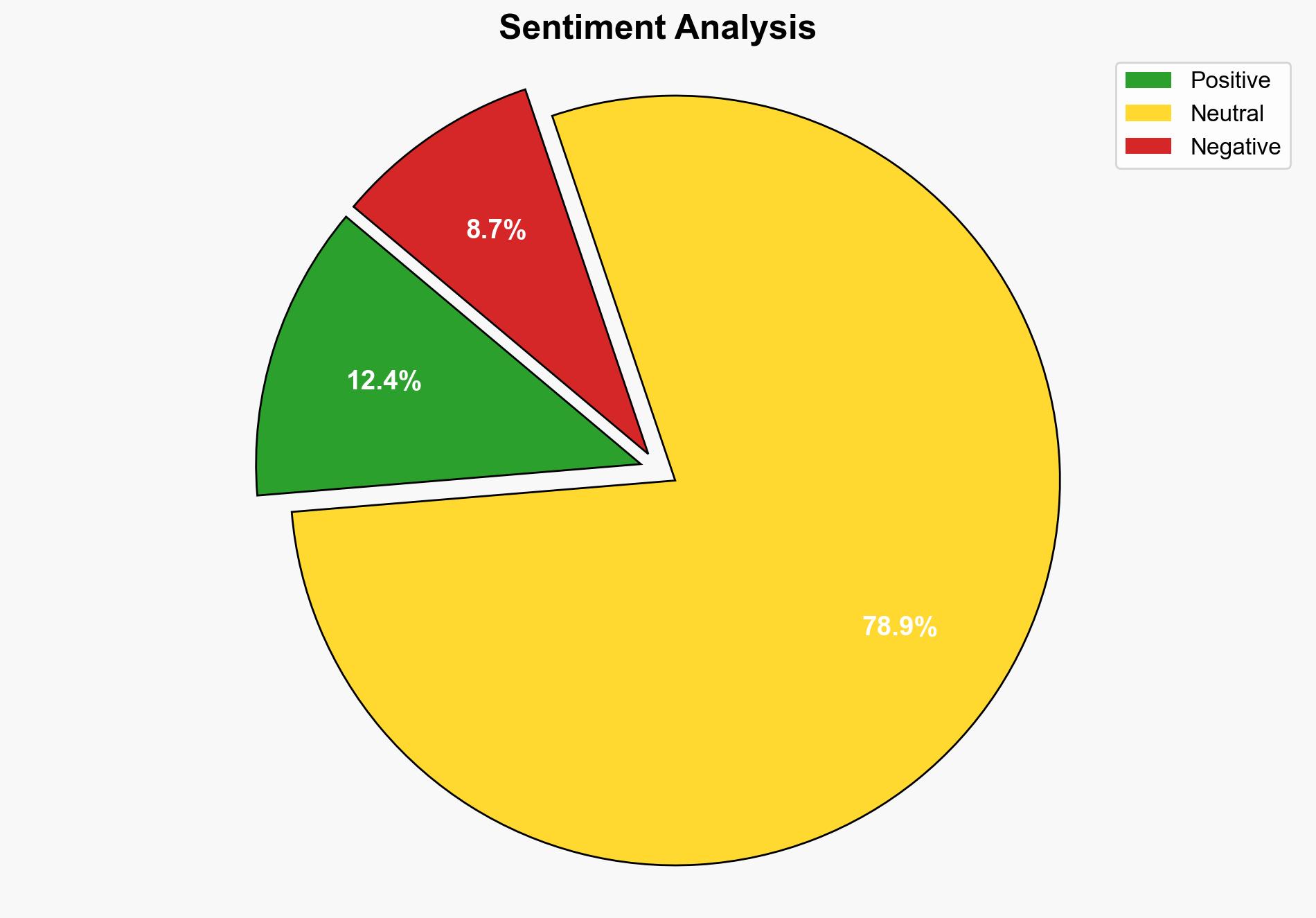
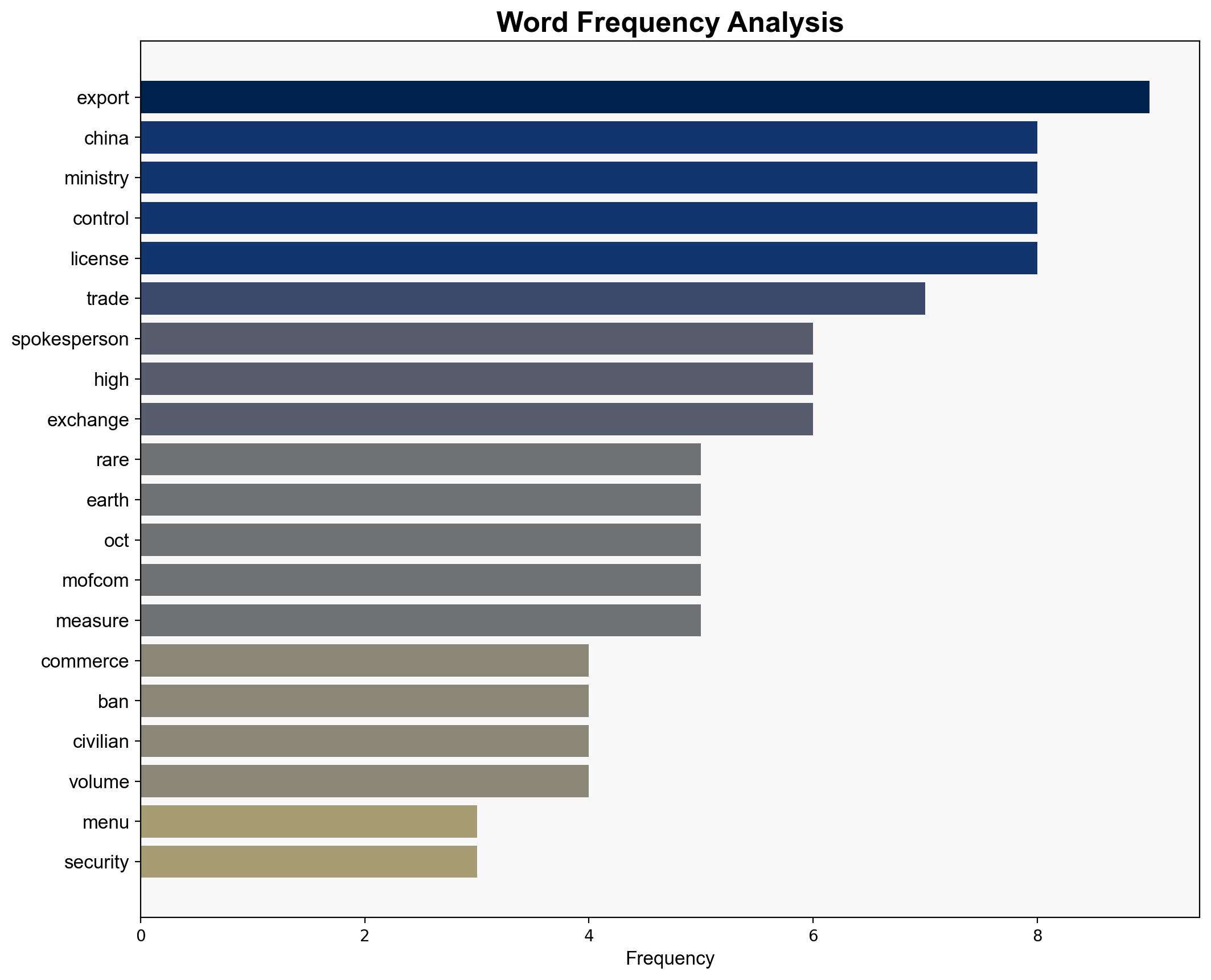
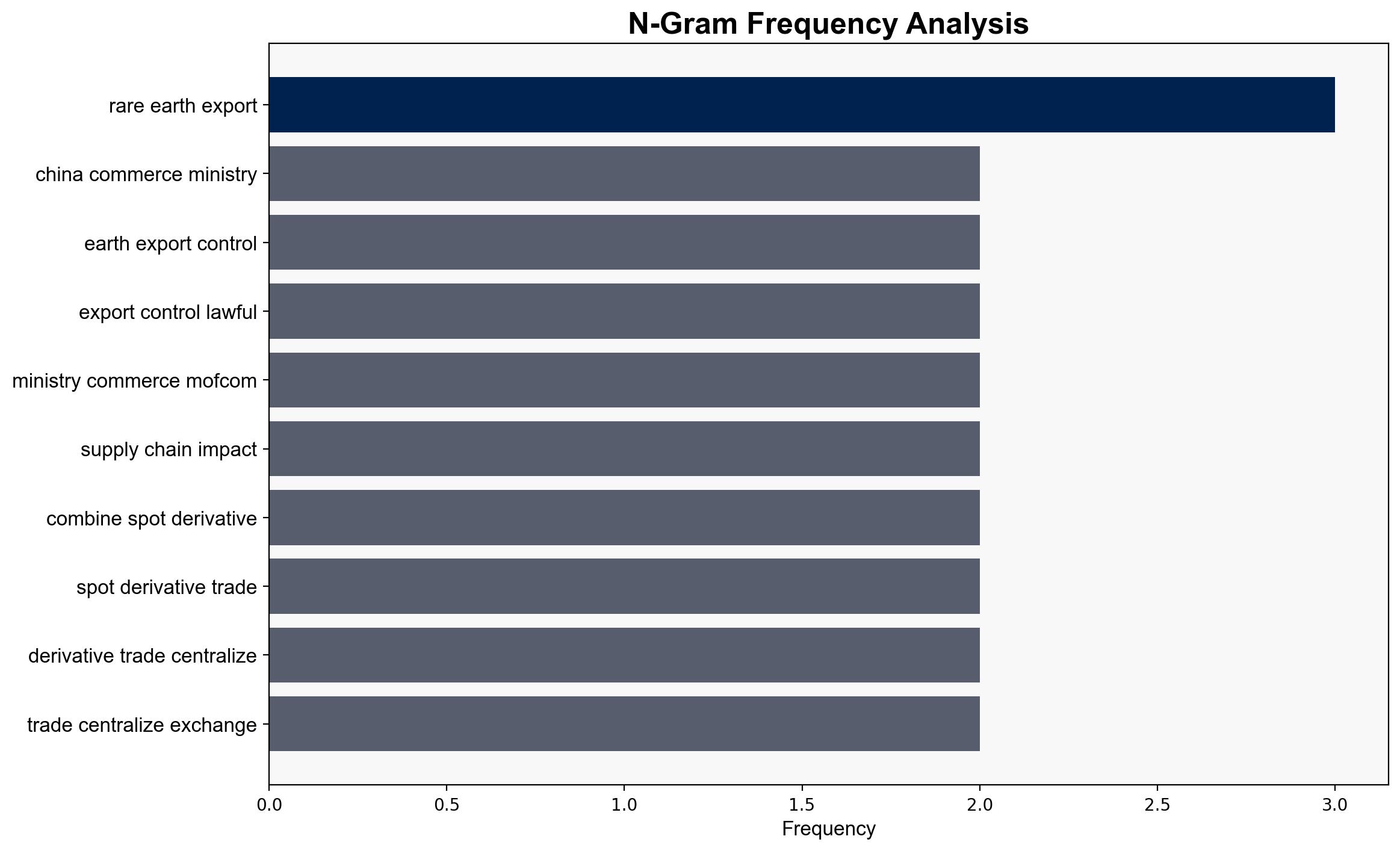
China’s recent rare-earth export controls are framed as lawful national security measures rather than outright bans, with potential limited impact on global supply chains. The most supported hypothesis is that China aims to refine its export control system to maintain leverage in trade negotiations while avoiding significant economic disruption. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action is to monitor China’s licensing processes and engage in diplomatic channels to mitigate potential trade tensions.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: China’s export controls are primarily a strategic maneuver to strengthen its negotiating position with the U.S. by demonstrating its capacity to influence critical supply chains without causing immediate disruption.
Hypothesis 2: The controls are a genuine effort to enhance national security by regulating the export of materials with military applications, with economic impacts being a secondary consideration.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis 1 is better supported due to China’s emphasis on lawful measures, the issuance of licenses for civilian trade, and the explicit mention of maintaining supply chain stability.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions include China’s willingness to issue licenses for civilian use and the expectation of limited supply chain impact. Red flags involve potential underestimation of the control’s economic impact and the risk of misinterpretation by international stakeholders. The lack of detailed criteria for license issuance is a blind spot.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The strategic risk lies in potential escalation of trade tensions if the U.S. perceives these controls as aggressive. Economically, disruptions could affect sectors reliant on rare-earth elements, such as technology and defense. Geopolitically, this move could prompt other nations to seek alternative suppliers, impacting China’s market dominance.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage in diplomatic discussions to clarify the scope and intent of China’s export controls.
- Monitor the issuance of licenses and assess impacts on specific industries.
- Scenario Projections:
- Best Case: Controls lead to improved trade negotiations without significant supply chain disruption.
- Worst Case: Controls escalate into broader trade conflicts, affecting global markets.
- Most Likely: Controls serve as a bargaining tool with manageable economic impacts.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
China’s Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM), U.S. administration under Donald Trump, and stakeholders in the rare-earth supply chain.
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, trade negotiations, supply chain management, geopolitical strategy