State to create new agency on cybersecurity – Standard Digital
Published on: 2025-11-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: State to create new agency on cybersecurity – Standard Digital
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
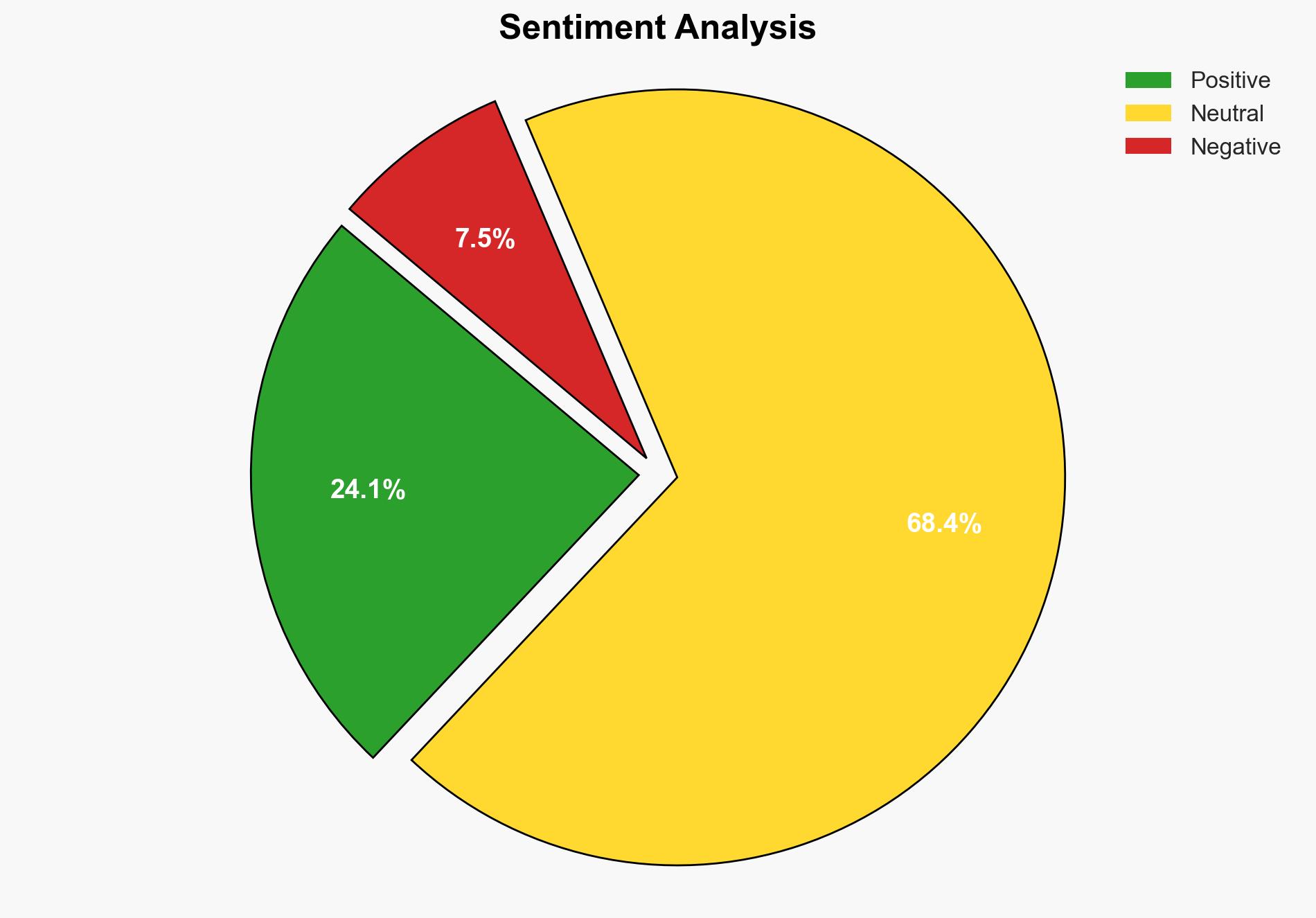
The creation of a new state agency dedicated to cybersecurity in Kenya is a strategic move to bolster the country’s digital economy and enhance national cyber resilience. The most supported hypothesis is that this agency will effectively address the growing cyber threats and foster economic growth by attracting investment and creating jobs. Confidence level: Moderate. Recommended action: Support the establishment of the agency with a focus on international collaboration and capacity building.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The new cybersecurity agency will significantly enhance Kenya’s ability to manage cyber threats, attract investment, and create jobs, thereby strengthening the digital economy.
Hypothesis 2: The creation of the agency may face challenges such as bureaucratic inefficiencies, insufficient funding, and lack of skilled personnel, which could hinder its effectiveness in addressing cyber threats and supporting economic growth.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the government’s commitment, as indicated by the involvement of high-level officials and the alignment with national economic goals. However, the success of this initiative will depend on overcoming potential bureaucratic and resource-related challenges.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: The government has the political will and resources to establish and sustain the new agency. There is sufficient local talent to fill cybersecurity roles. The agency will effectively coordinate with existing bodies like the Office of the Data Protection Commissioner (ODPC).
Red Flags: Potential overlap of responsibilities with existing agencies, lack of clarity in the agency’s mandate, and possible resistance from entrenched interests within the current cybersecurity framework.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The establishment of a dedicated cybersecurity agency could lead to improved national security and economic growth. However, risks include potential bureaucratic delays, insufficient inter-agency coordination, and the possibility of cyber threats outpacing the agency’s capabilities. Politically, failure to deliver on promises could undermine public trust. Economically, failure to attract investment could slow digital economy growth.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Ensure clear delineation of roles and responsibilities between the new agency and existing bodies to avoid overlap and inefficiencies.
- Invest in training and capacity building to address potential skill shortages in the cybersecurity sector.
- Foster international partnerships to leverage global expertise and resources in cybersecurity.
- Best-case scenario: The agency successfully mitigates cyber threats, attracts investment, and creates jobs, boosting the digital economy.
- Worst-case scenario: Bureaucratic inefficiencies and resource constraints hinder the agency’s effectiveness, leading to increased vulnerability to cyber threats.
- Most-likely scenario: The agency makes gradual progress in enhancing cybersecurity but faces challenges in fully realizing its potential due to resource and coordination issues.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
John Tanui (Principal Secretary, State Department of ICT and Digital Economy), Nicholas Mulila (Chief Corporate Security Officer, Safaricom), John Paul Okwiri (CEO, Konza Technopolis).
7. Thematic Tags
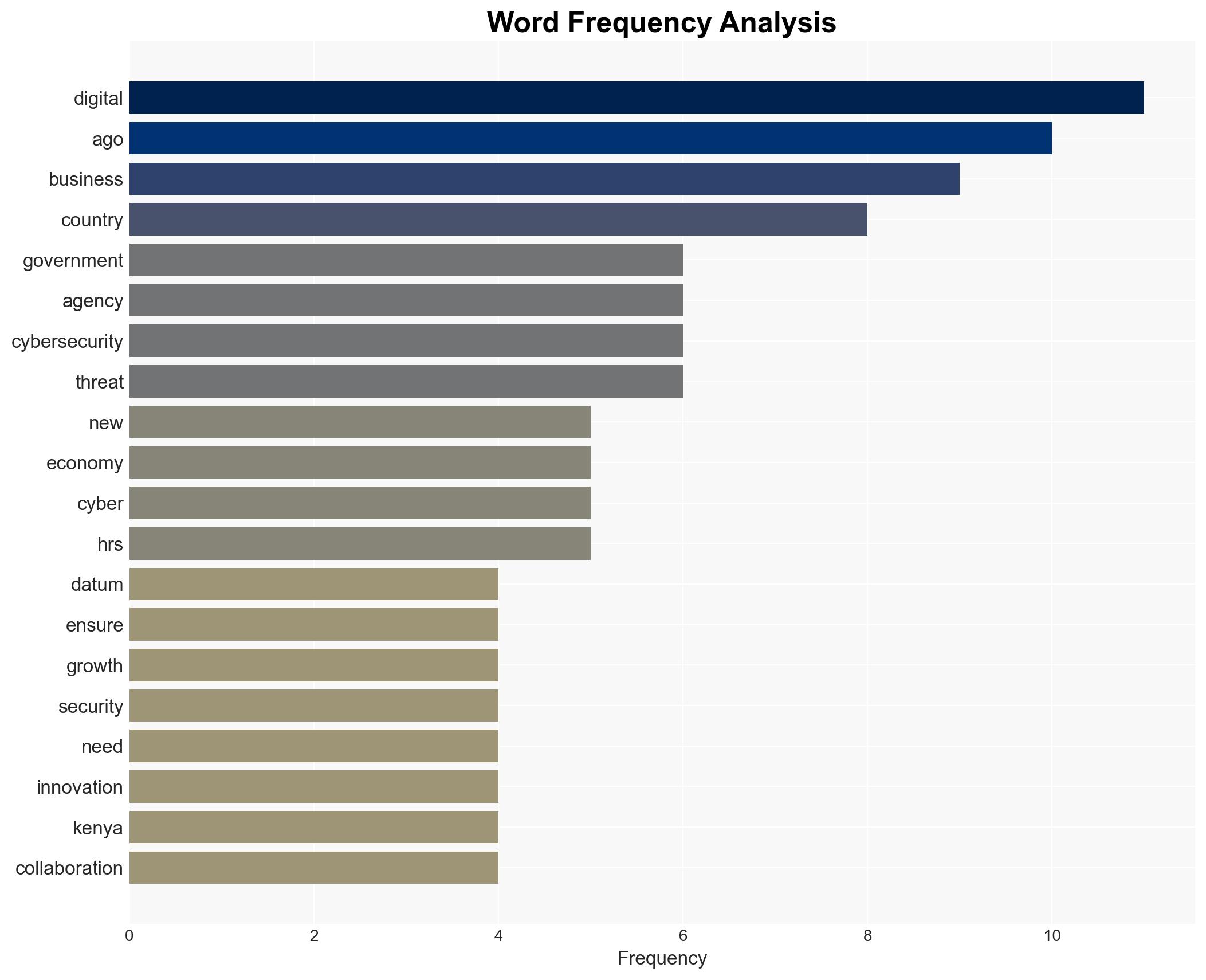
Cybersecurity, Digital Economy, Kenya, National Security, Economic Growth
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Methodology