Google Issues Security Fix for Actively Exploited Chrome V8 Zero-Day Vulnerability – Internet
Published on: 2025-11-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
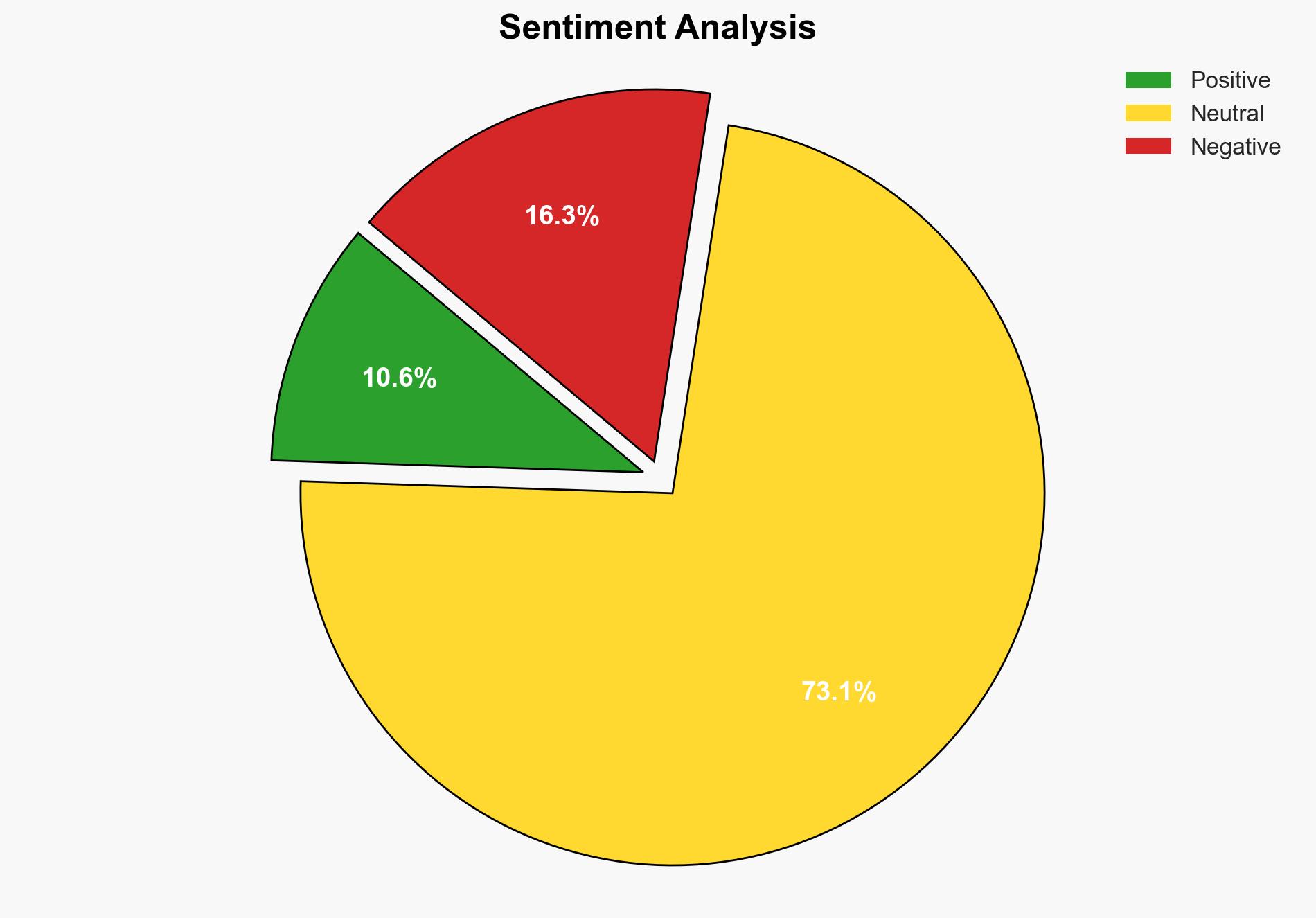
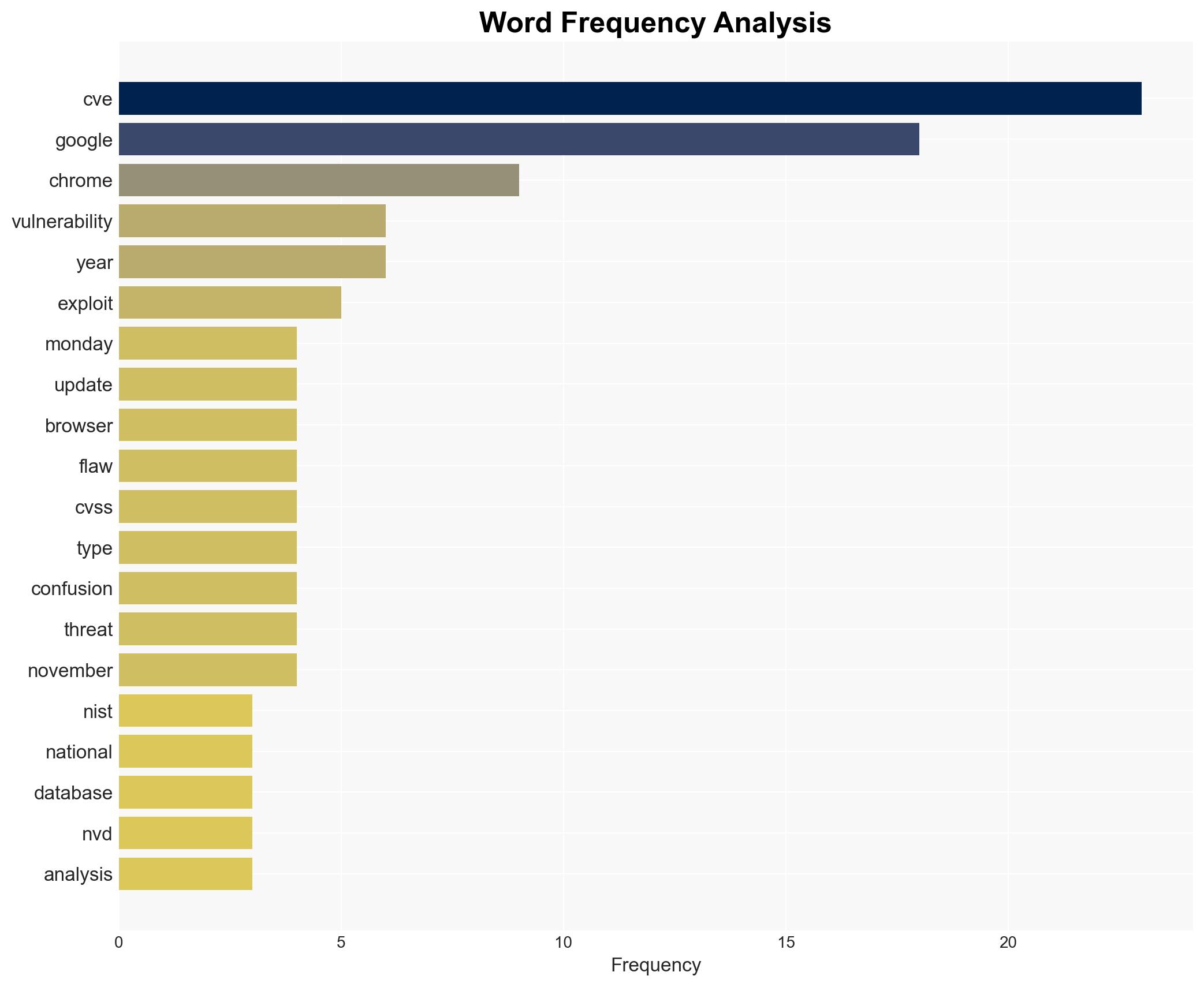
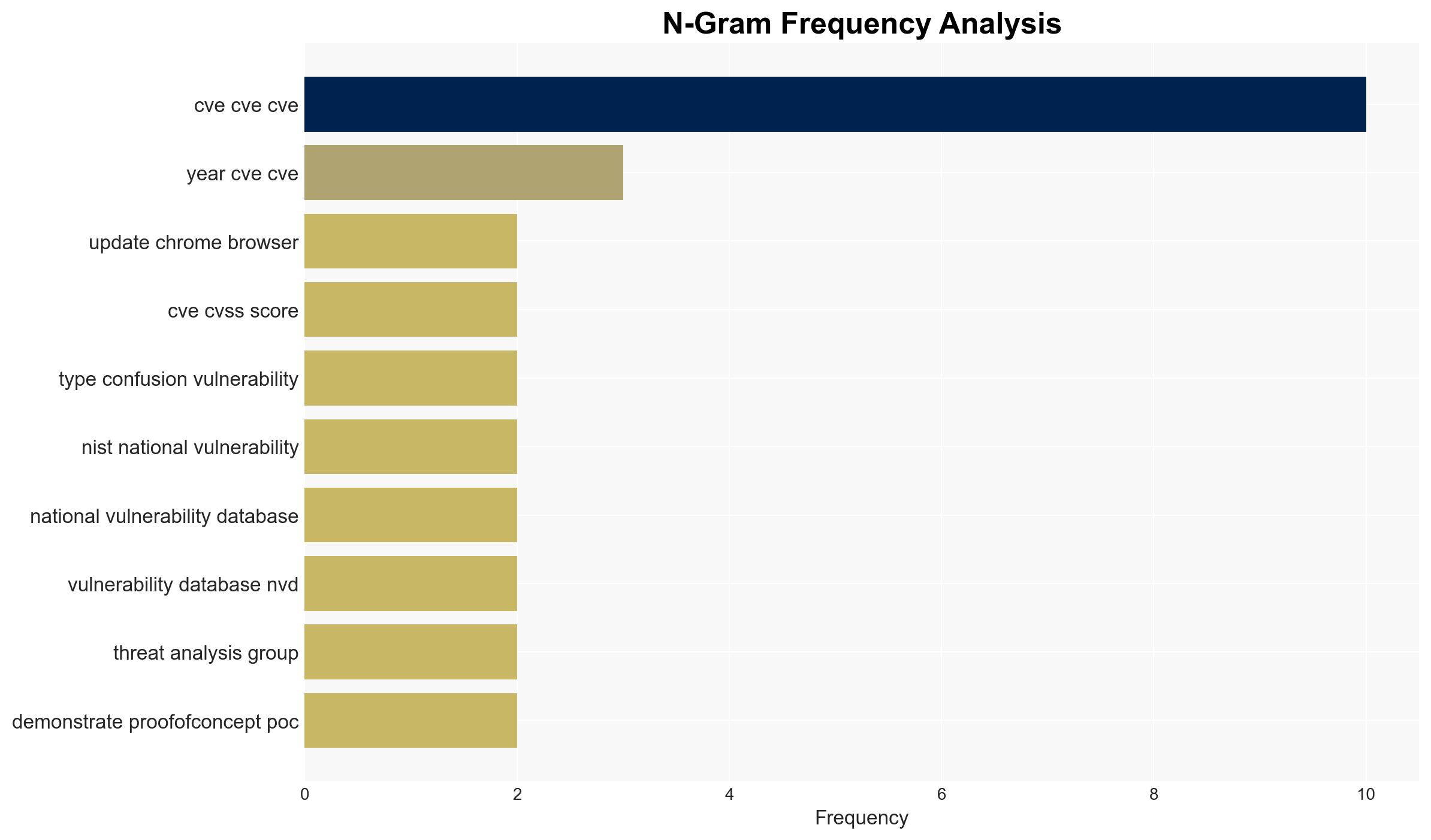
The most supported hypothesis is that the zero-day vulnerability in Chrome’s V8 engine, CVE-2025-13223, is being actively exploited by sophisticated threat actors, potentially state-sponsored, to target specific high-value entities. The strategic recommendation is to prioritize patch deployment across all systems and enhance monitoring for unusual activity. Confidence Level: Moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The vulnerability is being exploited by state-sponsored actors to target high-value entities for espionage or disruption.
Hypothesis 2: The exploitation is primarily conducted by cybercriminal groups aiming for financial gain through data theft or ransomware deployment.
Assessment: Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the timing of the discovery by Google’s Threat Analysis Group and the nature of the vulnerability, which allows for remote code execution. The lack of widespread financial gain indicators and the sophistication required to exploit such a vulnerability suggest state-sponsored involvement.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the exploitation is targeted and not yet widespread, given the lack of publicized mass attacks. It is also assumed that Google’s rapid response indicates a high threat level.
Red Flags: The rapid patch release by Google may indicate a severe threat level. The lack of detailed information on the targets suggests potential information control or ongoing investigations.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to significant data breaches, intellectual property theft, or disruption of critical infrastructure. If state-sponsored, it could escalate geopolitical tensions, especially if linked to sensitive sectors or government entities. Economically, affected companies could face reputational damage and financial losses.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Ensure immediate deployment of the security patch across all systems using Chrome.
- Enhance network monitoring for indicators of compromise related to this vulnerability.
- Engage in information sharing with industry partners and government agencies to identify and mitigate potential threats.
- Best-case scenario: The patch is deployed swiftly, and no significant breaches occur.
- Worst-case scenario: The vulnerability is exploited before patch deployment, leading to major data breaches or infrastructure disruptions.
- Most-likely scenario: Targeted attacks continue until patch deployment is widespread, with potential minor breaches.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Clément Lecigne from Google’s Threat Analysis Group is credited with discovering the flaw. Google’s rapid response team is crucial in mitigating the threat.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·