Supreme Court Weighs Limits of Presidential Tariff Power – pymnts.com
Published on: 2025-11-06
Intelligence Report: Supreme Court Weighs Limits of Presidential Tariff Power – pymnts.com
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
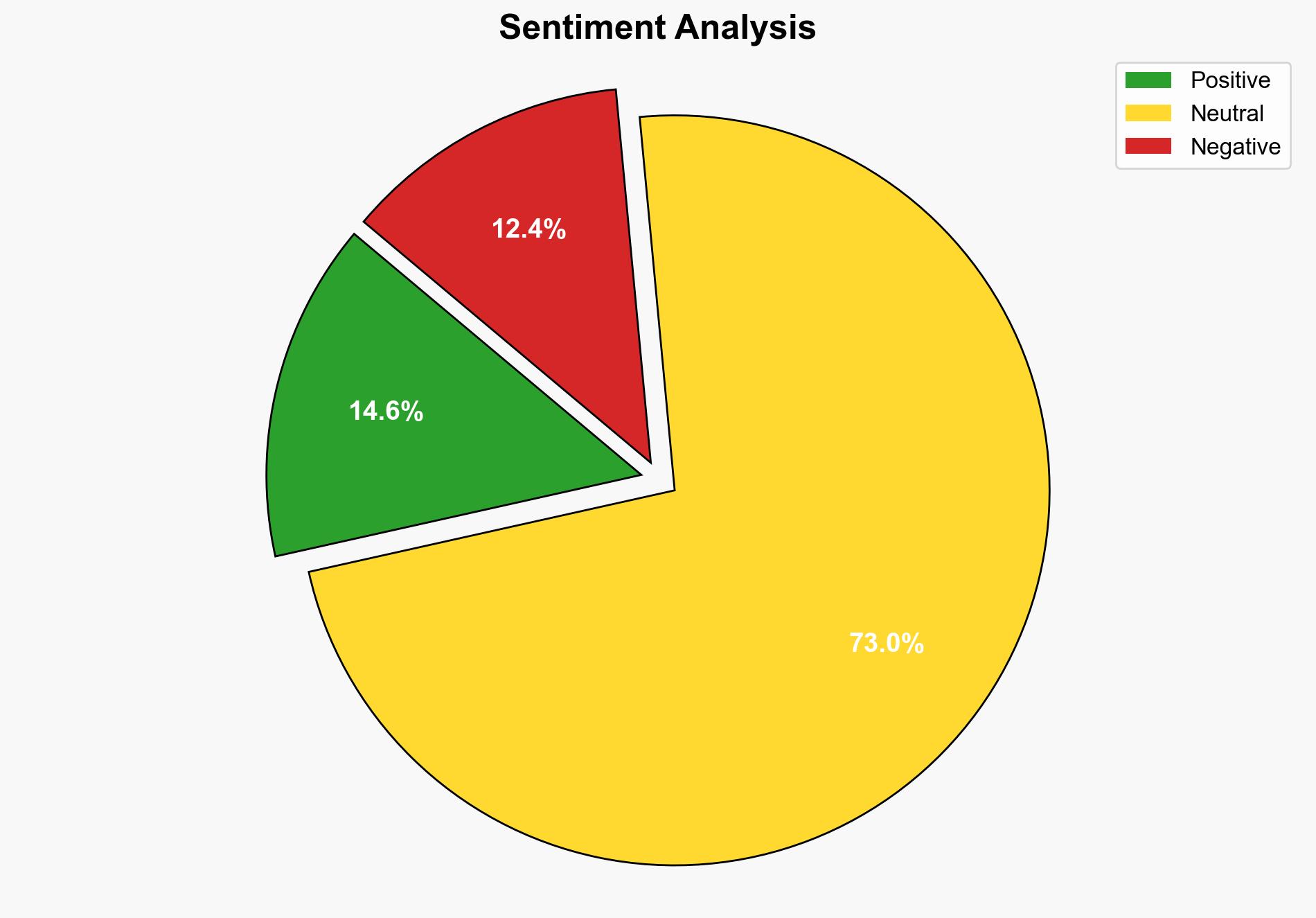
The Supreme Court’s deliberation on the limits of presidential tariff power could redefine the balance between executive and legislative authorities in trade policy. The hypothesis that the court will limit presidential power is better supported due to the skepticism expressed by justices. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Monitor court proceedings closely and prepare for potential shifts in trade policy affecting international business operations.
2. Competing Hypotheses
1. **Hypothesis A**: The Supreme Court will uphold the president’s authority to impose tariffs under the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA), maintaining the status quo of executive power in trade matters.
2. **Hypothesis B**: The Supreme Court will limit the president’s authority, reinforcing congressional power over tariffs and trade policy.
Structured Analytic Technique: Analysis of Competing Hypotheses (ACH) 2.0 was applied. Evidence such as the skepticism from justices, including Amy Coney Barrett and Neil Gorsuch, towards the government’s argument supports Hypothesis B more strongly. The court’s conservative majority questioning the executive’s broad use of IEEPA suggests a potential shift towards limiting presidential power.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
– **Assumptions**: It is assumed that the court’s decision will be influenced primarily by legal interpretations rather than political considerations. The reliance on justices’ questioning as an indicator of their final decision may be misleading.
– **Red Flags**: The absence of a clear consensus among justices and the potential for political bias in decision-making. The impact of external economic pressures on judicial decisions is not fully explored.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
– **Economic Impact**: A decision limiting presidential tariff power could stabilize international trade relations and reduce market volatility. Conversely, upholding the power could lead to increased tariffs, affecting global supply chains.
– **Geopolitical Risks**: Changes in tariff policy could alter U.S. relationships with key trading partners, potentially leading to retaliatory measures.
– **Operational Risks**: Businesses reliant on international suppliers may face increased costs and supply chain disruptions if tariffs are maintained or expanded.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- **Mitigation**: Businesses should diversify supply chains and explore domestic sourcing options to mitigate potential tariff impacts.
- **Opportunity**: Companies could capitalize on potential tariff reductions by expanding into new international markets.
- **Projections**:
- **Best Case**: The court limits presidential tariff power, stabilizing trade policies and reducing market uncertainty.
- **Worst Case**: The court upholds broad executive tariff powers, leading to increased trade tensions and economic instability.
- **Most Likely**: A nuanced decision that partially limits executive power while preserving some flexibility for national security considerations.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
– Amy Coney Barrett
– Neil Gorsuch
– John Sauer
– John Roberts
7. Thematic Tags
national security threats, economic policy, trade relations, judicial review