Amazon API Gateway REST APIs now supports private integration with Application Load Balancer – Amazon.com
Published on: 2025-11-21
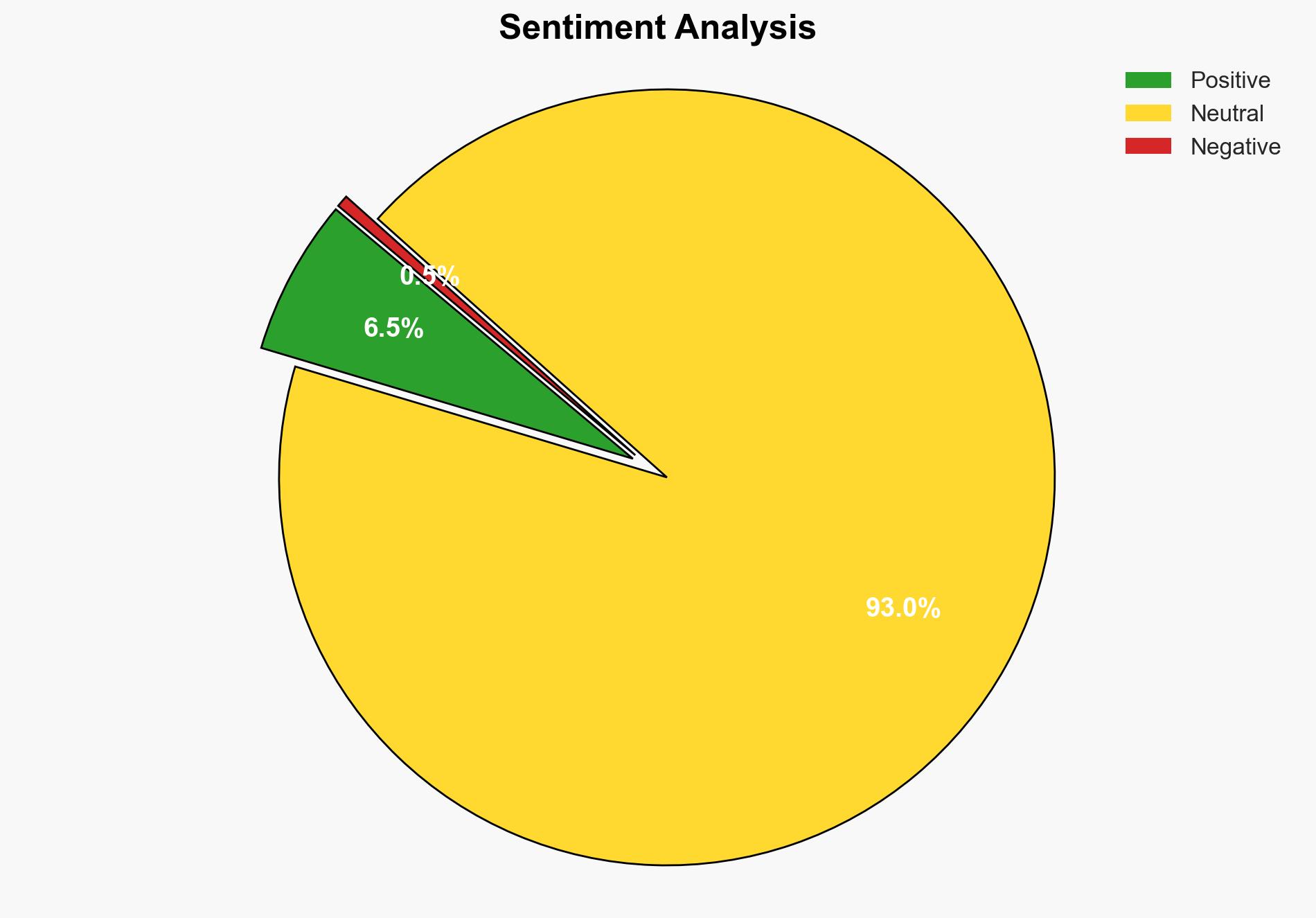
AI-powered OSINT brief from verified open sources. Automated NLP signal extraction with human verification. See our Methodology and Why WorldWideWatchers.
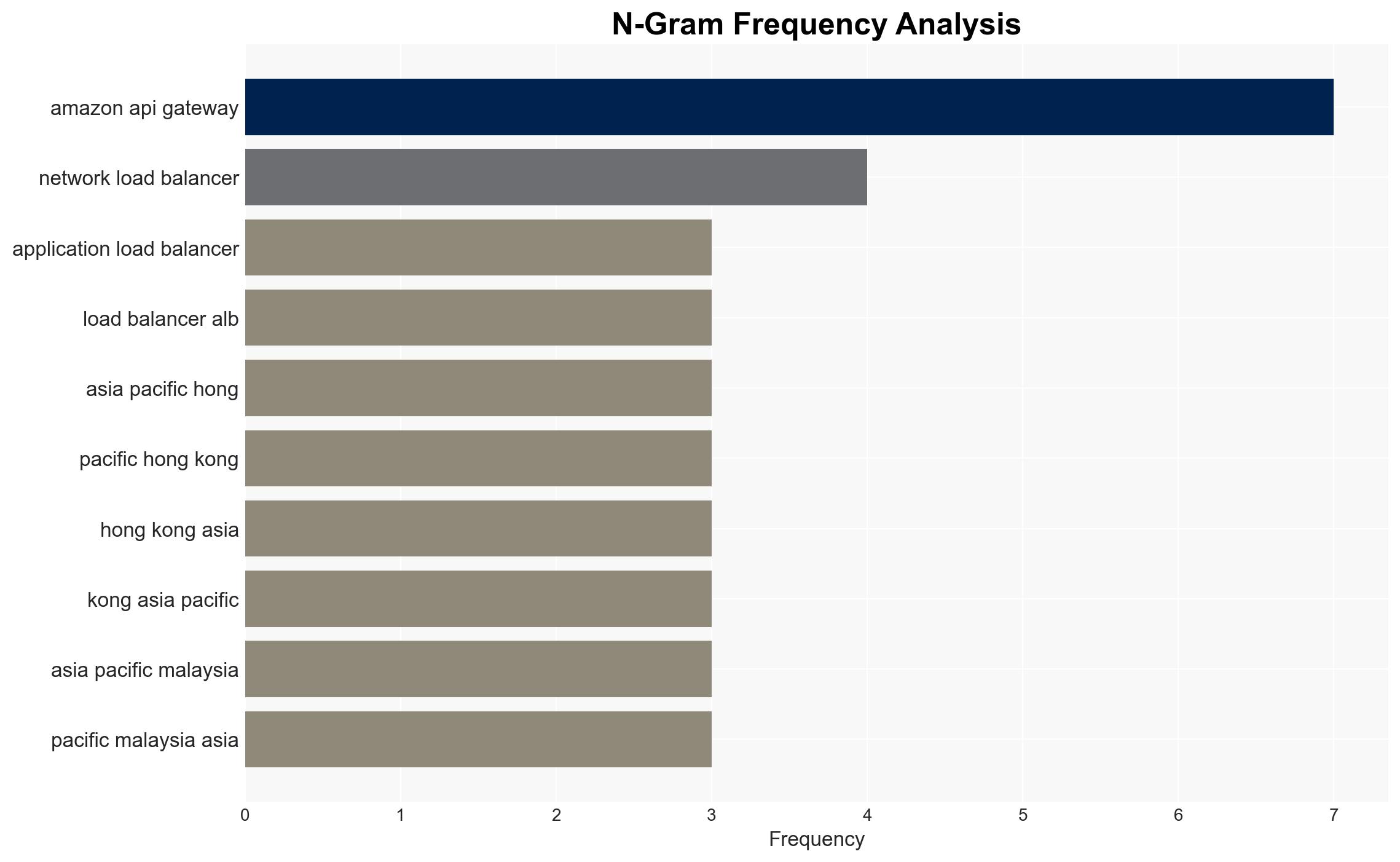
Intelligence Report: Amazon API Gateway REST APIs and Private Integration with ALB
1. BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front)
With a high confidence level, the integration of Amazon API Gateway REST APIs with Application Load Balancer (ALB) is a strategic move to enhance AWS’s competitive positioning by offering more efficient and cost-effective solutions. This development is likely to attract more enterprises seeking flexible and scalable cloud solutions, thereby increasing AWS’s market share. Recommended action includes monitoring competitor responses and preparing for potential shifts in customer demand.
2. Competing Hypotheses
Hypothesis 1: The integration is primarily aimed at improving AWS’s competitive edge by reducing latency and infrastructure costs, thus attracting more enterprise clients.
Hypothesis 2: The integration is a defensive strategy to retain existing customers by enhancing service offerings and preventing migration to competitors.
Hypothesis 1 is more likely given the emphasis on new capabilities and cost efficiencies that align with AWS’s growth strategy. The broad regional availability supports an aggressive market expansion rather than a mere defensive posture.
3. Key Assumptions and Red Flags
Assumptions: It is assumed that the integration will function as advertised without significant technical issues. It is also assumed that competitors will not immediately match these capabilities.
Red Flags: Potential over-reliance on AWS’s documentation and marketing materials could bias analysis. Lack of independent performance verification is a gap.
Deception Indicators: None identified, but vigilance is required for potential overstatements in AWS’s promotional content.
4. Implications and Strategic Risks
The integration could lead to increased AWS adoption, impacting competitors like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud. This may trigger competitive responses, such as price reductions or new feature rollouts, escalating the cloud service competition. Economically, AWS’s enhanced offerings could pressure smaller cloud providers, potentially leading to market consolidation. Cyber risks include potential vulnerabilities in new integrations that could be exploited if not properly secured.
5. Recommendations and Outlook
- Monitor competitor actions and customer feedback to assess the integration’s market impact.
- Enhance security protocols around new integrations to mitigate cyber risks.
- Best-case scenario: AWS gains significant market share, solidifying its leadership in cloud services.
- Worst-case scenario: Technical issues or security vulnerabilities undermine customer trust.
- Most-likely scenario: AWS experiences moderate growth with increased enterprise adoption.
6. Key Individuals and Entities
No specific individuals are mentioned in the source text. Key entities include Amazon Web Services (AWS) and its competitors, such as Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud.
7. Thematic Tags
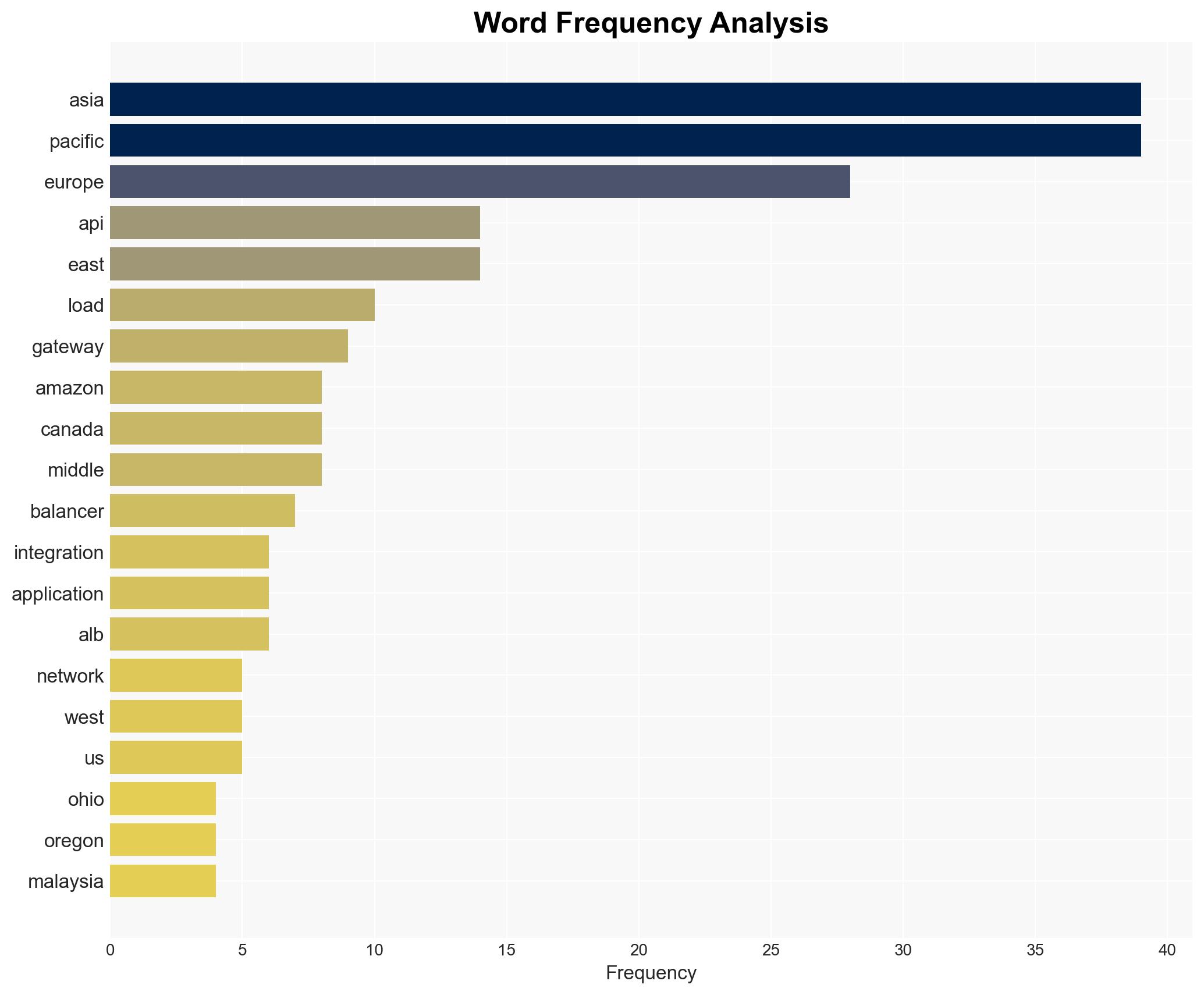
Regional Focus, Regional Focus: Global, with specific emphasis on AWS regions including North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, and South America
Structured Analytic Techniques Applied
- Causal Layered Analysis (CLA): Analyze events across surface happenings, systems, worldviews, and myths.
- Cross-Impact Simulation: Model ripple effects across neighboring states, conflicts, or economic dependencies.
- Scenario Generation: Explore divergent futures under varying assumptions to identify plausible paths.
- Network Influence Mapping: Map influence relationships to assess actor impact.
Explore more:
Regional Focus Briefs ·
Daily Summary ·
Support us