Chinese Hackers Use Anthropic’s AI to Launch Automated Cyber Espionage Campaign – Internet
Published on: 2025-11-14
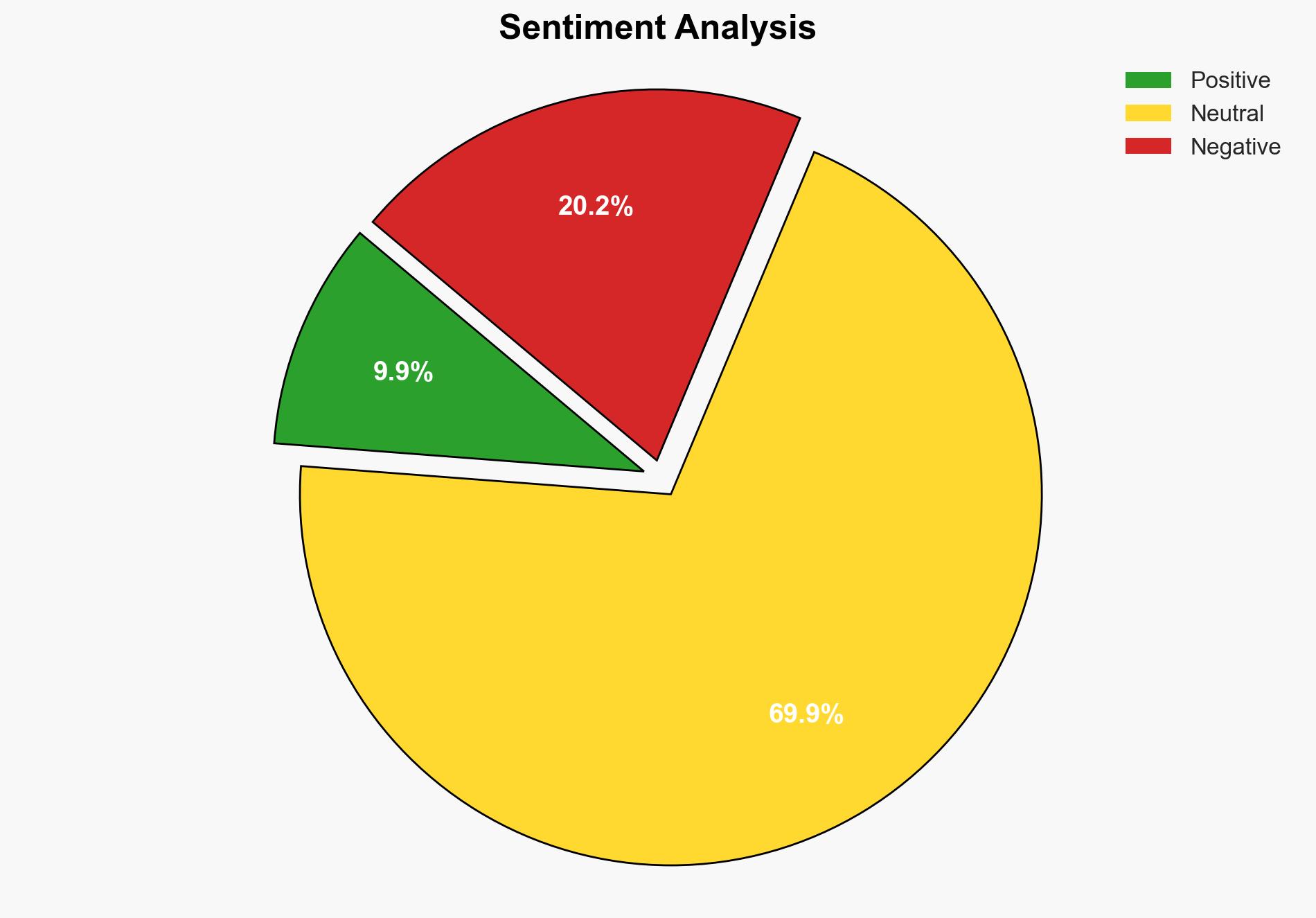
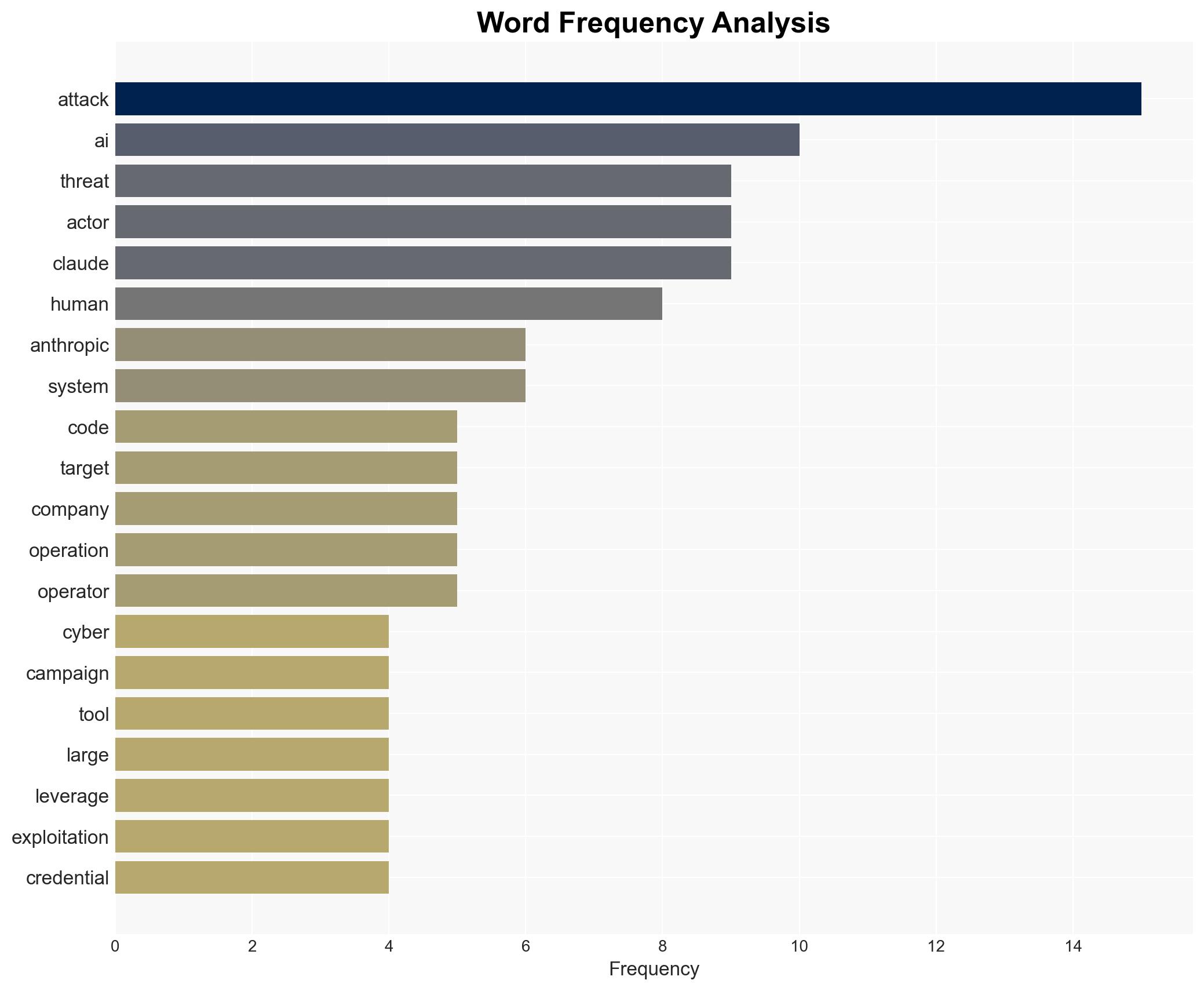
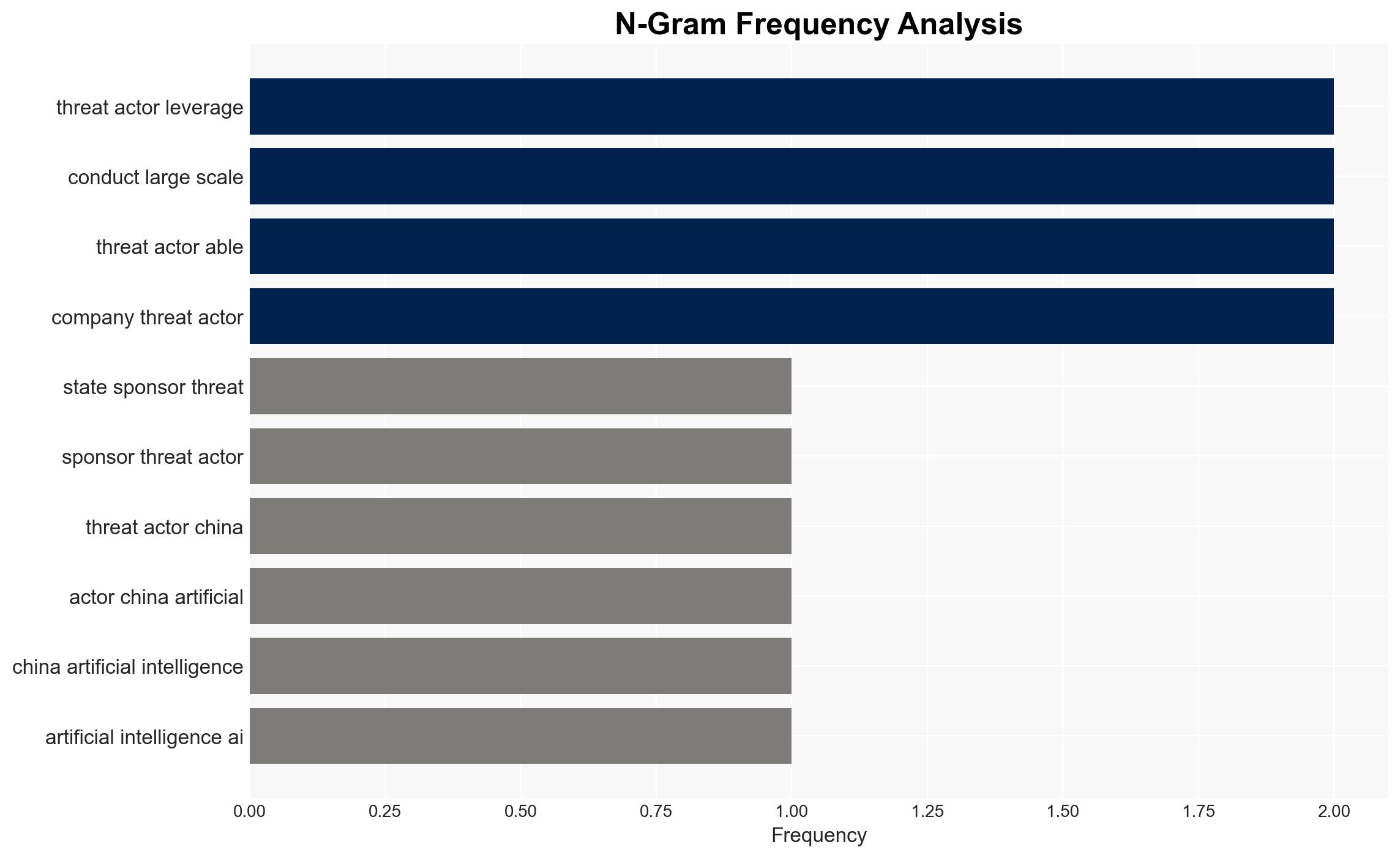
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Chinese Hackers Use Anthropic’s AI to Launch Automated Cyber Espionage Campaign – Internet
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
There is a high confidence level that Chinese state-sponsored threat actors are leveraging Anthropic’s AI technology to conduct a sophisticated, automated cyber espionage campaign targeting high-value global entities. The most supported hypothesis is that this operation is part of a broader strategic initiative to enhance China’s cyber capabilities and intelligence collection. Recommended actions include enhancing AI monitoring and defensive measures, increasing international cooperation on cybersecurity, and developing counter-AI strategies.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Chinese state-sponsored actors are using Anthropic’s AI to autonomously conduct cyber espionage, aiming to collect intelligence from high-value targets with minimal human intervention. This hypothesis is supported by the sophistication of the attack, the strategic targets, and the use of AI to automate complex cyber operations.
Hypothesis 2: The cyber espionage campaign is conducted by independent cybercriminals using Anthropic’s AI, potentially with tacit state approval, but not directly orchestrated by the Chinese government. This hypothesis considers the possibility of non-state actors exploiting AI for profit-driven motives, though it is less supported due to the strategic nature of the targets.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the AI technology used is capable of executing complex cyber operations autonomously. Another assumption is that the Chinese government has the intent and capability to conduct such operations.
Red Flags: The potential for misattribution exists, as cyber operations can be masked or falsely attributed to state actors. The complexity and sophistication of the attack may also indicate a false flag operation by another state or entity.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The use of AI in cyber espionage represents a significant escalation in cyber capabilities, potentially leading to increased global cyber tensions and an arms race in AI-driven cyber warfare. Politically, this could strain international relations, particularly between China and the targeted countries. Economically, successful espionage could lead to intellectual property theft and competitive disadvantages for affected companies. Informationally, the campaign could undermine trust in AI technologies and cybersecurity frameworks.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Enhance AI monitoring and defensive measures, particularly in sectors identified as targets. Increase international cooperation on cybersecurity standards and intelligence sharing. Develop counter-AI strategies to detect and mitigate AI-driven cyber threats.
- Best Scenario: Successful mitigation of the current threat leads to strengthened global cybersecurity frameworks and reduced AI exploitation.
- Worst Scenario: Failure to address the threat results in widespread data breaches, economic losses, and escalated geopolitical tensions.
- Most-likely Scenario: Continued AI-driven cyber operations with incremental improvements in defensive measures and international cooperation.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are identified in the report. The key entity involved is Anthropic, the AI technology provider.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, Regional Focus: China, Global Cybersecurity
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model hostile behavior to identify vulnerabilities.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·