Report reveals 25 surge in global water use over two decades – Phys.Org
Published on: 2025-11-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Surge in Global Water Use and Strategic Implications
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
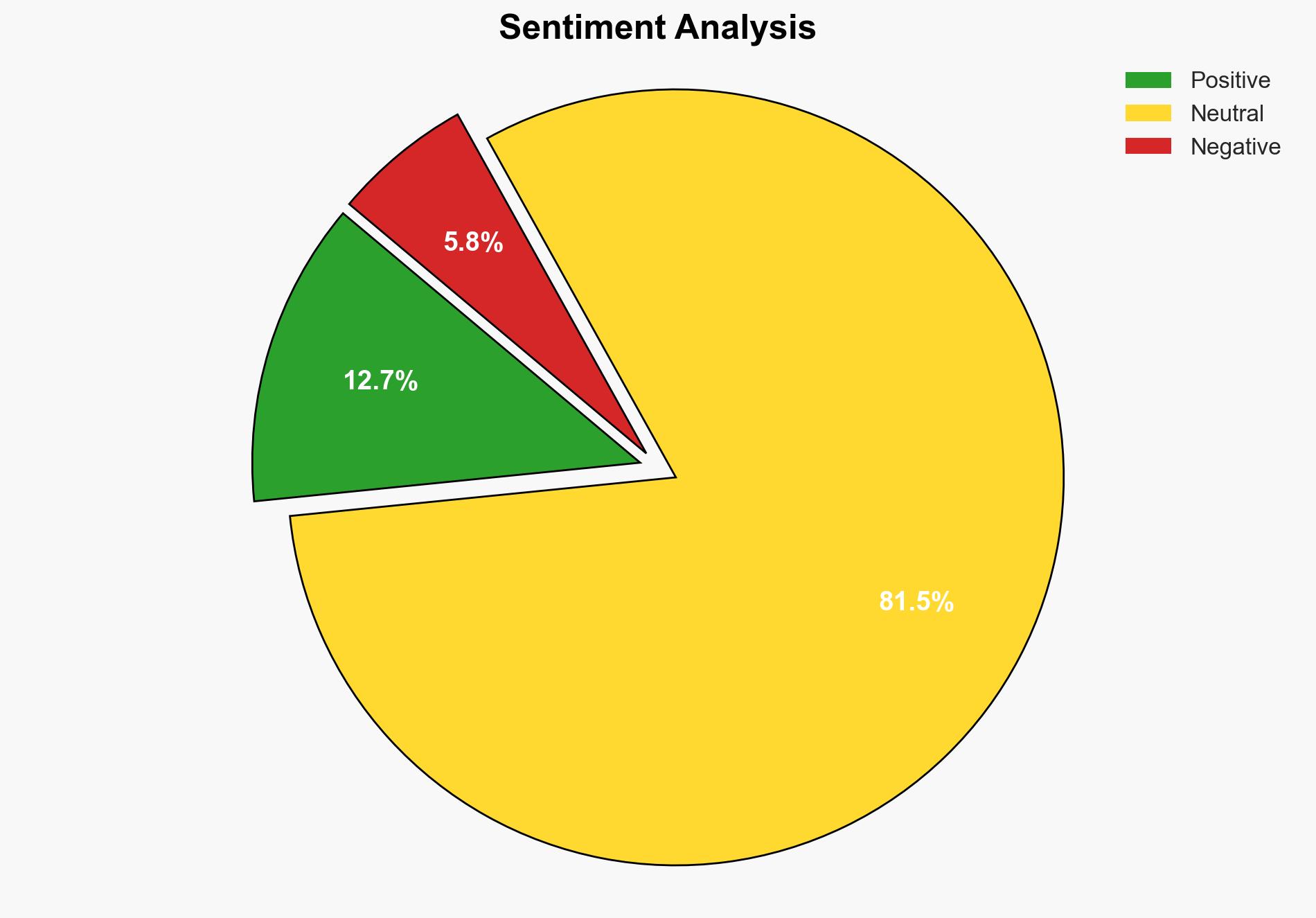
The global increase in water use by 25% over two decades poses significant strategic risks related to resource scarcity, particularly in water-scarce regions. The most supported hypothesis is that inefficient water management and increased demand from global trade are primary drivers. Strategic action should focus on enhancing water efficiency and international cooperation. Confidence Level: Moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The surge in global water use is primarily due to inefficient water management practices and increased demand from water-intensive global trade.
Hypothesis 2: The increase is mainly driven by population growth and urbanization, leading to higher domestic and industrial water consumption.
Assessment: Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the report’s emphasis on global trade and inefficient water management as significant factors. The detailed data on water use in trade-intensive regions supports this interpretation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: The data accurately represents global water use trends; water management practices have not significantly improved in the past two decades.
Red Flags: Potential bias in data interpretation due to reliance on specific case studies (e.g., Pakistan); lack of comprehensive data on all contributing factors such as climate change impacts.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The continued increase in water use could exacerbate geopolitical tensions over water resources, particularly in already water-scarce regions. Economic impacts include potential disruptions in global trade, particularly for water-intensive products. There is also a risk of misinformation or manipulation of water data to influence policy or public perception.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Enhance international cooperation for water management and establish global standards for water use efficiency.
- Invest in technology and infrastructure to improve water efficiency, particularly in agriculture and industry.
- Best-case scenario: Global collaboration leads to improved water management and reduced consumption.
- Worst-case scenario: Water scarcity leads to increased conflict and economic instability.
- Most-likely scenario: Incremental improvements in water efficiency, but challenges persist in water-scarce regions.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Rick Hogeboom – Associate Professor and Co-author of the report.
University of Twente – Key contributor to the research.
World Bank – Publisher of the Global Water Monitoring Report.
7. Thematic Tags
Regional Focus, Global Water Use, Resource Scarcity, Water Management, International Cooperation, Economic Impact
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us
·