Young Shutdown lesson dont depend on DC – Boston Herald
Published on: 2025-11-18
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
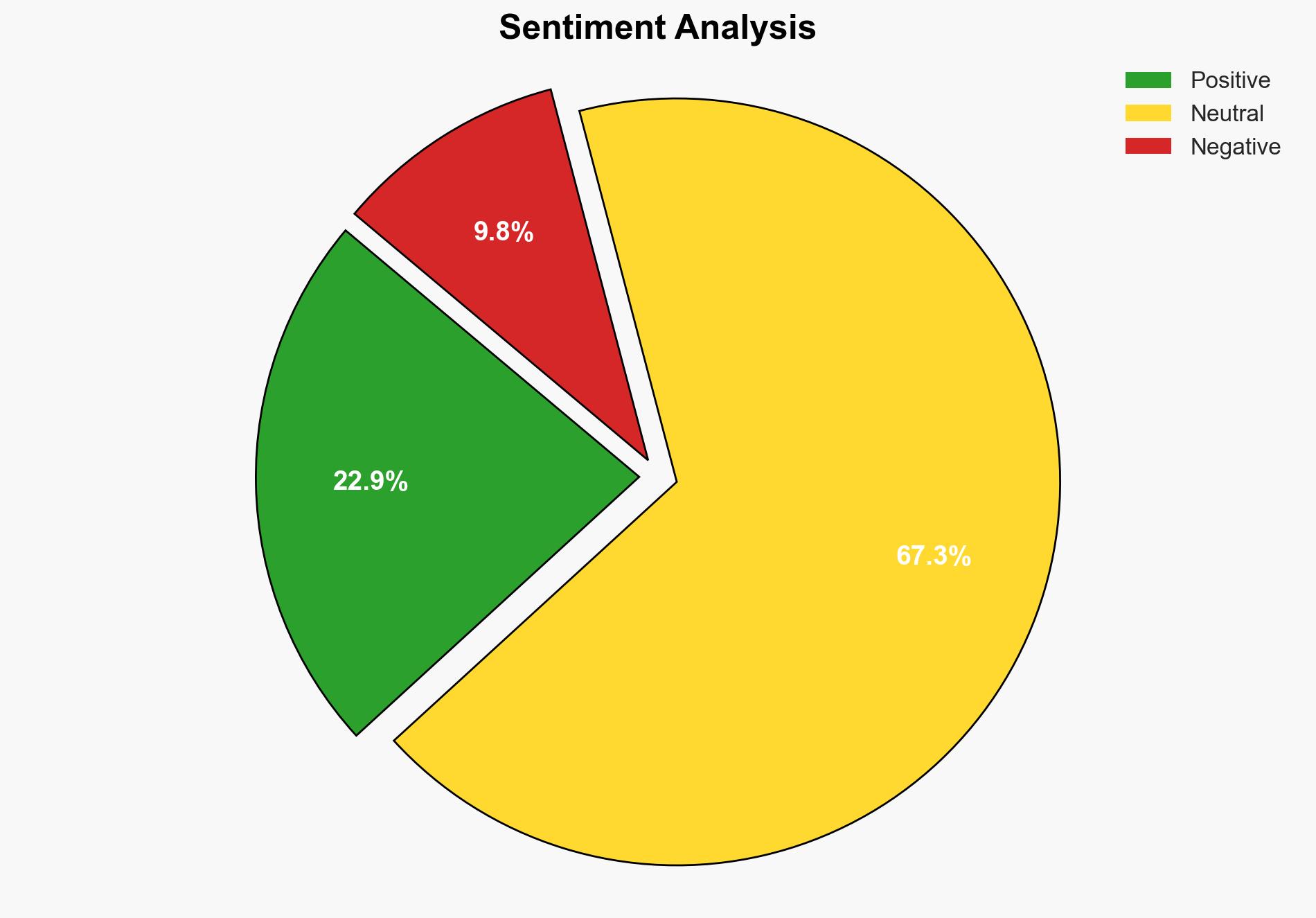
The strategic analysis suggests that the federal government’s unreliability in consistently funding social programs like SNAP highlights the need for a diversified approach to social welfare, involving both state-level management and private sector participation. The most supported hypothesis is that decentralizing the administration of social welfare programs will enhance their resilience and adaptability. Confidence Level: Moderate.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Decentralizing social welfare programs to state and local governments, supplemented by private sector involvement, will improve program reliability and adaptability.
Hypothesis 2: Maintaining federal control over social welfare programs ensures uniformity and equity across states, preventing disparities in service delivery.
The evidence suggests that decentralization (Hypothesis 1) is more likely to enhance program resilience due to the federal government’s demonstrated unreliability during shutdowns. State-level management can be more responsive and adaptable to local needs, while private sector involvement can provide additional support and innovation.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that state governments have the capacity and resources to effectively manage social welfare programs. It is also assumed that private sector involvement will be consistent and substantial.
Red Flags: Potential for increased inequality if states with fewer resources struggle to fund programs. Risk of private sector involvement being insufficient or inconsistent.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
Implications: A shift towards state-managed and privately supported welfare programs could lead to innovation and tailored solutions but may also result in disparities between states.
Strategic Risks: Political resistance to decentralization, potential for increased inequality, and reliance on private sector contributions that may fluctuate with economic conditions.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Actionable Steps: Encourage pilot programs for state-managed welfare initiatives with federal oversight to ensure equity. Foster public-private partnerships to enhance program funding and innovation.
- Best Scenario: Successful decentralization leads to more efficient and responsive welfare programs with robust private sector support.
- Worst Scenario: Increased disparities in welfare provision across states, with some states unable to adequately support their populations.
- Most-likely Scenario: A mixed approach where some states excel in managing programs while others face challenges, leading to a push for federal standardization in certain areas.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Ryan Young, Senior Economist at the Competitive Enterprise Institute, advocates for decentralization and private sector involvement.
7. Thematic Tags
Cybersecurity, Social Welfare, Federalism, Public-Private Partnerships, Economic Resilience
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us