WTF are synthetic audiences – Digiday
Published on: 2025-11-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report: Synthetic Audiences in Programmatic Marketing
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
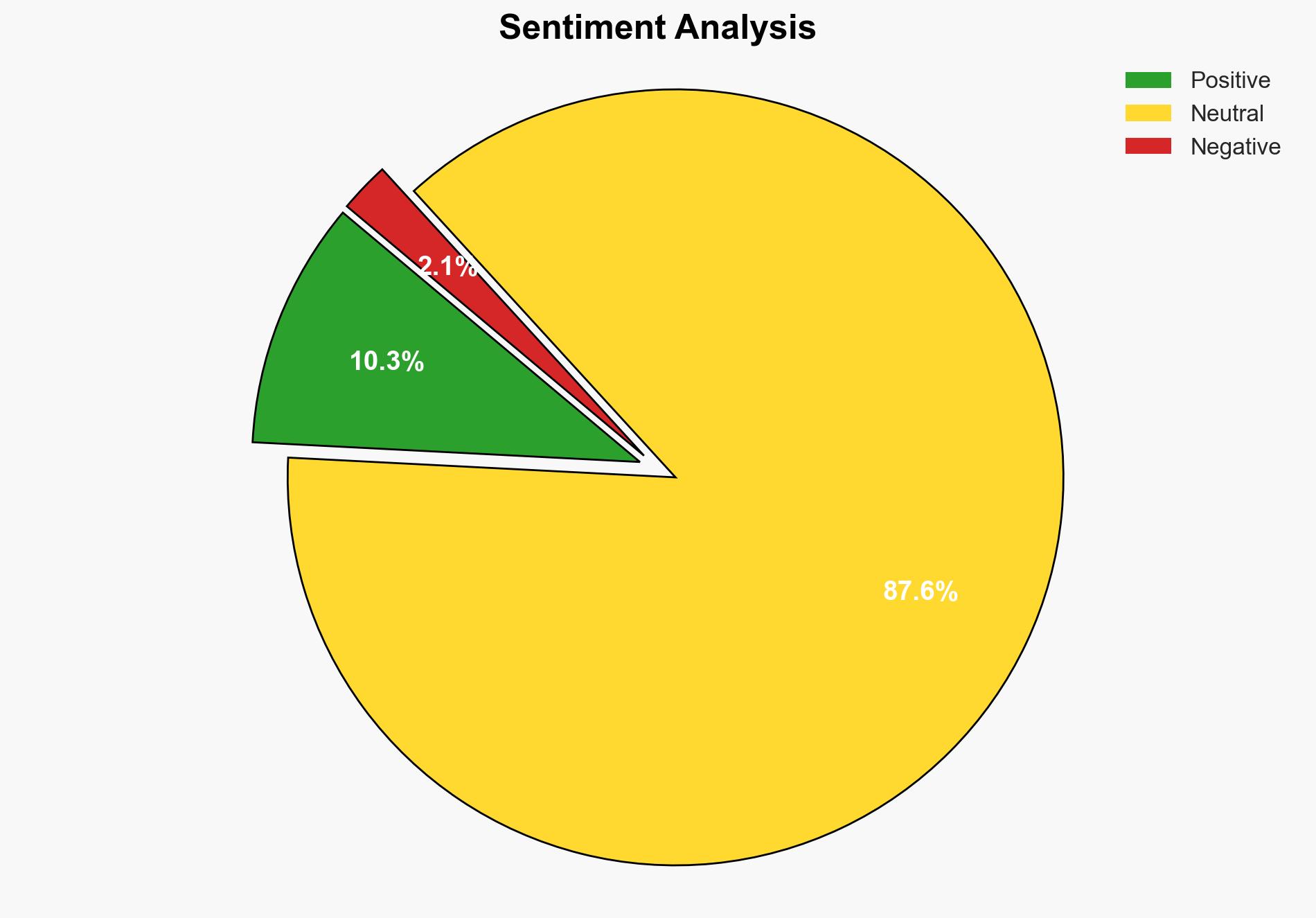
The development and utilization of synthetic audiences in programmatic marketing present both opportunities and risks. The most supported hypothesis is that synthetic audiences will become a mainstream tool for market testing and audience analysis due to their cost-effectiveness and scalability. However, there are significant concerns regarding data privacy and the potential for misuse. Confidence Level: Moderate. Recommended action includes establishing clear ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks to govern the use of synthetic audiences.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Synthetic audiences will revolutionize market research by providing scalable, cost-effective, and rapid insights, leading to widespread adoption across industries.
Hypothesis 2: The adoption of synthetic audiences will face significant resistance due to ethical concerns, data privacy issues, and potential regulatory hurdles, limiting their impact.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely due to the current trajectory of AI integration in marketing and the demand for efficient data-driven decision-making. However, Hypothesis 2 cannot be dismissed given the growing scrutiny on data privacy and ethical AI use.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions:
– AI technology will continue to advance, improving the accuracy and reliability of synthetic audiences.
– Organizations will prioritize cost-effectiveness and efficiency in market research.
Red Flags:
– Lack of transparency in how synthetic audiences are created and used.
– Potential for synthetic data to be used deceptively, misleading stakeholders about audience behaviors.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The use of synthetic audiences could lead to significant shifts in market research methodologies, potentially reducing the need for traditional focus groups and surveys. However, the reliance on AI-generated data poses risks of data manipulation and privacy violations. Politically, there could be calls for stricter regulations on AI in marketing, while economically, companies that fail to adapt may lose competitive advantage. Cyber risks include potential breaches of synthetic data systems.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Develop and implement ethical guidelines for the creation and use of synthetic audiences.
- Engage with regulatory bodies to establish clear frameworks governing AI in marketing.
- Invest in cybersecurity measures to protect synthetic data systems.
Best-case scenario: Synthetic audiences become a trusted tool, enhancing market research capabilities while adhering to ethical standards.
Worst-case scenario: Misuse of synthetic audiences leads to significant privacy breaches and loss of consumer trust, resulting in stringent regulations that stifle innovation.
Most-likely scenario: Gradual adoption of synthetic audiences with ongoing debates over ethical and privacy concerns, leading to a balanced regulatory environment.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Cynthia Vega (Kantar Data Consulting), Alex Cooper (Electric Twin)
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, AI Ethics, Market Research, Data Privacy
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
- Cognitive Bias Stress Test: Structured challenge to expose and correct biases.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us