12 reasons not to root your Android phone – and the only time I would – ZDNet
Published on: 2025-11-20
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
Intelligence Report:
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
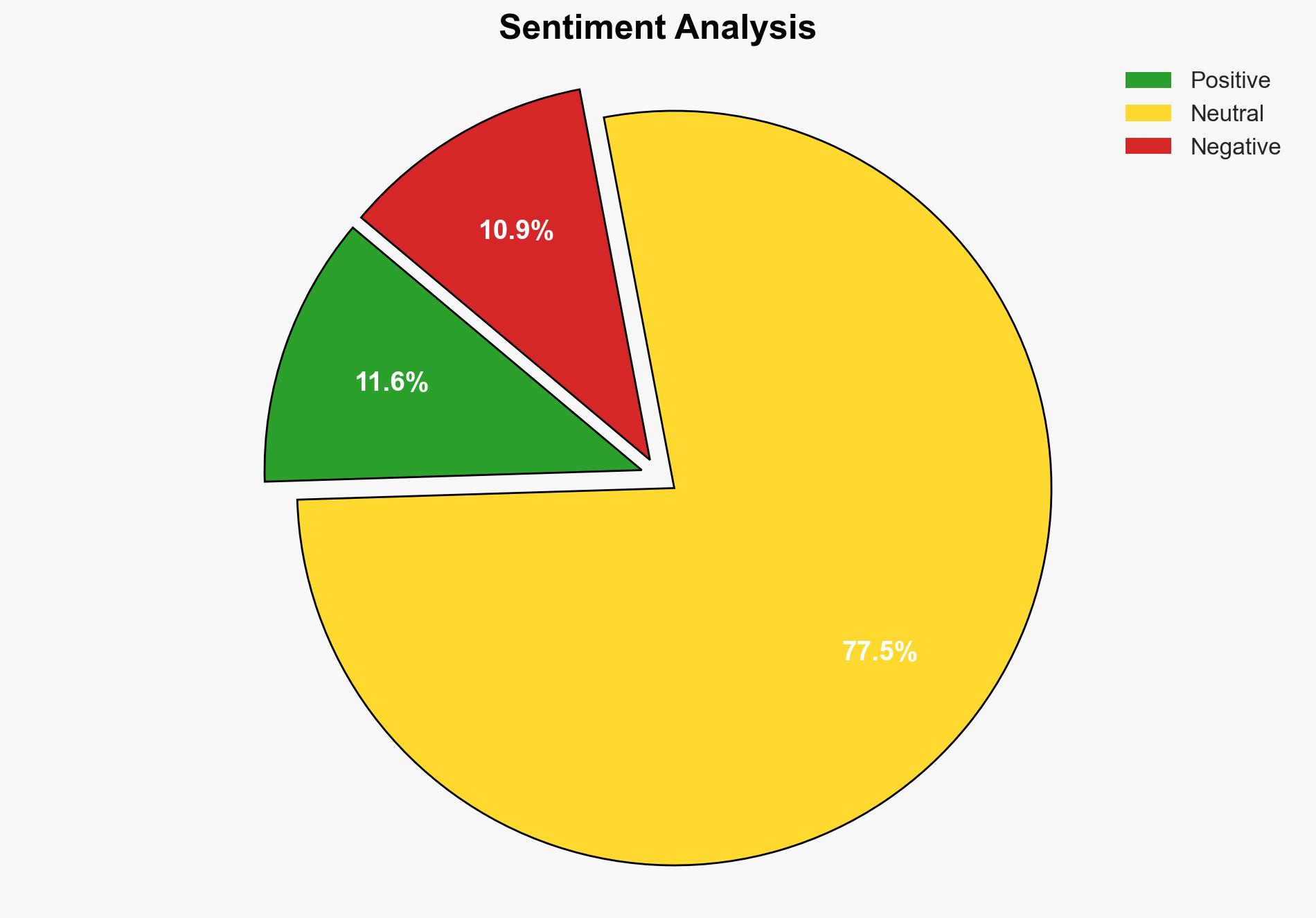
The strategic judgment is that rooting Android phones presents significant cybersecurity risks, outweighing the benefits for most users. The most supported hypothesis is that rooting is generally inadvisable due to potential security vulnerabilities and warranty voidance. Confidence level is moderate due to variability in user expertise and specific needs. Recommended action is to discourage rooting unless users have advanced technical skills and a compelling need that outweighs the risks.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: Rooting an Android phone is beneficial for users seeking customization and enhanced control over their device, justifying the risks involved.
Hypothesis 2: Rooting an Android phone poses significant security risks and potential device malfunction, making it inadvisable for the average user.
Assessment: Hypothesis 2 is more likely given the structured evidence of security vulnerabilities, warranty voidance, and the potential for device bricking. The complexity and variability of the rooting process further support this hypothesis.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: Users have varying levels of technical expertise; the rooting process and risks are consistent across devices; rooted devices are more susceptible to malware.
Red Flags: Over-reliance on community forums for firmware; potential bias in sources advocating for rooting without acknowledging risks; lack of official support from manufacturers.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
Rooting Android phones can lead to increased cybersecurity threats, including malware infections and data breaches. Economically, users may incur costs from voided warranties and device replacements. Politically, widespread rooting could undermine trust in Android security, affecting Google’s market position. Informationally, rooted devices may be more vulnerable to unauthorized data access.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Encourage users to evaluate the necessity of rooting against potential risks and to seek professional advice if unsure.
- Promote awareness of security best practices for those who choose to root their devices.
- Best-case scenario: Users gain desired customization without encountering security issues.
- Worst-case scenario: Rooted devices become vectors for widespread malware attacks.
- Most-likely scenario: A small subset of technically proficient users successfully root their devices, while the majority avoid it due to perceived risks.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
Google (Android OS provider), Magisk (rooting tool developer), Android device manufacturers.
7. Thematic Tags
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Adversarial Threat Simulation: Model and simulate actions of cyber adversaries to anticipate vulnerabilities and improve resilience.
- Indicators Development: Detect and monitor behavioral or technical anomalies across systems for early threat detection.
- Bayesian Scenario Modeling: Quantify uncertainty and predict cyberattack pathways using probabilistic inference.
Explore more:
Cybersecurity Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us