‘No other option’ Future of peacekeeping roles in Gaza – RTE
Published on: 2025-10-15
Intelligence Report: ‘No other option’ Future of peacekeeping roles in Gaza – RTE
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
The establishment of an international stabilization force (ISF) in Gaza is a critical component of a proposed peace plan, but it faces significant challenges. The most supported hypothesis suggests that while international efforts, including those from Ireland, are geared towards establishing this force, local resistance and geopolitical complexities may hinder its success. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action includes diplomatic engagement with regional stakeholders and preparation for potential operational challenges.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The ISF will be successfully established in Gaza, leading to stabilization and a reduction in conflict. This hypothesis is supported by international backing, including efforts from France, Germany, and the Trump administration, as well as Ireland’s experience in peacekeeping missions.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The ISF will face significant resistance from local entities such as Hamas, leading to a failure in achieving long-term stabilization. This hypothesis considers the entrenched positions of local factions and the complexities of dismantling existing military infrastructures.
Using ACH 2.0, Hypothesis B is better supported due to the historical challenges of peacekeeping in volatile regions and the current geopolitical tensions in Gaza.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that international support will be consistent and that local entities will eventually cooperate.
– **Red Flags**: The potential for local resistance, particularly from Hamas, is a significant red flag. The lack of a clear mandate and the possibility of insufficient resources and capabilities are also concerning.
– **Blind Spots**: The impact of regional actors such as Egypt and Israel on the peacekeeping mission is not fully addressed.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Geopolitical Risks**: The involvement of multiple international actors could lead to conflicting interests, complicating the mission.
– **Operational Risks**: The need for heavy protection and advanced surveillance capabilities highlights potential operational challenges.
– **Escalation Scenarios**: Failure to establish the ISF could lead to increased violence and instability in the region, with broader implications for Middle Eastern geopolitics.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Engage in diplomatic efforts with regional stakeholders to build consensus and support for the ISF.
- Prepare for operational challenges by ensuring adequate resources and capabilities, including drone surveillance and armored protection.
- Scenario Projections:
- **Best Case**: Successful establishment of the ISF leads to long-term stabilization and peace in Gaza.
- **Worst Case**: The ISF fails to gain traction, resulting in increased conflict and regional instability.
- **Most Likely**: Partial success with ongoing challenges from local resistance and geopolitical complexities.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– John Kennedy (historical reference)
– Donald Trump
– Ciarn Ahern
– Colm Mongin
– Mark Mellett
– Garry McKeon
– Emmanuel Macron
7. Thematic Tags
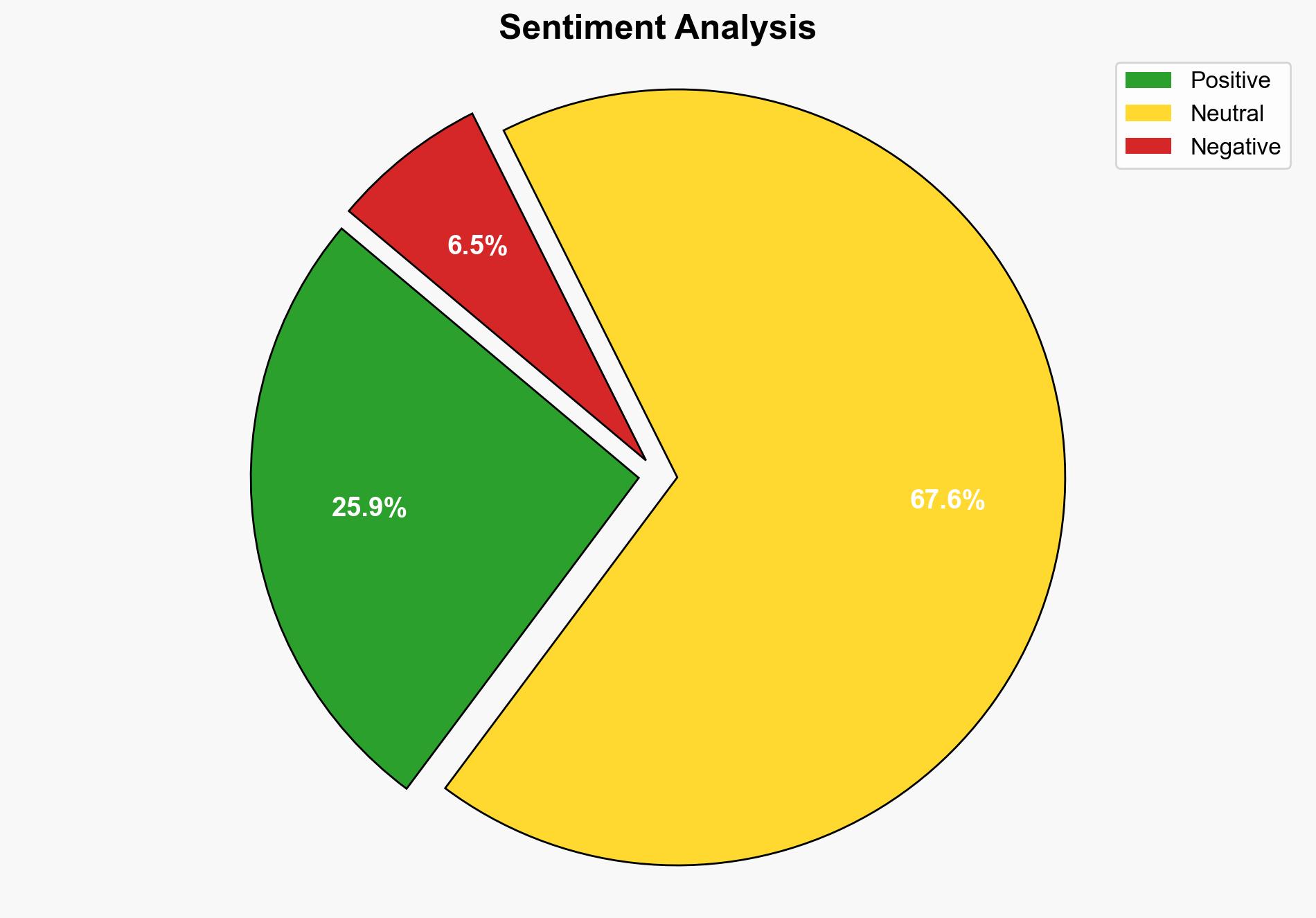
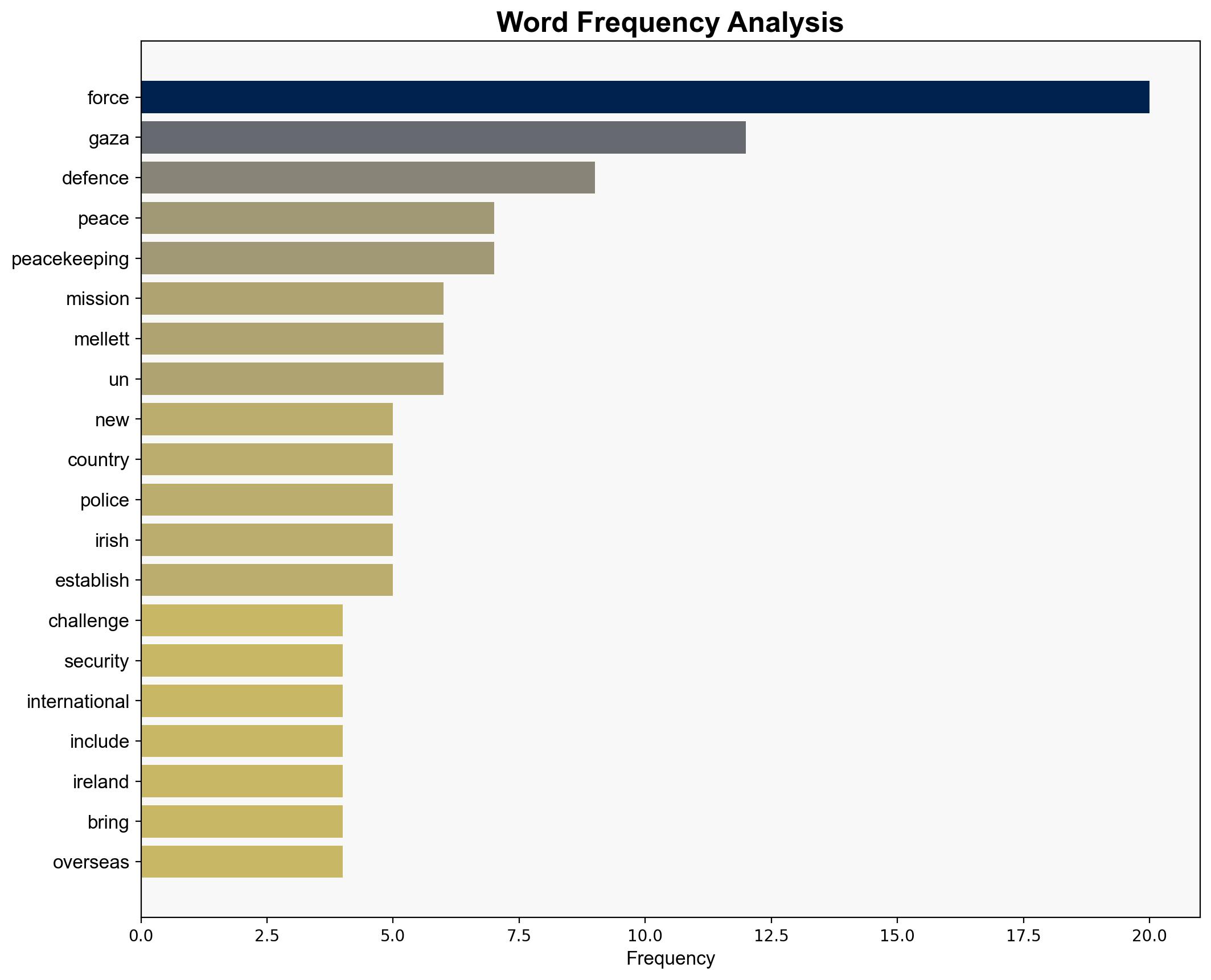
national security threats, regional focus, peacekeeping, geopolitical complexities