Refugee camps set to be uninhabitable by 2050 as extreme weather worsens – Globalsecurity.org
Published on: 2025-11-11
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Refugee camps set to be uninhabitable by 2050 as extreme weather worsens – Globalsecurity.org
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
With a high confidence level, it is assessed that refugee camps will become increasingly uninhabitable by 2050 due to worsening extreme weather conditions, exacerbating humanitarian crises and potentially destabilizing regions. Strategic action is recommended to enhance climate resilience and improve resource allocation to vulnerable communities.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Refugee camps will become uninhabitable primarily due to climate change-induced extreme weather, leading to increased displacement and regional instability.
Hypothesis 2: While climate change will exacerbate conditions, the primary driver of uninhabitability will be inadequate infrastructure and resource management, which could be mitigated with proper intervention.
Assessment: Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the evidence of increasing extreme weather events and their direct impact on refugee camps. However, Hypothesis 2 cannot be dismissed as infrastructure improvements could mitigate some effects, though they require significant investment and international cooperation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: Climate change will continue to worsen without significant global intervention. Current infrastructure and resource management in refugee camps are insufficient to handle extreme weather.
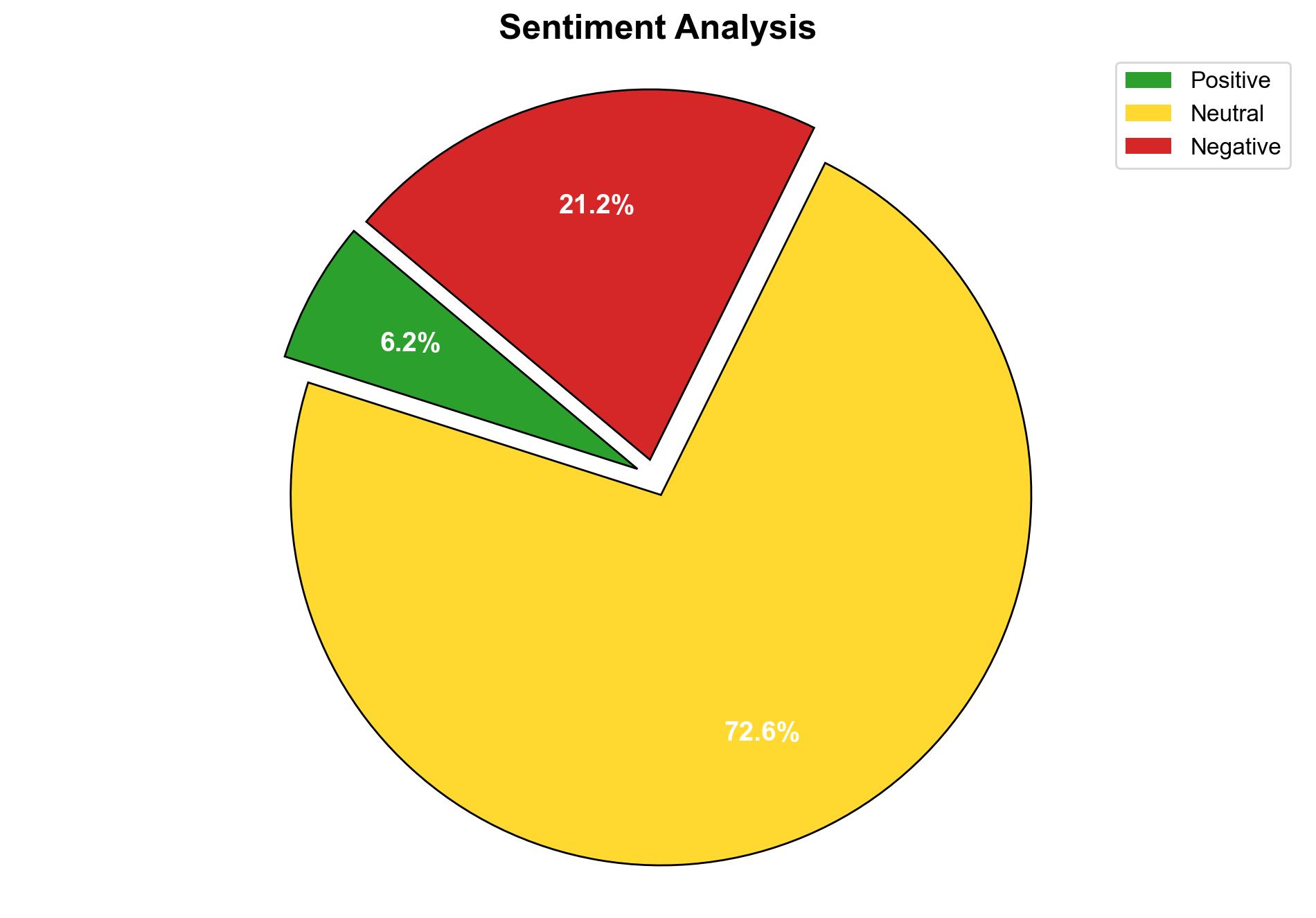
Red Flags: Potential underreporting of the impact of climate change on refugee populations. Over-reliance on climate change as the sole factor without considering socio-political dynamics.
Deception Indicators: Possible bias in reports emphasizing climate change to secure funding, overlooking other critical factors like governance and conflict.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The increasing uninhabitability of refugee camps poses several risks: potential for regional instability as displaced populations seek refuge in already strained neighboring countries; increased recruitment by armed groups exploiting vulnerable populations; and heightened geopolitical tensions over resource allocation. Economic impacts include strain on humanitarian aid budgets and potential disruption of local economies.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance climate resilience in refugee camps through infrastructure investment and sustainable resource management.
- Strengthen international cooperation to ensure equitable distribution of climate finance to vulnerable communities.
- Develop early warning systems and contingency plans for extreme weather events.
- Best-case scenario: Successful international collaboration leads to improved living conditions and reduced displacement.
- Worst-case scenario: Failure to address climate impacts results in widespread humanitarian crises and regional instability.
- Most-likely scenario: Incremental improvements in some areas, but overall conditions continue to deteriorate without significant intervention.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Filippo Grandi, UN High Commissioner for Refugees, advocating for increased climate finance and international action.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus: Africa, Middle East, South Asia
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology