A Programmatic Kill Switch Why Googles RTB Control Isnt Sparking Panic – AdExchanger
Published on: 2025-11-17
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Strategic Analysis of Google’s RTB Control Mechanism
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
With a moderate level of confidence, the most supported hypothesis is that Google’s proposed RTB control mechanism is primarily a strategic move to preempt regulatory pressure rather than a genuine shift towards user privacy. The recommended action is to monitor Google’s implementation closely and assess the impact on the programmatic advertising ecosystem, while preparing for potential regulatory changes that may follow this precedent.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Google’s RTB control mechanism is a genuine effort to enhance user privacy and comply with increasing regulatory demands.
Hypothesis 2: The mechanism is a strategic maneuver to maintain market dominance by preempting regulatory actions and setting industry standards that favor Google’s business model.
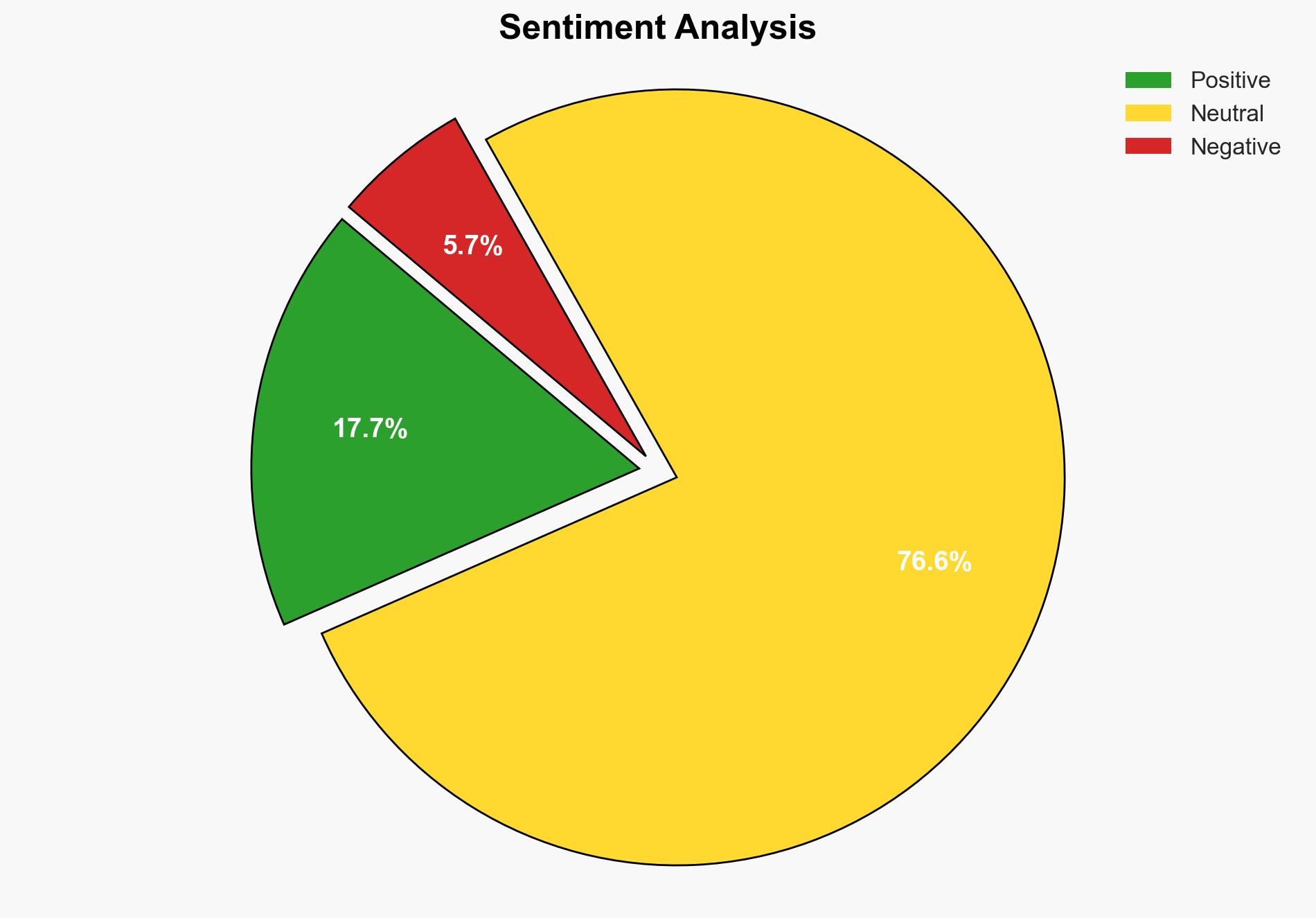
The second hypothesis is more likely due to Google’s historical behavior of implementing changes that ultimately reinforce its market position. The vague details and opt-out nature of the mechanism suggest a limited impact on user privacy, aligning with a strategy to placate regulators without significant operational changes.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that Google has the technical capability to implement the proposed RTB control effectively. Another assumption is that regulatory bodies will accept this mechanism as a sufficient privacy measure.
Red Flags: The lack of detailed information on how the mechanism will function raises concerns about its efficacy. The opt-out model historically results in low user engagement, suggesting limited impact on data privacy.
Deception Indicators: Google’s emphasis on audits and compliance could be a tactic to divert attention from the limited scope of the changes.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The introduction of this mechanism could set a precedent for similar actions by other tech giants, potentially leading to a fragmented regulatory landscape. If regulators perceive this as inadequate, it could trigger stricter regulations, impacting the entire digital advertising ecosystem. Economically, smaller firms may struggle to adapt, leading to reduced competition and innovation.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor regulatory responses to Google’s settlement and prepare for potential legislative changes.
- Engage with industry stakeholders to develop a unified response to Google’s mechanism, ensuring fair competition.
- Best-case scenario: The mechanism satisfies regulatory bodies, preventing further legal actions and maintaining market stability.
- Worst-case scenario: Regulators deem the mechanism insufficient, leading to stringent regulations that disrupt the advertising industry.
- Most-likely scenario: The mechanism results in minor adjustments within the industry, with Google maintaining its dominant position while facing ongoing scrutiny.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Alan Chapell, Privacy Attorney and Contributor to Marketecture Monopoly Report.
Google, as the primary entity involved in the RTB control mechanism.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, Regional Focus: Global, with specific attention to the United States and European Union regulatory environments
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Forecast futures under uncertainty via probabilistic logic.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·