How a Transparent Company Culture Strengthens Cybersecurity and Data Resilience – SPONSOR CONTENT FROM VEEAM – Harvard Business Review
Published on: 2025-11-14
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: How a Transparent Company Culture Strengthens Cybersecurity and Data Resilience – SPONSOR CONTENT FROM VEEAM – Harvard Business Review
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
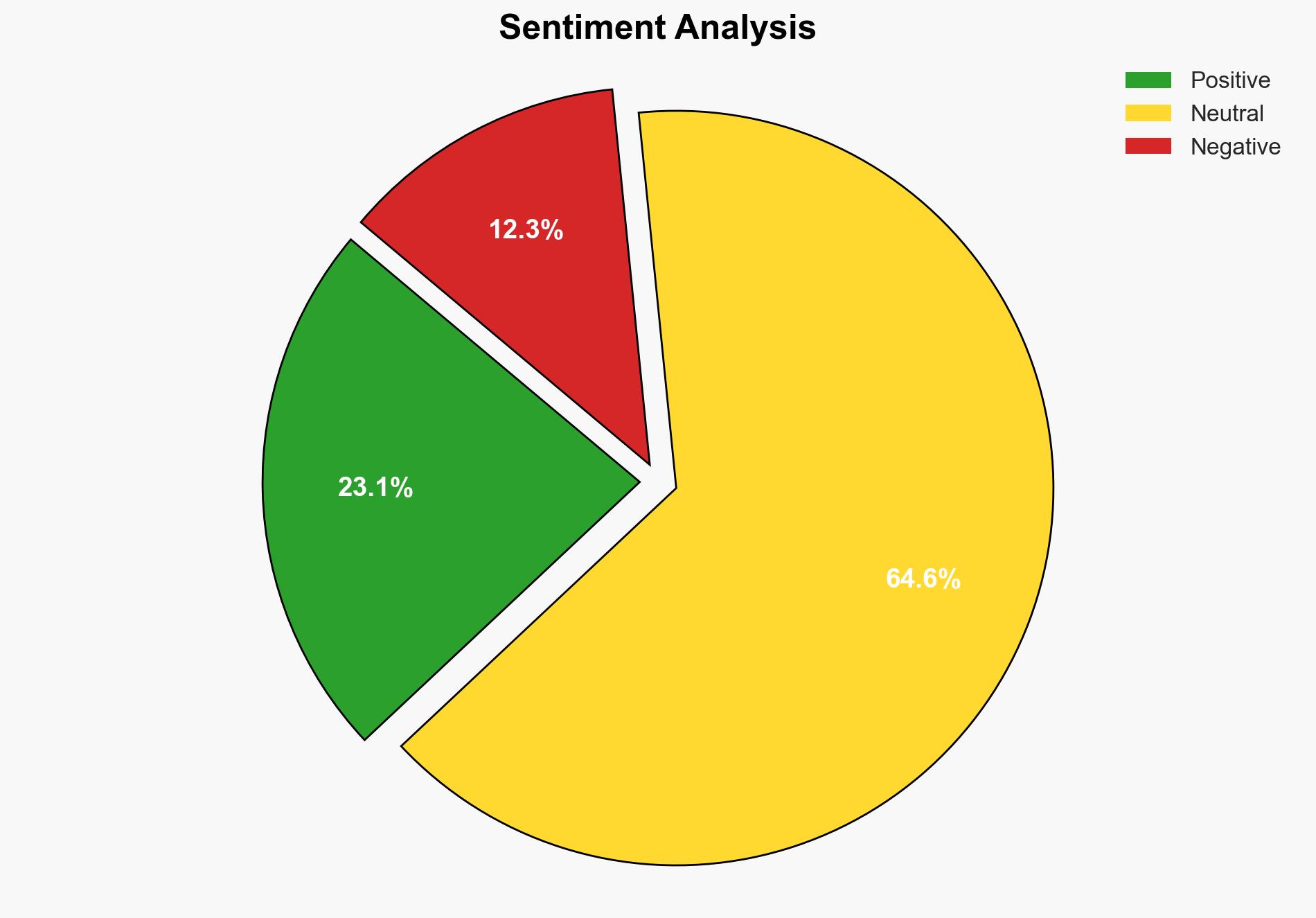
It is assessed with moderate confidence that fostering a transparent company culture significantly enhances cybersecurity and data resilience. The most supported hypothesis is that transparency and open communication within organizations lead to quicker identification and response to cybersecurity threats, thereby strengthening overall resilience. Recommended actions include implementing anonymous reporting systems and promoting a culture of openness to mitigate risks associated with cyber threats.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: A transparent company culture enhances cybersecurity by encouraging employees to report threats and vulnerabilities without fear of reprisal, leading to faster incident response and recovery.
Hypothesis 2: A transparent company culture has minimal impact on cybersecurity because technological solutions and formal policies are the primary determinants of a company’s cyber resilience.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to evidence suggesting that cultural factors, such as openness and accountability, facilitate early threat detection and response, which are critical in mitigating cyber risks. Hypothesis 2 is less supported as it underestimates the role of human factors in cybersecurity.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that employees are willing to report cybersecurity issues if provided with a safe environment. It is also assumed that leadership is committed to fostering a transparent culture.
Red Flags: Potential bias exists in over-relying on cultural factors while underestimating the importance of technological defenses. There may also be deception indicators if organizations claim transparency but lack genuine implementation.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The primary implication is that organizations with transparent cultures are better positioned to handle cyber threats, reducing the risk of operational downtime and reputational damage. However, if transparency is not genuinely implemented, it could lead to a false sense of security, increasing vulnerability to cyber attacks. Escalation scenarios include potential economic losses and informational breaches if transparency is not effectively integrated with technological defenses.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Implement anonymous reporting systems to encourage employees to report cybersecurity issues without fear of reprisal.
- Conduct regular training sessions to enhance employees’ ability to identify and respond to cyber threats.
- Promote a culture of openness and accountability, ensuring leadership commitment to transparency.
- Best Scenario: Organizations achieve high cyber resilience through effective integration of cultural and technological defenses.
- Worst Scenario: Failure to genuinely implement transparency leads to increased vulnerability and significant cyber incidents.
- Most-likely Scenario: Organizations see moderate improvements in cybersecurity through enhanced transparency, but challenges remain in fully integrating cultural and technological solutions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Dave Russell, SVP Product Strategy, Veeam; Vamshi Kommineni, Group Product Manager, Azure Storage, Microsoft.
7. Thematic Tags
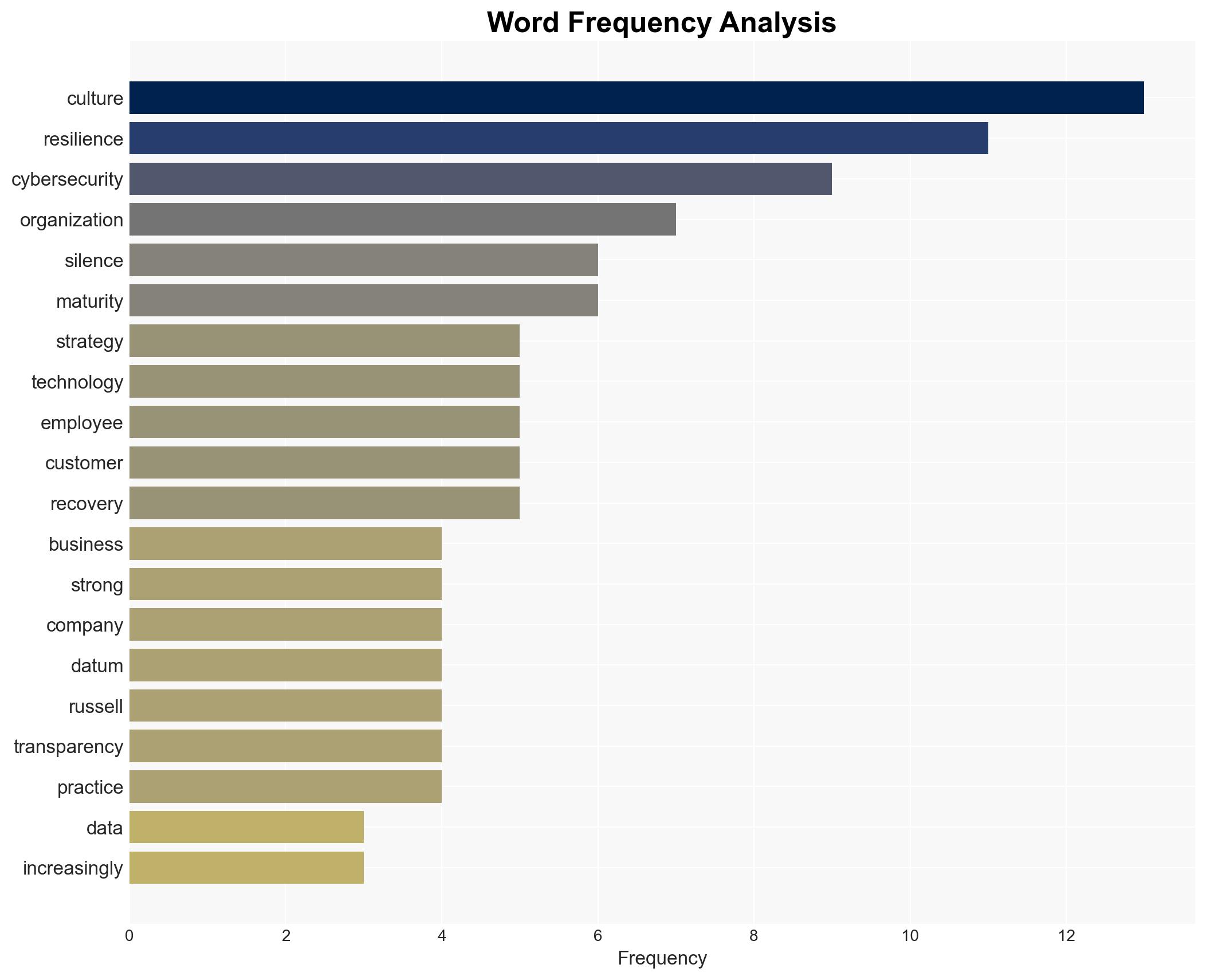
Cybersecurity, Organizational Culture, Data Resilience, Transparency, Risk Management
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·